Preface
© 2021 Vector Informatik GmbH - All rights reserved - https://www.vector.com/ - This material may not be reproduced, displayed, modified or distributed without the express prior written permission of the copyright holder. Squore is protected by an Interdeposit Certification registered with Agence pour la Protection des Programmes under the Inter Deposit Digital Number IDDN.FR.001.390035.001.S.P.2013.000.10600.
Foreword
This edition of the Reference Manual was released by Vector Informatik GmbH.
It is part of the user documentation of the Squore software product edited and distributed by Vector Informatik GmbH.
For information on how to use and configure Squore, the full suite of manuals includes:
User Manual |
Target Audience |
|---|---|
New users before their first installation |
|
IT personnel and Squore administrators |
|
End users, new users wanting to discover Squore features |
|
Continuous Integration Managers |
|
Squore configuration maintainers, Quality Assurance personnel |
|
Eclipse IDE users |
|
End Users, Squore configuration maintainers |
|
End Users, Continuous Integration Managers |
|
End Users, Quality Assurance personnel |
|
You can also use the online help from any page when using the Squore web interface by clicking ? > Help. |
Licence
No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted, stored in a retrieval system, nor translated into any human or computer language, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical, manual or otherwise, without the prior written permission of the copyright owner, Vector Informatik GmbH. Vector Informatik GmbH reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes from time to time without obligation to notify authorised users of such changes. Consult Vector Informatik GmbH to determine whether any such changes have been made. The terms and conditions governing the licensing of Vector Informatik GmbH software consist solely of those set forth in the written contracts between Vector Informatik GmbH and its customers. All third-party products are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
Warranty
Vector Informatik GmbH makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this material, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Vector Informatik GmbH shall not be liable for errors contained herein nor for incidental or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance or use of this material.
This edition of the Reference Manual applies to Squore 20.1.11 and to all subsequent releases and modifications until otherwise indicated in new editions.
Responsabilities
Approval of this version of the document and any further updates are the responsibility of Vector Informatik GmbH.
Contacting Vector Informatik GmbH Product Support
If the information provided in this manual is erroneous or inaccurate, or if you encounter problems during your installation, contact Vector Informatik GmbH Product Support: https://portal.vector.com/
You will need a valid customer account to submit a support request. You can create an account on the support website if you do not have one already.
For any communication:
-
support@vector.com
-
Vector Informatik GmbH Product Support
Vector Informatik GmbH - Holderäckerstr. 36 / 70499 Stuttgart - Germany
Getting the Latest Version of this Manual
The version of this manual included in your Squore installation may have been updated. If you would like to check for updated user guides, consult the Vector Informatik GmbH documentation site to consult or download the latest Squore manuals at https://support.squoring.com/documentation/latest. Manuals are constantly updated and published as soon as they are available.
1. Introduction
The Reference Manual provides a complete reference for the metrics, glossary and standards used in Squore 20.1.11.
This manual is intended for Squore administrators and end-users. It gives useful information about the technical background of Squore and important knowledge basis to understand what is measured and how.
2. Coding Standards
This chapter describes the list of metrics and rules for each language supported by &squan_sources;. Note that this is not the complete list of metrics and rules in Squore, only the ones generated by our source code parser. Some of the rules may also be disabled by default in your configuration. For more information about your analysis model, consult Squore’s Model Viewer and Analysis Model Editor, which provide more information about each metric and rule.
ABAP
ABAP Metrics
Andthen Operators
Number of comment blocks
Header Blocks Of Comment
Blank Lines
Brace Lines
Case Blocks
Case Labels
Catch Statements
Cloned Code
Code Cloning Line Counting
Cyclomatic Complexity
Control Flow Token
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
Number of Check instruction
Comment Lines
Clones Number
Continue Statements
Public Constant
Protected Constant
Private Constant
Commented Statements
Default Statement
Distinct Operands
Distinct Operators
Public Data
Protected Data
Private Data
Else Statements
Call to exit
Comments containing FIXME
For Statements
File Type Count
Structures Added
Structures Modified
Structures Removed
Header Lines Of Comment
Header Lines Of Code
Cloned Code
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
If Statements
Line Count
Loop Statements
Mixed Lines
Maximum Nested Structures
Number of Parameters
Non-Cyclic Paths
Orelse operators
Partially parsed files
Return Statements
Repeated Code Blocks
Skipped Lines of Comment code
Source Lines Of Code
Executable Statements
Switch Statements
Throw Statements
Comments containing TODO
Operand Occurrences
Operator Occurrences
Try Statements
Lines Added
Lines Modified
Lines Removed
While Statements
-
Mnemonic WHIL
-
Description Number of 'while' statements in the function
ABAP Ruleset
Avoid using APPEND statements in loops
Avoid using APPEND in SQL SELECT statements
Avoid using BREAK-POINT
Avoid using CHECK in SQL SELECT statements
Avoid using COMMIT WORK statements in loops
Avoid obsolete DATA BEGIN OF OCCURS statement
Avoid using INSERT statements in loops
Avoid using INSERT in SQL SELECT statements
Avoid using SQL INTO statements in loops
Avoid using SELECT *
Avoid using the SQL "BYPASSING BUFFER" clause
Avoid using SELECT DISTINCT Statement
Avoid SELECT SQL statement without a WHERE clause
Avoid SELECT SQL statement with a WHERE clause containing the NOT EQUAL operator
Avoid using SQL Aggregate Functions
Avoid using SUBMIT statements in loops
Avoid using UPDATE, MODIFY, DELETE statements in loops
Avoid UPDATE or DELETE SQL Statement without a WHERE clause
Avoid using GROUP BY in queries
Avoid using the JOIN SQL clause
Avoid using LIKE in SQL queries
Avoid using the WAIT statement
The class name should conform to the defined standard
Commented-out Source Code is not allowed
Missing Default
Missing final else
Forbid call to a system function
Forbid calls to dialog transactions
Forbid use of GENERATE REPORT / SUBROUTINE POOL / DYNPRO
Forbid calls to GET RUN TIME.
Forbid use of INSERT/DELETE REPORT/TEXTPOOL
Forbid uses of OFFSET in ASSIGN
Forbid use of SYSTEM-CALL
-
Mnemonic FORBIDSYSTEMCALL
-
Description This statement is only for !Internal use in SAP Basis development!. Its use is subject to various restrictions, not all of which may be listed in the documentation. Changes and further development, which may be incompatible, may occur at any time, without warning or notice!
The form name should conform to the defined standard
The function name should conform to the defined standard
Avoid calling a function module without handling exceptions
The macro name should conform to the defined standard
The method name should conform to the defined standard
Factorizable Classes
Factorizable Files
Factorizable Functions
Factorizable Packages
Cloned Classes
Cloned Files
Cloned Functions
Cloned Algorithmic
Continue shall not be used
FIXME shall not be commited in sources code
Do not use "Native SQL" instructions
Avoid Duplicated Blocks in Function
TODO shall not be commited in sources code
Missing case in switch
Prevent use of EDITOR-CALLS
The program or report name should conform to the defined standard
Relaxed violation
Multiple exits are not allowed
-
Mnemonic RETURN
-
Description A function shall have a single point of exit at the end (see [MISRA-C:2004]: RULE 14.7).
ADA
ADA Metrics
Andthen Operators
Number of comment blocks
Header Blocks Of Comment
Blank Lines
Brace Lines
Case Blocks
Case Labels
Cloned Code
Code Cloning Line Counting
Cyclomatic Complexity
Control Flow Token
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
Comment Lines
Clones Number
Commented Statements
Declare operators
Default Statement
Distinct Operands
Distinct Operators
Else Statements
Entry Statements
Exception When blocks
Exception handlers
Comments containing FIXME
For Statements
Structures Added
Structures Modified
Structures Removed
Goto Statements
Header Lines Of Comment
Header Lines Of Code
Cloned Code
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
If Statements
Generic object
Label Statements
Line Count
Loop Statements
Mixed Lines
AND operators
Constants
Private constant
Public constants
Declared functions
Private functions/Procedures
Public functions
Exceptions
Private exceptions
Public exceptions
Separate functions/procedures
OR operators
Separate packages
Protected objects
Renamed objects
Subtypes
Separate tasks
Types
Derived types
Private types
Public types
Variables
Private variables
Public variables
With statements
Maximum Nested Structures
Number of Parameters
Non-Cyclic Paths
Orelse operators
Partially parsed files
Raise statements
Return Statements
Repeated Code Blocks
Skipped Lines of Comment code
Source Lines Of Code
Executable Statements
Switch Statements
Comments containing TODO
Operand Occurrences
Operator Occurrences
Lines Added
Lines Modified
Lines Removed
While Statements
-
Mnemonic WHIL
-
Description Number of 'while' statements in the function
ADA Ruleset
Backward Goto shall not be used
Commented-out Source Code is not allowed
Missing final else
Exit Label shall be named
Use 'exit when' instead of if… exit syntax
Each loop shall be named
Abort shall not be used
Factorizable Classes
Factorizable Files
Factorizable Functions
Factorizable Packages
Cloned Classes
Cloned Files
Cloned Functions
Cloned Algorithmic
Delay shall not be used
FIXME shall not be commited in sources code
Goto shall not be used
Avoid Duplicated Blocks in Function
TODO shall not be commited in sources code
There shall be no 'when others' in exception handler
Missing case in switch
Parameters shall be ordered: 'IN', 'OUT', 'IN OUT'.
Relaxed violation
Multiple exits are not allowed
Multiple Exit in loop
-
Mnemonic SGLEXT
-
Description There shall be a single exit by loop.
C
C Metrics
Andthen Operators
Assignment Operators
Number of comment blocks
Header Blocks Of Comment
Blank Lines
Brace Lines
Break in Loop
Break in Switch
Case Blocks
Calls To
Called Functions
Calls From
Calling Functions
Called External Functions
Case Labels
Cloned Code
Code Cloning Line Counting
Cyclomatic Complexity
Recursive Calls
Control Flow Token
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
Called Depth
Calling Depth
Call Graph Depth
Minimum Number of Indirect Cycles
Comment Lines
Clones Number
Continue Statements
Comparison Operators
Commented Statements
Minimum Number of Cycles
Default Statement
Distinct Operands
Distinct Operators
Do While Statements
Else Statements
Comments containing FIXME
For Statements
Structures Added
Structures Modified
Structures Removed
Goto Statements
Header Lines Of Comment
Header Lines Of Code
Cloned Code
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
If Statements
Line Count
Use of longjump
Loop Statements
Memory Allocation
Memory Freeing
Mixed Lines
Maximum Nested Structures
Number of Parameters
Non-Cyclic Paths
Use of offsetof
Orelse operators
Partially parsed files
Number of #DEFINE
Number of #ELIF
Number of #ELSE
Number of #ENDIF
Number of #ERROR
Number of #IF
Number of #IFDEF
Number of #IFNDEF
Number of Include
Compiler FLAG Nested Level
Number of #PRAGMA
Number of #UNDEF
Number of #WARNING
Return Statements
Repeated Code Blocks
Use of setjump
Signal Functions
Skipped Lines of Comment code
Source Lines Of Code
Special Operators
Executable Statements
IO Functions
String Conversions
Switch Statements
System Functions
Ternary operators
Time Handling
Comments containing TODO
Operand Occurrences
Operator Occurrences
Lines Added
Lines Modified
Lines Removed
While Statements
-
Mnemonic WHIL
-
Description Number of 'while' statements in the function
C Ruleset
Missing Break
Backward Goto shall not be used
Missing compound statement
Missing compound if
Commented-out Source Code is not allowed
Missing Default
Dynamic Memory Allocation shall not be used
Missing final else
Macro longjmp or setjmp shall not be used
Nesting Level of Preprocessing directives is too high
Assignment in Boolean
Assignment without Comparison
Factorizable Classes
Factorizable Files
Factorizable Functions
Factorizable Packages
Cloned Classes
Cloned Files
Cloned Functions
Cloned Algorithmic
There shall be a no code before first case
Continue shall not be used
Fallthrough shall be avoided
FIXME shall not be commited in sources code
Goto shall not be used
Label out a switch
Recursion are not allowed
Avoid Duplicated Blocks in Function
TODO shall not be commited in sources code
Macro offsetof shall not be used
Missing case in switch
Relaxed violation
Multiple exits are not allowed
Risky Empty Statement
Multiple break in loop are not allowed
Signal or Raise shall not be used
IO Functions shall not be used
'atof, atoi or atol' shall not be used
'abort, exit, getenv or system' shall not be used
Time Handling Functions shall not be used
-
Mnemonic TIMEHDL
-
Description The time handling functions of library <time.h> shall not be used: time, strftime, clock, difftime, mktime (see [MISRA-C:2004]: RULE 20.12).
COBOL
COBOL Metrics
Arithmetic Operators
Blank Lines
CALL Statements
Cloned Code
Code Cloning Line Counting
Cyclomatic Complexity
Control Flow Token
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
Comment Lines
Comment lines with code
Comment lines without alphabetic characters
Real comment lines with alphabetic characters
Clones Number
Conditions
Commented Statements
Debug lines
DISPLAY statements
Distinct Operands
Distinct Operands in Data Div.
Distinct Operands in Procedure Div.
Distinct Operators
Distinct Operators in Data Div.
Distinct Operators in Procedure Div.
Else Statements
EVALUATE Statements
Call to exit
File Declarations
Files Used
Comments containing FIXME
Goto Statements
Cloned Code
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
Is IDMS active
IDMS instructions called
IDMS records called
IDMS calls for modification
IDMS calls for reading/searching
IDMS subschema definition
If Statements
Line Count
Maximum Nested Structures
Number of Parameters
Number of paragraphs
Partially parsed files
PERFORM Statements
Repeated Code Blocks
Data Declarations
Data Used
Number of Sections
Source Lines Of Code
Executable Statements
STOP Statements
TIMES Clauses
Comments containing TODO
Operand Occurrences
Operand Occurrences in Data Div.
Operand Occurrences in Procedure Div.
Operator Occurrences
Operator Occurrences in Data Div.
Operator Occurrences in Procedure Div.
Lines Added
Lines Modified
Lines Removed
UNTIL Clauses
VARYING Clauses
WHEN Clauses
-
Mnemonic WHEN
-
Description Number of WHEN and WHENOTHER clauses in EVALUATE Statements
COBOL Ruleset
BLOCK Clause
Column 7 for * and D Only
Comment Division
Comment FD
Comment First Level
Comment Variable 01 and 77
Empty lines around DIVISION
Empty line after EXIT
Bad statement indentation
Bad indentation of scope terminator
Empty line after SECTION
Variable declaration format
Paragraphs having exact same name
Missing END-EVALUATE
Close file once
Close open file
Open file once
Use FILE STATUS
Single GOBACK
IDMS FIND CURRENT
IDMS One modify by PERFORM
IDMS One same call
IDMS Ready Protected Update
IDMS Return Code
Missing END-IF
Avoid using inline PERFORM with too many lines of code
Standard Label
Missing END-ADD
Missing END-CALL
Missing END-COMPUTE
Missing END-DELETE
Missing END-DIVIDE
Missing END-MULTIPLY
Missing END-READ
Missing END-RETURN
Missing END-REWRITE
Missing END-SEARCH
Missing END-START
Missing END-STRING
Missing END-SUBTRACT
Missing END-UNSTRING
Missing END-WRITE
Missing FILLER
No more than 3 nested IF
Nested Program
ALTER shall not be used
Factorizable Classes
Factorizable Files
Factorizable Functions
Factorizable Packages
Cloned Classes
Cloned Files
Cloned Functions
Cloned Algorithmic
No Conditional GOTO
No MOVE CORRESPONDING
COMPUTE instead of ADD
COMPUTE instead of SUBTRACT
No DEBUG MODE
COMPUTE instead of DIVIDE
FIXME shall not be commited in sources code
No INITIALIZE
COMPUTE instead of MULTIPLY
No procedural COPY
No RENAMES
Avoid Duplicated Blocks in Function
TODO shall not be commited in sources code
No Variables S9(9)
Avoid GOTO jumps out of PERFORM range
Avoid OPEN/CLOSE inside loops
Avoid accessing data by using the position and length
Use COMP for OCCURS
Avoid mixing paragraphs and sections
Perform with no THRU
Bad paragraph position used in PERFORM
READ-WRITE Instruction
Avoid using READ statement without AT END clause
Relaxed violation
Statement shall be in uppercase
Use SYNCHRONIZED
Homonymous variable shall not be used
Use WHEN OTHER
-
Mnemonic WHENOTHER
-
Description EVALUATE shall end by a WHEN OTHER clause.
C++
C++ Metrics
Constant Data
Number of Attributes
Number of data without accessibility
Andthen Operators
Public Data
Protected Data
Private data
Assignment Operators
Static Data
Number of comment blocks
Header Blocks Of Comment
Blank Lines
Brace Lines
Break in Loop
Break in Switch
Case Blocks
Case Labels
Catch Statements
Cloned Code
Code Cloning Line Counting
Cyclomatic Complexity
Control Flow Token
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
Comment Lines
Clones Number
Continue Statements
Comparison Operators
Commented Statements
Depth of Descendant Tree
Default Statement
Depth of Inheritance Tree
Distinct Operands
Distinct Operators
Do While Statements
Else Statements
Comments containing FIXME
For Statements
Structures Added
Structures Modified
Structures Removed
Goto Statements
Header Lines Of Comment
Header Lines Of Code
Cloned Code
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
If Statements
Line Count
Loop Statements
Constant Methods
Multiple Inheritance Indicator
Mixed Lines
Methods without Accessibility
Public Methods
Protected Methods
Private Methods
Static Methods
Number of Ancestors
Number of Descendants
Maximum Nested Structures
Number Of Children
Number of Parameters
Non-Cyclic Paths
Orelse operators
Partially parsed files
Number of #DEFINE
Number of #ELIF
Number of #ELSE
Number of #ENDIF
Number of #ERROR
Number of #IF
Number of #IFDEF
Number of #IFNDEF
Number of Include
Compiler FLAG Nested Level
Number of #PRAGMA
Number of #UNDEF
Number of #WARNING
Return Statements
Repeated Code Blocks
Skipped Lines of Comment code
Source Lines Of Code
Special Operators
Executable Statements
Switch Statements
Ternary operators
Throw Statements
Comments containing TODO
Operand Occurrences
Operator Occurrences
Try Statements
Lines Added
Lines Modified
Lines Removed
While Statements
Weighted Method per Class
-
Mnemonic XWMC
-
Description Sum of cyclomatic complexities of methods implemented outside the class definition
C++ Ruleset
Missing Break
Backward Goto shall not be used
Missing compound statement
Missing compound if
Commented-out Source Code is not allowed
Missing Default
Missing final else
Nesting Level of Preprocessing directives is too high
Assignment in Boolean
Assignment without Comparison
Factorizable Classes
Factorizable Files
Factorizable Functions
Factorizable Packages
Cloned Classes
Cloned Files
Cloned Functions
Cloned Algorithmic
There shall be a no code before first case
Continue shall not be used
Fallthrough shall be avoided
FIXME shall not be commited in sources code
Goto shall not be used
Label out a switch
Avoid Duplicated Blocks in Function
TODO shall not be commited in sources code
Missing case in switch
Relaxed violation
Multiple exits are not allowed
Risky Empty Statement
Multiple break in loop are not allowed
-
Mnemonic SGLBRK
-
Description For any iteration statement there shall be at most one 'break' statement used for loop termination (see [MISRA-C:2004]: RULE 14.6).
C#
C# Metrics
Constant Data
Internal Data
Number of Attributes
Number of data without accessibility
Andthen Operators
Public Data
Protected Internal Data
Protected Data
Private data
Assignment Operators
Static Data
Number of comment blocks
Header Blocks Of Comment
Blank Lines
Brace Lines
Break in Loop
Break in Switch
Case Blocks
Case Labels
Catch Statements
Cloned Code
Code Cloning Line Counting
Cyclomatic Complexity
Control Flow Token
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
Comment Lines
Clones Number
Continue Statements
Comparison Operators
Commented Statements
Depth of Descendant Tree
Default Statement
Depth of Inheritance Tree
Distinct Operands
Distinct Operators
Do While Statements
Else Statements
Comments containing FIXME
For Statements
Foreach Statements
Structures Added
Structures Modified
Structures Removed
Goto Statements
Header Lines Of Comment
Header Lines Of Code
Cloned Code
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
If Statements
Line Count
Loop Statements
Constant Methods
Multiple Inheritance Indicator
Internal Methods
Mixed Lines
Methods without Accessibility
Public Methods
Protected Internal Methods
Protected Methods
Private Methods
Static Methods
Number of Ancestors
Number of Descendants
Maximum Nested Structures
Number Of Children
Number of Parameters
Non-Cyclic Paths
Orelse operators
Partially parsed files
Constant Properties
Properties with Get
Internal Properties
Properties
Properties without Accessibility
Public Properties
Protected Internal Properties
Protected Properties
Private Properties
Properties with Set
Static Properties
Number of #DEFINE
Number of #ELIF
Number of #ELSE
Number of #ENDIF
Number of #ENDREGION
Number of #ERROR
Number of #IF
Number of #IFDEF
Number of #IFNDEF
Compiler FLAG Nested Level
Number of #PRAGMA
Number of #REGION
Number of #UNDEF
Number of #WARNING
Return Statements
Repeated Code Blocks
Skipped Lines of Comment code
Source Lines Of Code
Special Operators
Executable Statements
Switch Statements
Ternary operators
Throw Statements
Comments containing TODO
Operand Occurrences
Operator Occurrences
Try Statements
Lines Added
Lines Modified
Lines Removed
While Statements
-
Mnemonic WHIL
-
Description Number of 'while' statements in the function
C# Ruleset
Backward Goto shall not be used
Missing compound statement
Missing compound if
Commented-out Source Code is not allowed
Missing Default
Missing final else
Assignment in Boolean
Assignment without Comparison
Factorizable Classes
Factorizable Files
Factorizable Functions
Factorizable Packages
Cloned Classes
Cloned Files
Cloned Functions
Cloned Algorithmic
There shall be a no code before first case
Continue shall not be used
Fallthrough shall be avoided
FIXME shall not be commited in sources code
Goto shall not be used
Label out a switch
Avoid Duplicated Blocks in Function
TODO shall not be commited in sources code
Missing case in switch
Relaxed violation
Multiple exits are not allowed
Risky Empty Statement
Multiple break in loop are not allowed
-
Mnemonic SGLBRK
-
Description For any iteration statement there shall be at most one 'break' statement used for loop termination (see [MISRA-C:2004]: RULE 14.6).
Fortran
Fortran Metrics
Andthen Operators
Number of arithmetic if
Number of comment blocks
Header Blocks Of Comment
Blank Lines
Brace Lines
Break in Loop
Case Blocks
Case Labels
Cloned Code
Code Cloning Line Counting
Cyclomatic Complexity
Control Flow Token
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
Comment Lines
Clones Number
Continue Statements
Commented Statements
Number of declarative statements
Default Statement
Distinct Operands
Distinct Operators
Do While Statements
Else Statements
Comments containing FIXME
For Statements
Structures Added
Structures Modified
Structures Removed
Goto Statements
Header Lines Of Comment
Header Lines Of Code
Cloned Code
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
If Statements
Line Count
Loop Statements
Mixed Lines
Maximum Nested Structures
Number of Parameters
Non-Cyclic Paths
Orelse operators
% of parsed tokens
Partially parsed files
Return Statements
Repeated Code Blocks
Skipped Lines of Comment code
Source Lines Of Code
Executable Statements
Switch Statements
Comments containing TODO
Operand Occurrences
Operator Occurrences
Lines Added
Lines Modified
Lines Removed
-
Mnemonic LREM
-
Description Number of lines removed since the previous version.
Fortran Ruleset
Use of allocate/deallocate
Backward Goto shall not be used
Use of contains
Missing Default
Use of continue is deprecated (Fortran)
Missing final else
Use of Fortran 77
Function size
Use of module
Incorrect Function Name
Incorrect Module Name
Parameter name
Incorrect Program Name
Incorrect Subroutine Name
Number of parameters
Factorizable Classes
Factorizable Files
Factorizable Functions
Factorizable Packages
Cloned Classes
Cloned Files
Cloned Functions
Cloned Algorithmic
Continue shall not be used
'cycle' shall not be used
FIXME shall not be commited in sources code
Goto shall not be used
Label out a switch
Avoid Duplicated Blocks in Function
'stop' shall not be used
TODO shall not be commited in sources code
Missing case in switch
Relaxed violation
Multiple exits are not allowed
Use of SAVE and DATA
Multiple exit
-
Mnemonic SGLEXIT
-
Description For any iteration statement there shall be at most one 'exit' statement used for loop termination.
Java
Java Metrics
Constant Data
Number of Attributes
Number of data without accessibility
Andthen Operators
Public Data
Protected Data
Private data
Assignment Operators
Static Data
Number of comment blocks
Header Blocks Of Comment
Blank Lines
Brace Lines
Break in Loop
Break in Switch
Case Blocks
Case Labels
Catch Statements
Cloned Code
Code Cloning Line Counting
Cyclomatic Complexity
Control Flow Token
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
Comment Lines
Clones Number
Continue Statements
Comparison Operators
Commented Statements
Depth of Descendant Tree
Default Statement
Depth of Inheritance Tree
Distinct Operands
Distinct Operators
Do While Statements
Else Statements
Comments containing FIXME
For Statements
Structures Added
Structures Modified
Structures Removed
Header Lines Of Comment
Header Lines Of Code
Cloned Code
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
If Statements
Line Count
Loop Statements
Multiple Inheritance Indicator
Mixed Lines
Methods without Accessibility
Public Methods
Protected Methods
Private Methods
Static Methods
Number of Ancestors
Number of Descendants
Maximum Nested Structures
Number Of Children
Number of Parameters
Non-Cyclic Paths
Orelse operators
Partially parsed files
Return Statements
Repeated Code Blocks
Skipped Lines of Comment code
Source Lines Of Code
Special Operators
Executable Statements
Switch Statements
Ternary operators
Throw Statements
Comments containing TODO
Operand Occurrences
Operator Occurrences
Try Statements
Lines Added
Lines Modified
Lines Removed
While Statements
-
Mnemonic WHIL
-
Description Number of 'while' statements in the function
Java Ruleset
Missing Break
Missing compound statement
Missing compound if
Commented-out Source Code is not allowed
Missing Default
Missing final else
Assignment in Boolean
Assignment without Comparison
Factorizable Classes
Factorizable Files
Factorizable Functions
Factorizable Packages
Cloned Classes
Cloned Files
Cloned Functions
Cloned Algorithmic
There shall be a no code before first case
Continue shall not be used
Fallthrough shall be avoided
FIXME shall not be commited in sources code
Avoid Duplicated Blocks in Function
TODO shall not be commited in sources code
Missing case in switch
Relaxed violation
Multiple exits are not allowed
Risky Empty Statement
Multiple break in loop are not allowed
-
Mnemonic SGLBRK
-
Description For any iteration statement there shall be at most one 'break' statement used for loop termination (see [MISRA-C:2004]: RULE 14.6).
Javascript
Javascript Metrics
Andthen Operators
Number of comment blocks
Header Blocks Of Comment
Blank Lines
Brace Lines
Break in Loop
Break in Switch
Case Blocks
Case Labels
Catch Statements
Cloned Code
Code Cloning Line Counting
Cyclomatic Complexity
Control Flow Token
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
Comment Lines
Clones Number
Continue Statements
Commented Statements
Default Statement
Distinct Operands
Distinct Operators
Do While Statements
Else Statements
Comments containing FIXME
Max Nested Functions
For Statements
Structures Added
Structures Modified
Structures Removed
Header Lines Of Comment
Header Lines Of Code
Cloned Code
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
If Statements
Line Count
Loop Statements
Mixed Lines
Maximum Nested Structures
Number of Parameters
Non-Cyclic Paths
Orelse operators
Partially parsed files
Return Statements
Repeated Code Blocks
Skipped Lines of Comment code
Source Lines Of Code
Executable Statements
Switch Statements
Ternary operators
Throw Statements
Comments containing TODO
Operand Occurrences
Operator Occurrences
Try Statements
Lines Added
Lines Modified
Lines Removed
While Statements
-
Mnemonic WHIL
-
Description Number of 'while' statements in the function
Javascript Ruleset
Missing Break
Missing compound statement
Missing compound if
Commented-out Source Code is not allowed
Missing Default
Missing final else
Assignment in Boolean
Assignment without Comparison
Factorizable Classes
Factorizable Files
Factorizable Functions
Factorizable Packages
Cloned Classes
Cloned Files
Cloned Functions
Cloned Algorithmic
There shall be a no code before first case
Continue shall not be used
Fallthrough shall be avoided
FIXME shall not be commited in sources code
Label out a switch
Avoid Duplicated Blocks in Function
TODO shall not be commited in sources code
Missing case in switch
Relaxed violation
Multiple exits are not allowed
Risky Empty Statement
Multiple break in loop are not allowed
-
Mnemonic SGLBRK
-
Description For any iteration statement there shall be at most one 'break' statement used for loop termination (see [MISRA-C:2004]: RULE 14.6).
MindC
MindC Metrics
Andthen Operators
Assignment Operators
Number of comment blocks
Header Blocks Of Comment
Blank Lines
Brace Lines
Break in Loop
Break in Switch
Case Blocks
Calls To
Called Functions
Calls From
Calling Functions
Called External Functions
Case Labels
Cloned Code
Code Cloning Line Counting
Cyclomatic Complexity
Recursive Calls
Control Flow Token
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
Called Depth
Calling Depth
Call Graph Depth
Minimum Number of Indirect Cycles
Comment Lines
Clones Number
Continue Statements
Comparison Operators
Commented Statements
Minimum Number of Cycles
Default Statement
Distinct Operands
Distinct Operators
Do While Statements
Else Statements
Comments containing FIXME
For Statements
Structures Added
Structures Modified
Structures Removed
Goto Statements
Header Lines Of Comment
Header Lines Of Code
Cloned Code
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
If Statements
Line Count
Use of longjump
Loop Statements
Memory Allocation
Memory Freeing
Mixed Lines
Maximum Nested Structures
Number of Parameters
Non-Cyclic Paths
Use of offsetof
Orelse operators
Partially parsed files
Number of #DEFINE
Number of #ELIF
Number of #ELSE
Number of #ENDIF
Number of #ERROR
Number of #IF
Number of #IFDEF
Number of #IFNDEF
Number of Include
Compiler FLAG Nested Level
Number of #PRAGMA
Number of #UNDEF
Number of #WARNING
Return Statements
Repeated Code Blocks
Use of setjump
Signal Functions
Skipped Lines of Comment code
Source Lines Of Code
Special Operators
Executable Statements
IO Functions
String Conversions
Switch Statements
System Functions
Ternary operators
Time Handling
Comments containing TODO
Operand Occurrences
Operator Occurrences
Lines Added
Lines Modified
Lines Removed
While Statements
-
Mnemonic WHIL
-
Description Number of 'while' statements in the function
MindC Ruleset
Missing Break
Backward Goto shall not be used
Missing compound statement
Missing compound if
Commented-out Source Code is not allowed
Missing Default
Dynamic Memory Allocation shall not be used
Missing final else
Macro longjmp or setjmp shall not be used
Nesting Level of Preprocessing directives is too high
Assignment in Boolean
Assignment without Comparison
Factorizable Classes
Factorizable Files
Factorizable Functions
Factorizable Packages
Cloned Classes
Cloned Files
Cloned Functions
Cloned Algorithmic
There shall be a no code before first case
Continue shall not be used
Fallthrough shall be avoided
FIXME shall not be commited in sources code
Goto shall not be used
Label out a switch
Recursion are not allowed
Avoid Duplicated Blocks in Function
TODO shall not be commited in sources code
Macro offsetof shall not be used
Missing case in switch
Relaxed violation
Multiple exits are not allowed
Risky Empty Statement
Multiple break in loop are not allowed
Signal or Raise shall not be used
IO Functions shall not be used
'atof, atoi or atol' shall not be used
'abort, exit, getenv or system' shall not be used
Time Handling Functions shall not be used
-
Mnemonic TIMEHDL
-
Description The time handling functions of library <time.h> shall not be used: time, strftime, clock, difftime, mktime (see [MISRA-C:2004]: RULE 20.12).
Objective-C
Objective-C Metrics
Constant Data
Number of Attributes
Number of data without accessibility
Andthen Operators
Public Data
Protected Data
Private data
Assignment Operators
Static Data
Number of comment blocks
Header Blocks Of Comment
Blank Lines
Brace Lines
Break in Loop
Break in Switch
Case Blocks
Case Labels
Catch Statements
Cloned Code
Code Cloning Line Counting
Cyclomatic Complexity
Control Flow Token
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
Comment Lines
Clones Number
Continue Statements
Comparison Operators
Commented Statements
Depth of Descendant Tree
Default Statement
Depth of Inheritance Tree
Distinct Operands
Distinct Operators
Do While Statements
Else Statements
Comments containing FIXME
For Statements
Structures Added
Structures Modified
Structures Removed
Goto Statements
Header Lines Of Comment
Header Lines Of Code
Cloned Code
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
If Statements
Line Count
Loop Statements
Multiple Inheritance Indicator
Mixed Lines
Methods without Accessibility
Public Methods
Protected Methods
Private Methods
Static Methods
Number of Ancestors
Number of Descendants
Maximum Nested Structures
Number Of Children
Number of Parameters
Non-Cyclic Paths
Orelse operators
Partially parsed files
Properties
Number of #DEFINE
Number of #ELIF
Number of #ELSE
Number of #ENDIF
Number of #ERROR
Number of #IF
Number of #IFDEF
Number of #IFNDEF
Number of Include
Compiler FLAG Nested Level
Number of #PRAGMA
Number of #UNDEF
Number of #WARNING
Return Statements
Repeated Code Blocks
Skipped Lines of Comment code
Source Lines Of Code
Special Operators
Executable Statements
Switch Statements
Ternary operators
Throw Statements
Comments containing TODO
Operand Occurrences
Operator Occurrences
Try Statements
Lines Added
Lines Modified
Lines Removed
While Statements
Weighted Method per Class
-
Mnemonic XWMC
-
Description Sum of cyclomatic complexities of methods implemented outside the class definition
Objective-C Ruleset
Missing Break
Backward Goto shall not be used
Missing compound statement
Missing compound if
Commented-out Source Code is not allowed
Missing Default
Missing final else
Assignment in Boolean
Assignment without Comparison
Factorizable Classes
Factorizable Files
Factorizable Functions
Factorizable Packages
Cloned Classes
Cloned Files
Cloned Functions
Cloned Algorithmic
There shall be a no code before first case
Continue shall not be used
Fallthrough shall be avoided
FIXME shall not be commited in sources code
Goto shall not be used
Label out a switch
Avoid Duplicated Blocks in Function
TODO shall not be commited in sources code
Missing case in switch
Relaxed violation
Multiple exits are not allowed
Risky Empty Statement
Multiple break in loop are not allowed
-
Mnemonic SGLBRK
-
Description For any iteration statement there shall be at most one 'break' statement used for loop termination (see [MISRA-C:2004]: RULE 14.6).
PHP
PHP Metrics
Constant Data
Number of Attributes
Number of data without accessibility
Andthen Operators
Public Data
Protected Data
Private data
Static Data
Number of comment blocks
Header Blocks Of Comment
Blank Lines
Brace Lines
Case Labels
Catch Statements
Cloned Code
Code Cloning Line Counting
Cyclomatic Complexity
Control Flow Token
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
Comment Lines
Clones Number
Continue Statements
Commented Statements
Depth of Descendant Tree
Default Statement
Depth of Inheritance Tree
Distinct Operands
Distinct Operators
Do While Statements
Else Statements
Call to exit
Comments containing FIXME
For Statements
Foreach Statements
Structures Added
Structures Modified
Structures Removed
Goto Statements
Header Lines Of Comment
Header Lines Of Code
HTML Lines of Code
Cloned Code
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
If Statements
Line Count
Loop Statements
Constant Methods
Multiple Inheritance Indicator
PHP/HTML Mixed Lines
Mixed Lines
Methods without Accessibility
Public Methods
Protected Methods
Private Methods
Static Methods
Number of Ancestors
Number of Descendants
Maximum Nested Structures
Number Of Children
Number of Parameters
Non-Cyclic Paths
Orelse operators
Partially parsed files
PHP Lines of Code
Return Statements
Repeated Code Blocks
Skipped Lines of Comment code
Source Lines Of Code
Executable Statements
Switch Statements
Ternary operators
Throw Statements
Comments containing TODO
Operand Occurrences
Operator Occurrences
Try Statements
Lines Added
Lines Modified
Lines Removed
While Statements
-
Mnemonic WHIL
-
Description Number of 'while' statements in the function
PHP Ruleset
Missing Break
Backward Goto shall not be used
Missing compound statement
Missing compound if
Commented-out Source Code is not allowed
Missing Default
Missing final else
Assignment in Boolean
Assignment without Comparison
Factorizable Classes
Factorizable Files
Factorizable Functions
Factorizable Packages
Cloned Classes
Cloned Files
Cloned Functions
Cloned Algorithmic
There shall be a no code before first case
Continue shall not be used
Fallthrough shall be avoided
FIXME shall not be commited in sources code
Goto shall not be used
Label out a switch
Avoid Duplicated Blocks in Function
TODO shall not be commited in sources code
Missing case in switch
Relaxed violation
Multiple exits are not allowed
Risky Empty Statement
Multiple break in loop are not allowed
-
Mnemonic SGLBRK
-
Description For any iteration statement there shall be at most one 'break' statement used for loop termination (see [MISRA-C:2004]: RULE 14.6).
Python
Python Metrics
Number of comment blocks
Header Blocks Of Comment
Blank Lines
Brace Lines
Break in Loop
Catch Statements
Cloned Code
Code Cloning Line Counting
Cyclomatic Complexity
Control Flow Token
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
Comment Lines
Clones Number
Continue Statements
Commented Statements
Depth of Descendant Tree
Depth of Inheritance Tree
Number of DocString lines
Distinct Operands
Distinct Operators
Else Statements
Call to exit
Comments containing FIXME
For Statements
Structures Added
Structures Modified
Structures Removed
Header Lines Of Comment
Header Lines Of Code
Cloned Code
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
If Statements
Line Count
Loop Statements
Multiple Inheritance Indicator
Mixed Lines
Number of Ancestors
Number of Descendants
Maximum Nested Structures
Number Of Children
Number of Parameters
Non-Cyclic Paths
% of parsed tokens
Partially parsed files
Return Statements
Repeated Code Blocks
Skipped Lines of Comment code
Source Lines Of Code
Executable Statements
Throw Statements
Comments containing TODO
Operand Occurrences
Operator Occurrences
Try Statements
Lines Added
Lines Modified
Lines Removed
While Statements
-
Mnemonic WHIL
-
Description Number of 'while' statements in the function
Python Ruleset
There shall be a init method in the class.
Missing compound statement
Missing compound if
Missing final else
Method should have "self" as first argument
Method without parameter
Assignment in Boolean
Assignment without Comparison
Factorizable Classes
Factorizable Files
Factorizable Functions
Factorizable Packages
Cloned Classes
Cloned Files
Cloned Functions
Cloned Algorithmic
Continue shall not be used
Exec shall not be used.
Use of exit is not recommended
FIXME shall not be commited in sources code
Label out a switch
Print shall not be used.
Avoid Duplicated Blocks in Function
'star' parameter shall not be used.
TODO shall not be commited in sources code
There shall be only one Statement per line
Relaxed violation
Multiple exits are not allowed
Risky Empty Statement
Multiple break in loop are not allowed
-
Mnemonic SGLBRK
-
Description For any iteration statement there shall be at most one 'break' statement used for loop termination (see [MISRA-C:2004]: RULE 14.6).
PL/SQL
PL/SQL Metrics
Andthen Operators
Number of comment blocks
Header Blocks Of Comment
Blank Lines
Brace Lines
Break in Loop
Case Blocks
Case Labels
Catch Statements
Cloned Code
Code Cloning Line Counting
Cyclomatic Complexity
Control Flow Token
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
Comment Lines
Clones Number
Continue Statements
Commented Statements
Default Statement
Distinct Operands
Distinct Operators
Else Statements
Comments containing FIXME
For Statements
Structures Added
Structures Modified
Structures Removed
Goto Statements
Header Lines Of Comment
Header Lines Of Code
Cloned Code
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
If Statements
Line Count
Loop Statements
Mixed Lines
Maximum Nested Structures
Number of Parameters
Non-Cyclic Paths
Orelse operators
Partially parsed files
Number of #DEFINE
Number of #ELIF
Number of #ELSE
Number of #ENDIF
Number of #ERROR
Number of #IF
Number of #IFDEF
Number of #IFNDEF
Number of Include
Compiler FLAG Nested Level
Number of #PRAGMA
Number of #UNDEF
Number of #WARNING
Return Statements
Repeated Code Blocks
Skipped Lines of Comment code
Source Lines Of Code
Executable Statements
Switch Statements
Comments containing TODO
Operand Occurrences
Operator Occurrences
Lines Added
Lines Modified
Lines Removed
While Statements
-
Mnemonic WHIL
-
Description Number of 'while' statements in the function
PL/SQL Ruleset
Backward Goto shall not be used
Commented-out Source Code is not allowed
Missing Default
Missing final else
Factorizable Classes
Factorizable Files
Factorizable Functions
Factorizable Packages
Cloned Classes
Cloned Files
Cloned Functions
Cloned Algorithmic
Commit Used
FIXME shall not be commited in sources code
Goto shall not be used
Rollback Used
Avoid Duplicated Blocks in Function
TODO shall not be commited in sources code
Missing case in switch
Relaxed violation
Multiple exits are not allowed
-
Mnemonic RETURN
-
Description A function shall have a single point of exit at the end (see [MISRA-C:2004]: RULE 14.7).
Swift
Swift Metrics
Number of data without accessibility
Andthen Operators
Number of comment blocks
Header Blocks Of Comment
Blank Lines
Brace Lines
Break in Loop
Break in Switch
Case Blocks
Case Labels
Catch Statements
Code Cloning Line Counting
Cyclomatic Complexity
Control Flow Token
Comment Lines
Continue Statements
Commented Statements
Default Statement
Distinct Operands
Distinct Operators
Do While Statements
Else Statements
Comments containing FIXME
For Statements
Structures Added
Structures Modified
Structures Removed
Header Lines Of Comment
Header Lines Of Code
If Statements
Line Count
Loop Statements
Mixed Lines
Methods without Accessibility
Maximum Nested Structures
Number of Parameters
Non-Cyclic Paths
Orelse operators
Partially parsed files
Return Statements
Repeated Code Blocks
Skipped Lines of Comment code
Source Lines Of Code
Executable Statements
Switch Statements
Ternary operators
Throw Statements
Comments containing TODO
Operand Occurrences
Operator Occurrences
Try Statements
Lines Added
Lines Modified
Lines Removed
While Statements
-
Mnemonic WHIL
-
Description Number of 'while' statements in the function
Swift Ruleset
Missing compound statement
Missing compound if
Commented-out Source Code is not allowed
Missing Default
Missing final else
Assignment in Boolean
Assignment without Comparison
Factorizable Classes
Factorizable Files
Factorizable Functions
Factorizable Packages
Cloned Classes
Cloned Files
Cloned Functions
Cloned Algorithmic
Continue shall not be used
FIXME shall not be commited in sources code
Avoid Duplicated Blocks in Function
TODO shall not be commited in sources code
Missing case in switch
Multiple exits are not allowed
Risky Empty Statement
Multiple break in loop are not allowed
-
Mnemonic SGLBRK
-
Description For any iteration statement there shall be at most one 'break' statement used for loop termination (see [MISRA-C:2004]: RULE 14.6).
TSQL
TSQL Metrics
Number of comment blocks
Header Blocks Of Comment
Blank Lines
Brace Lines
Break in Loop
Catch Statements
Cloned Code
Code Cloning Line Counting
Cyclomatic Complexity
Control Flow Token
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
Comment Lines
Clones Number
Continue Statements
Commented Statements
Delete Statements
Distinct Operands
Distinct Operators
Else Statements
Comments containing FIXME
Structures Added
Structures Modified
Structures Removed
Goto Statements
Header Lines Of Comment
Header Lines Of Code
Cloned Code
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
If Statements
Insert Statements
Label Statements
Line Count
Mixed Lines
Maximum Nested Structures
Number of Parameters
Non-Cyclic Paths
Partially parsed files
Return Statements
Repeated Code Blocks
Select Statements
Skipped Lines of Comment code
Source Lines Of Code
Executable Statements
Throw Statements
Comments containing TODO
Operand Occurrences
Operator Occurrences
Try Statements
Lines Added
Lines Modified
Lines Removed
Update Statements
While Statements
-
Mnemonic WHIL
-
Description Number of 'while' statements in the function
TSQL Ruleset
Backward Goto shall not be used
Commented-out Source Code is not allowed
Missing final else
Factorizable Classes
Factorizable Files
Factorizable Functions
Factorizable Packages
Cloned Classes
Cloned Files
Cloned Functions
Cloned Algorithmic
Continue shall not be used
FIXME shall not be commited in sources code
Goto shall not be used
Avoid Duplicated Blocks in Function
TODO shall not be commited in sources code
Relaxed violation
Multiple exits are not allowed
Multiple break in loop are not allowed
-
Mnemonic SGLBRK
-
Description For any iteration statement there shall be at most one 'break' statement used for loop termination (see [MISRA-C:2004]: RULE 14.6).
Typescript
Typescript Metrics
Number of data without accessibility
Andthen Operators
Number of comment blocks
Header Blocks Of Comment
Blank Lines
Brace Lines
Break in Loop
Break in Switch
Case Blocks
Case Labels
Catch Statements
Code Cloning Line Counting
Cyclomatic Complexity
Control Flow Token
Comment Lines
Continue Statements
Commented Statements
Default Statement
Distinct Operands
Distinct Operators
Do While Statements
Else Statements
Comments containing FIXME
Max Nested Functions
For Statements
Structures Added
Structures Modified
Structures Removed
Header Lines Of Comment
Header Lines Of Code
If Statements
Line Count
Loop Statements
Mixed Lines
Methods without Accessibility
Maximum Nested Structures
Number of Parameters
Non-Cyclic Paths
Orelse operators
Partially parsed files
Return Statements
Repeated Code Blocks
Skipped Lines of Comment code
Source Lines Of Code
Executable Statements
Switch Statements
Ternary operators
Throw Statements
Comments containing TODO
Operand Occurrences
Operator Occurrences
Try Statements
Lines Added
Lines Modified
Lines Removed
While Statements
-
Mnemonic WHIL
-
Description Number of 'while' statements in the function
Typescript Ruleset
Missing Break
Missing compound statement
Missing compound if
Commented-out Source Code is not allowed
Missing Default
Missing final else
Assignment in Boolean
Assignment without Comparison
Factorizable Classes
Factorizable Files
Factorizable Functions
Factorizable Packages
Cloned Classes
Cloned Files
Cloned Functions
Cloned Algorithmic
Continue shall not be used
Fallthrough shall be avoided
FIXME shall not be commited in sources code
Avoid Duplicated Blocks in Function
TODO shall not be commited in sources code
Missing case in switch
Multiple exits are not allowed
Risky Empty Statement
Multiple break in loop are not allowed
-
Mnemonic SGLBRK
-
Description For any iteration statement there shall be at most one 'break' statement used for loop termination (see [MISRA-C:2004]: RULE 14.6).
VB.net
VB.net Metrics
Constant Data
Fiend Attributes
Number of Attributes
Andthen Operators
Public Data
Protected Data
Private data
Shadowed Attributes
Shared Attributes
Number of comment blocks
Header Blocks Of Comment
Blank Lines
Brace Lines
Break in Loop
Stop Statements
Break in Switch
Case Blocks
Case Labels
Catch Statements
Cloned Code
Code Cloning Line Counting
Cyclomatic Complexity
Control Flow Token
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
Comment Lines
Clones Number
Continue Statements
Commented Statements
Depth of Descendant Tree
Default Statement
Depth of Inheritance Tree
Distinct Operands
Distinct Operators
Do While Statements
Friend Events
Else Statements
Events
Public Events
Protected Events
Private Events
Shadowed Events
Shared Events
Call to exit
Comments containing FIXME
For Statements
Structures Added
Structures Modified
Structures Removed
Goto Statements
Header Lines Of Comment
Header Lines Of Code
Cloned Code
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
If Statements
End Statements
Line Count
Loop Statements
Declare Members
Delegate Members
Multiple Inheritance Indicator
Mixed Lines
Must Members
Methods without Accessibility
Partial Members
Public Methods
Protected Methods
Private Methods
Shadowed Members
Shared Members
Number of Ancestors
Number of Descendants
Maximum Nested Structures
Number Of Children
Number of Methods
Number of Parameters
Non-Cyclic Paths
Orelse operators
% of parsed tokens
Partially parsed files
Friend Properties
Must Properties
Properties
Public Properties
Protected Properties
Private Properties
Shadowed Properties
Shared Properties
Return Statements
Repeated Code Blocks
Skipped Lines of Comment code
Source Lines Of Code
Executable Statements
Switch Statements
Ternary operators
Throw Statements
Comments containing TODO
Operand Occurrences
Operator Occurrences
Try Statements
Lines Added
Lines Modified
Lines Removed
While Statements
-
Mnemonic WHIL
-
Description Number of 'while' statements in the function
VB.net Ruleset
Backward Goto shall not be used
Missing Case Else clause
Missing final else
Use of Exit Do statement
Use of Exit Function statement
Use of Exit For statement
Use of Exit Property statement
Use of Exit Select statement
Use of Exit Sub statement
Use of Exit Try statement
Use of Exit While statement
Factorizable Classes
Factorizable Files
Factorizable Functions
Factorizable Packages
Cloned Classes
Cloned Files
Cloned Functions
Cloned Algorithmic
Continue shall not be used
FIXME shall not be commited in sources code
Goto shall not be used
Avoid Duplicated Blocks in Function
TODO shall not be commited in sources code
No case in Select
Relaxed violation
Multiple exits are not allowed
Multiple Exit Do statement
Multiple Exit (Function, Sub or Property) statement
Multiple Exit For statement
Multiple Exit While statement
-
Mnemonic SGLEXITWHILE
-
Description For any iteration statement there shall be at most one Exit statement used for loop termination.
Xaml
Xaml Metrics
Andthen Operators
Number of attributes
Number of comment blocks
Blank Lines
Break in Loop
Break in Switch
Case Blocks
Case Labels
Catch Statements
Cloned Code
Code Cloning Line Counting
Cyclomatic Complexity
Control Flow Token
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
Comment Lines
Clones Number
Continue Statements
Commented Statements
Default Statement
Distinct Operands
Distinct Operators
Do While Statements
Else Statements
Number of XML elements
Comments containing FIXME
For Statements
Structures Added
Structures Modified
Structures Removed
Goto Statements
Cloned Code
Cloned Control Flow Tokens
If Statements
Line Count
Loop Statements
Maximum Nested Structures
Number of Parameters
Non-Cyclic Paths
Orelse operators
Partially parsed files
Return Statements
Repeated Code Blocks
Source Lines Of Code
Executable Statements
Switch Statements
Ternary operators
Number of text blocks
Throw Statements
Comments containing TODO
Operand Occurrences
Operator Occurrences
Try Statements
Lines Added
Lines Modified
Lines Removed
While Statements
-
Mnemonic WHIL
-
Description Number of 'while' statements in the function
Xaml Ruleset
Missing Break
Backward Goto shall not be used
Comment Before Paragraph
Missing compound statement
Missing compound if
Commented-out Source Code is not allowed
Missing Default
Missing final else
No Resources
Resources Folder
Assignment in Boolean
Assignment without Comparison
Factorizable Classes
Factorizable Files
Factorizable Functions
Factorizable Packages
Cloned Classes
Cloned Files
Cloned Functions
Cloned Algorithmic
There shall be a no code before first case
Continue shall not be used
Fallthrough shall be avoided
FIXME shall not be commited in sources code
Goto shall not be used
Label out a switch
Avoid Duplicated Blocks in Function
TODO shall not be commited in sources code
Missing case in switch
Relaxed violation
Resources Filename
Multiple exits are not allowed
Risky Empty Statement
Multiple break in loop are not allowed
-
Mnemonic SGLBRK
-
Description For any iteration statement there shall be at most one 'break' statement used for loop termination (see [MISRA-C:2004]: RULE 14.6).
3. Repository Connectors
Folder Path
Description
The simplest method to analyse source code in Squore is to provide a path to a folder containing your code.
|
Remember that the path supplied for the analysis is a path local to the machine running the analysis, which may be different from your local machine. If you analyse source code on your local machine and then send results to the server, you will not be able to view the source code directly in Squore, since it will not have access to the source code on the other machine. A common workaround to this problem is to use UNC paths (\\Server\Share, smb://server/share…) or a mapped server drive in Windows. |
Usage
Folder Path has the following options:
-
Datapath (path, mandatory):
-
Absolute Path: the absolute path to the folder containing the files you want to include in the analysis. The path specified must be accessible from the server and user must have Access Server Resources permission.
-
Authorized Paths: a list of server paths accessible for all users, regardless of the Access Server Resources permission. This list can only be configured by a Squore administrator : Configure Authorized Server Paths.
-
The full command line syntax for Folder Path is:
-r "type=FROMPATH,path=[text]"Zip Upload
Description
This Repository Connector allows you to upload a zip file containing your sources to analyse. Select a file to upload in the project wizard and it will be extracted and analysed on the server.
|
The contents of the zip file are extracted into Squore Server’s temp folder. If you want to uploaded files to persist, contact your Squore administrator so that the uploaded zip files and extracted sources are moved to a location that is not deleted at each server restart. |
Usage
This Repository Connector is only available from the web UI, not from the command line interface.
CVS
Description
The Concurrent Versions System (CVS), is a client-server free software revision control system in the field of software development.
For more details, refer to http://savannah.nongnu.org/projects/cvs.
|
The following is a list of commands used by the CVS Repository Connector to retrieve sources: |
Usage
CVS has the following options:
-
Repository (
repository, mandatory): Specify the location of the CVS Repository. -
Project (
project, mandatory): Specify the name of the project to get files from. -
Tag or Branch (
branch): Specify the tag or branch to get the files from.
The full command line syntax for CVS is:
-r "type=CVS,repository=[text],project=[text],branch=[text]"ClearCase
Description
IBM Rational ClearCase is a software configuration management solution that provides version control, workspace management, parallel development support, and build auditing. The command executed on the server to check out source code is: $cleartool $view_root_path $view $vob_root_path.
For more details, refer to http://www-03.ibm.com/software/products/en/clearcase.
|
The ClearCase tool is configured for Linux by default. It is possible to make it work for Windows by editing the configuration file |
Usage
ClearCase has the following options:
-
View root path (
view_root_path, mandatory, default: /view): Specify the absolute path of the ClearCase view. -
Vob Root Path (
vob_root_path, mandatory, default: /projets): Specify the absolute path of the ClearCase vob. -
View (
view): Specify the label of the view to analyse sources from. If no view is specified, the current ClearCase view will be used automatically, as retrieved by the command cleartool pwv -s. -
Server Display View (
server_display_view): When viewing source code from the Explorer after building the project, this parameter is used instead of the view parameter specified earlier. Leave this field empty to use the same value as for view. -
Sources Path (
sub_path): Specify a path in the view to restrict the scope of the source code to analyse. The value of this field must not contain the vob nor the view. Leave this field empty to analyse the code in the entire view. This parameter is only necessary if you want to restrict to a directory lower than root.
The full command line syntax for ClearCase is:
-r "type=ClearCase,view_root_path=[text],vob_root_path=[text],view=[text],server_display_view=[text],sub_path=[text]"Folder (use GNATHub)
Description
Retrieve Sources from a folder on the server, use GNATHub to limit the files (compatible with GNAT Pro versions 7.4.2 up to 18.2).
|
This Repository Connector will only be available after you configure your server or client config.xml with the path to your gnathub executable with a <path name="gnatub" path="C:\tools\GNAThub\gnathub.exe" /> definition. Consult the Configuration Manual for more information about referencing external executables. |
Usage
Folder (use GNATHub) has the following options:
-
Path of the source files (
path): Specify the absolute path to the files you want to include in the analysis. The path specified must be accessible from the server. -
Path of the gnathub.db file (
gnatdb): Specify the absolute path of the gnathub.db file. -
Root path for sources in the GNAT DB (
gnat_root): Specify the root path for sources in the GNAT DB
The full command line syntax for Folder (use GNATHub) is:
-r "type=GNAThub,path=[text],gnatdb=[text],gnat_root=[text]"Git
Description
Git is a free and open source distributed version control system designed to handle everything from small to very large projects with speed and efficiency.
For more details, refer to http://git-scm.com/.
|
The following is a list of commands used by the Git Repository Connector to retrieve sources: Git 1.7.1 is known to fail with a fatal: HTTP request failed error on CentOS 6.9. For this OS, it is recommended to upgrade to git 2.9 as provided by software collections on https://www.softwarecollections.org/en/scls/rhscl/rh-git29/ and point to the new binary in git_config.tcl or make the change permanent as described on https://access.redhat.com/solutions/527703. |
Usage
Git has the following options:
-
URL (
url, mandatory): URL of the git repository to get files from. The local, HTTP(s), SSH and Git protocols are supported. -
Branch or commit (
commit): This field allows specifying the SHA1 of a commit or a branch name. If a SHA1 is specified, it will be retieved from the default branch. If a branch label is specified, then its latest commit is analysed. Leave this field empty to analyse the latest commit of the default branch. -
Sub-directory (
subDir): Specify a subfolder name if you want to restrict the analysis to a subpath of the repository root. -
Authentication (
useAccountCredentials, default: NO_CREDENTIALS): Possible values for authentication are-
No credentials: Used when the underlying Git is open and does not require authetication
-
Use my Squore credentials: If the login/password are the same between Squore and the underlying git
-
Define credentials: To be prompted for login/password
-
-
Username (
username): -
Password (
password):
The full command line syntax for Git is:
-r "type=Git,url=[text],commit=[text],subDir=[text],useAccountCredentials=[multipleChoice],username=[text],password=[password]"PTC Integrity
Description
This Repository Connector allows analysing sources hosted in PTC Integrity, a software system lifecycle management and application lifecycle management platform developed by PTC.
For more details, refer to http://www.ptc.com/products/integrity/.
|
You can modify some of the settings of this repository connector if the si.exe and mksAPIViewer.exe binaries are not in your path. For versions that do not support the --xmlapi option, you can also turn off this method of retrieving file information. These settings are available by editing mks_conf.tcl in the repository connector’s configuration folder. |
Usage
PTC Integrity has the following options:
-
Server Hostname (
hostname, mandatory): Specify the name of the Integrity server. This value is passed to the command line using the parameter --hostname. -
Port (
port): Specify the port used to connect to the Integrity server. This value is passed to the command line using the parameter --port. -
Project (
project): Specify the name of the project containing the sources to be analysed. This value is passed to the command line using the --project parameter. -
Revision (
revision): Specify the revision number for the sources to be analysed. This value is passed to the command line using the --projectRevision parameter. -
Scope (
scope, default: name:.c,name:*.h)*: Specifies the scope (filter) for the Integrity sandbox extraction. This value is passed to the command line using the --scope parameter. -
Authentication (
useAccountCredentials, default: NO_CREDENTIALS): -
Username (
username): -
Password (
password):
The full command line syntax for PTC Integrity is:
-r "type=MKS,hostname=[text],port=[text],project=[text],revision=[text],scope=[text],useAccountCredentials=[multipleChoice],username=[text],password=[password]"Perforce
Description
The Perforce server manages a central database and a master repository of file versions. Perforce supports both Git clients and clients that use Perforce’s own protocol.
For more details, refer to http://www.perforce.com/.
|
The Perforce repository connector assumes that the specified depot exists on the specified Perforce server, that Squore can access this depot and that the Perforce user defined has the right to access it. The host where the analysis takes place must have a Perforce command-line client (p4) installed and fully functional. The P4PORT environment variable is not read by Squore. You have to set it in the form. The path to the p4 command can be configured in the perforce_conf.tcl file located in the configuration/repositoryConnectors/Perforce folder. The following is a list of commands used by the Perforce Repository Connector to retrieve sources: The format of the p4conf.txt file is: |
Usage
Perforce has the following options:
-
P4PORT (
p4port, mandatory): Specify the value of P4PORT using the format [protocol:]host:port (the protocol is optional). This parameter is necessary even if you have specified an environment variable on the machine where the analysis is running. -
Depot (
depot, mandatory): Specify the name of the depot (and optionnally subforders) containing the sources to be analysed. -
Revision (
label): Specify a label, changelist or date to retrieve the corresponding revision of the sources. Leave this field empty to analyse the most recent revision fo the sources. -
Authentication (
useAccountCredentials, default: NO_CREDENTIALS): -
Username (
username): -
Password (
password):
The full command line syntax for Perforce is:
-r "type=Perforce,p4port=[text],depot=[text],label=[text],useAccountCredentials=[multipleChoice],username=[text],password=[password]"SVN
Description
Connecting to an SVN server is supported using svn over ssh, or by using a username and password.
For more details, refer to https://subversion.apache.org/.
|
The following is a list of commands used by the SVN Repository Connector to retrieve sources (you can edit the common command base or the path to the executable in <SQUORE_HOME>/configuration/repositoryConnectors/SVN/svn_conf.tcl if needed): This Repository Connector includes a hybrid SVN mode saves you an extra checkout of your source tree when using the |
Usage
SVN has the following options:
-
URL (
url, mandatory): Specify the URL of the SVN repository to export and analyse. The following protocols are supported: svn://, svn+ssh://, http://, https:// . -
Revision (
rev): Specify a revision number in this field, or leave it blank to analyse files at the HEAD revision. -
External references (
externals, default: exclude): Specify if when extracting sources from SVN the system should also extract external references. -
Sources are already extracted in (
local_path): Specify a path to a folder where the sources have already been extracted. When using this option, sources are analysed in the specified folder instead of being checked out from SVN. At the end of the analysis, the url and revision numbers are attached to the analysed sources, so that any source code access from the web interface always retrieves files from SVN. This mode is mostly used to save an extra checkout in some continuous integration scenarios. -
Authentication (
useAccountCredentials, default: NO_CREDENTIALS): -
Username (
username): -
Password (
password):
The full command line syntax for SVN is:
-r "type=SVN,url=[text],rev=[text],externals=[multipleChoice],local_path=[directory],useAccountCredentials=[multipleChoice],username=[text],password=[password]"Synergy
Description
Rational Synergy is a software tool that provides software configuration management (SCM) capabilities for all artifacts related to software development including source code, documents and images as well as the final built software executable and libraries.
For more details, refer to http://www-03.ibm.com/software/products/en/ratisyne.
|
The Synergy Repository Connector assumes that a project already exists and that the Synergy user defined has the right to access it. The host where the analysis takes place must have Synergy installed and fully functional. Note that, using credentials is only supported on Windows, so use the NO_CREDENTIALS option when Synergy runs on a Linux host (consult IBM’s documentation at http://pic.dhe.ibm.com/infocenter/synhelp/v7m2r0/index.jsp?topic=%2Fcom.ibm.rational.synergy.manage.doc%2Ftopics%2Fsc_t_h_start_cli_session.html for more details). The following is a list of commands used by the Synergy Repository Connector to retrieve sources: |
Usage
Synergy has the following options:
-
Server URL (
server): Specify the Synergy server URL, if using a distant server. If specified, the value is used by the Synergy client via the -s parameter. -
Database (
db, mandatory): Specify the database path to analyse the sources it contains. -
Project Specification (
projectSpec, mandatory): Specify the project specification for the analysis. Source code contained in this project specification will be analysed recursively. -
Subfolder (
subFolder): Specify a subfolder name if you want to restrict the scope of the analysis to a particular folder. -
Include Subprojects (
subProject, default: yes): This option creates work area copies for the specified projects and all subprojects. If this option is not on, subprojects are ignored. -
Ignore links (
ignoreLinks, default: no): This option is used to ignore links to subprojects. This option is valid only on Linux systems. -
Authentication: (
useAccountCredentials, default: NO_CREDENTIALS): Note that, as stated in IBM's documentation, using credentials is only supported on Windows. The "No Credentials" option must be used when Synergy runs on a Linux host. For more information, consult http://pic.dhe.ibm.com/infocenter/synhelp/v7m2r0/index.jsp?topic=%2Fcom.ibm.rational.synergy.manage.doc%2Ftopics%2Fsc_t_h_start_cli_session.html. -
Username (
username): -
Password (
password):
The full command line syntax for Synergy is:
-r "type=Synergy,server=[text],db=[text],projectSpec=[text],subFolder=[text],subProject=[multipleChoice],ignoreLinks=[multipleChoice],useAccountCredentials=[multipleChoice],username=[text],password=[password]"TFS
Description
Team Foundation Server (TFS) is a Microsoft product which provides source code management, reporting, requirements management, project management, automated builds, lab management, testing and release management capabilities. This Repository Connector provides access to the sources hosted in TFS’s revision control system.
For more details, refer to https://www.visualstudio.com/products/tfs-overview-vs.
|
The TFS repository connector (Team Foundation Server - Team Foundation Version Control) assumes that a TFS command-line client is installed and fully functional on the machine where the analysis runs. Two types of clients are supported: Team Explorer Everywhere (the java client, enabled by default) and Visual Studio Client (tf.exe). Prior to using this repository connector, ensure that you have configured it to use the right client by adjusting settings in <SQUORE_HOME>/configuration/repositoryConnectors/TFS/tfs_conf.tcl file. The Repository Connector form must be filled according to the TFS standard (eg. the Project Path must begin with the '$' character…). Note that this repository connector works with a temporary workspace that is deleted at the end of the analysis. The following is a list of commands used by the TFS Repository Connector to retrieve sources (this example uses the Windows client): The following command is used when viewing sources in the web interface: When using the Java Team Explorer Everywhere client, / is replaced by - and the view command is replaced by print. |
Usage
TFS has the following options:
-
URL (
URL, mandatory): Specify the URL of the TFS server. -
Path (
path, mandatory): Path the project to be analysed. This path usually starts with $. -
Version (
version): Specify the version of the sources to analyse. This field accepts a changeset number, date, or label. Leave the field empty to analyse the most recent revision of the sources. -
Authentication (
useAccountCredentials, default: NO_CREDENTIALS): -
Username: (
username): -
Password (
password):
The full command line syntax for TFS is:
-r "type=TFS,URL=[text],path=[text],version=[text],useAccountCredentials=[multipleChoice],username=[text],password=[password]"Using Multiple Nodes
Squore allows using multiple repositories in the same analysis. If your project consists of some code that is spread over two distinct servers or SVN repositories, you can set up your project so that it includes both locations in the project analysis. This is done by labelling each source code node before specifying parameters, as shown below
-r "type=FROMPATH,alias=Node1,path=/home/projects/client-code"
-r "type=FROMPATH,alias=Node2,path=/home/projects/common/lib"Note that only alpha-numeric characters are allowed to be used as labels. In the artefact tree, each node will appear as a separate top-level folder with the label provided at project creation.
Using multiple nodes, you can also analyse sources using different Repository Connectors in the same analysis:
-r "type=FROMPATH,alias=Node1,path=/home/projects/common-config"
-r "type=SVN,alias=Node2,url=svn+ssh://10.10.0.1/var/svn/project/src,rev=HEAD"4. Data Providers
This chapter describe the available Data Providers and the default parameters that they accept via the Command Line Interface.
AntiC
Description
AntiC is a part of the jlint static analysis suite and is launched to analyse C and C++ source code and produce findings.
For more details, refer to http://jlint.sourceforge.net/.
|
On Linux, the antiC executable must be compiled manually before you run it for the first time by running the command: |
Usage
AntiC has the following options:
-
Source code directory to analyse (
dir): Leave this parameter empty if you want to analyse all sources specified above.
The full command line syntax for AntiC is:
-d "type=Antic_auto,dir=[directory]"Automotive Coverage Import
Description
Automotive Coverage Import provides a generic import mechanism for coverage results at function level.
Usage
Automotive Coverage Import has the following options:
-
CSV file (
csv): Enter the path to the CSV containing the coverage data.The expected format of each line contained in the file is PATH;NAME;TESTED_C1;OBJECT_C1;TESTED_MCC;OBJECT_MCC;TESTED_MCDC;OBJECT_MCDC
The full command line syntax for Automotive Coverage Import is:
-d "type=Automotive_Coverage,csv=[file]"Automotive Tag Import
Description
This data provider allows setting values for attributes in the project.
Usage
Automotive Tag Import has the following options:
-
CSV file (
csv): Specify the path to the file containing the metrics.
The full command line syntax for Automotive Tag Import is:
-d "type=Automotive_Tag_Import,csv=[file]"BullseyeCoverage Code Coverage Analyzer

Description
BullseyeCoverage is a code coverage analyzer for C++ and C. The coverage report file is used to generate metrics.
For more details, refer to http://www.bullseye.com/.
Usage
BullseyeCoverage Code Coverage Analyzer has the following options:
-
HTML report (
html): Specify the path to the HTML report file generated by BullseyeCoverage.
The full command line syntax for BullseyeCoverage Code Coverage Analyzer is:
-d "type=BullseyeCoverage,html=[file]"CANoe
Description
Import data from CANoe XML test results
For more details, refer to https://www.vector.com/int/en/products/products-a-z/software/canoe/.
Usage
CANoe has the following options:
-
Results folder (
dir): Specify the folder containing XML test results files from CANoe. -
File suffix (
suff, default: .xml): Provide the suffix of CANoe test results files. -
Create Test artefacts? (
createTests, default: YES): Shoult Test artefacts be created? -
Test path (
testPath, default: Tests): Define test path (for example Test/HIL Test), by default the value is Tests.
The full command line syntax for CANoe is:
-d "type=CANoe,dir=[directory],suff=[text],createTests=[multipleChoice],testPath=[text]"CPD

Description
CPD is an open source tool which generates Copy/Paste metrics. The dectection of duplicated blocks is set to 100 tokens. CPD provides an XML file which can be imported to generate metrics as well as findings.
For more details, refer to http://pmd.sourceforge.net/pmd-5.3.0/usage/cpd-usage.html.
Usage
CPD has the following options:
-
CPD XML results (
xml): Specify the path to the XML results file generated by CPD. The minimum supported version is PMD/CPD 4.2.5.
The full command line syntax for CPD is:
-d "type=CPD,xml=[file]"Cppcheck

Description
Cppcheck is a static analysis tool for C/C++ applications. The tool provides an XML output which can be imported to generate findings.
For more details, refer to http://cppcheck.sourceforge.net/.
Usage
Cppcheck has the following options:
-
Cppcheck XML results (
xml): Specify the path to the XML results file from Cppcheck. Note that the minimum required version of Cppcheck for this data provider is 1.61.
The full command line syntax for Cppcheck is:
-d "type=CPPCheck,xml=[file]"Cppcheck (plugin)
_cppcheck.png)
Description
Cppcheck is a static analysis tool for C/C++ applications. The tool provides an XML output which can be imported to generate findings.
For more details, refer to http://cppcheck.sourceforge.net/.
|
On Windows, this data provider requires an extra download to extract the Cppcheck binary in <SQUORE_HOME>/addons/tools/CPPCheck_auto/ and the MS Visual C++ 2010 Redistributable Package available from http://www.microsoft.com/en-in/download/details.aspx?id=5555. On Linux, you can install the cppcheck application anywhere you want. The path to the Cppcheck binary for Linux can be configured in config.tcl. For more information, refer to the Installation and Administration Guide’s 'Third-Party Plugins and Applications' section. |
Usage
Cppcheck (plugin) has the following options:
-
Source code folder (
dir): Specify the folder containing the source files to analyse. If you want to analyse all of source repositories specified for the project, leave this field empty. -
Ignore List (
ignores): Specify a semi-colon-separated list of source files or source file directories to exclude from the check. For example: "lib/;folder2/". Leave this field empty to deactivate this option and analyse all files with no exception.
The full command line syntax for Cppcheck (plugin) is:
-d "type=CPPCheck_auto,dir=[directory],ignores=[text]"CPPTest

Description
Parasoft C/Ctest is an integrated solution for automating a broad range of best practices proven to improve software development team productivity and software quality for C and C. The tool provides an XML output file which can be imported to generate findings and metrics.
For more details, refer to http://www.parasoft.com/product/cpptest/.
Usage
CPPTest has the following options:
-
Directory which contains the XML results files (
results_dir): Specify the path to the CPPTest results directory. This data provider is compatible with files exported from CPPTest version 7.2.10.34 and up. -
Results file extensions (
pattern, default: *.xml): Specify the pattern of the results files
The full command line syntax for CPPTest is:
-d "type=CPPTest,results_dir=[directory],pattern=[text]"Cantata

Description
Cantata is a Test Coverage tool. It provides an XML output file which can be imported to generate coverage metrics at function level.
For more details, refer to http://www.qa-systems.com/cantata.html.
Usage
Cantata has the following options:
-
Cantata XML results (
xml): Specify the path to the XML results file from Cantata 6.2
The full command line syntax for Cantata is:
-d "type=Cantata,xml=[file]"CheckStyle

Description
CheckStyle is an open source tool that verifies that Java applications adhere to certain coding standards. It produces an XML file which can be imported to generate findings.
For more details, refer to http://checkstyle.sourceforge.net/.
Usage
CheckStyle has the following options:
-
CheckStyle results file (
xml): Point to the XML file that contains Checkstyle results. Note that the minimum supported version is Checkstyle 5.3.
The full command line syntax for CheckStyle is:
-d "type=CheckStyle,xml=[file]"CheckStyle (plugin)
_CheckStyle.png)
Description
CheckStyle is an open source tool that verifies that Java applications adhere to certain coding standards. It produces an XML file which can be imported to generate findings.
For more details, refer to http://checkstyle.sourceforge.net/.
|
This data provider requires an extra download to extract the CheckStyle binary in <SQUORE_HOME>/addons/tools/CheckStyle_auto/. For more information, refer to the Installation and Administration Guide’s 'Third-Party Plugins and Applications' section. You may also deploy your own version of CheckStyle and make the Data Provider use it by editing <SQUORE_HOME>/configuration/tools/CheckStyle_auto/config.tcl. |
Usage
CheckStyle (plugin) has the following options:
-
Configuration file (
configFile): A Checkstyle configuration specifies which modules to plug in and apply to Java source files. Modules are structured in a tree whose root is the Checker module. Specify the name of the configuration file only, and the data provider will try to find it in the CheckStyle_auto folder of your custom configuration. If no custom configuration file is found, a default configuration will be used. -
Xmx (
xmx, default: 1024m): Maximum amount of memory allocated to the java process launching Checkstyle. -
Excluded directory pattern (
excludedDirectoryPattern): Java regular expression of directories to exclude from CheckStyle, for example: ^test|generated-sources|.*-report$ or ou ^lib$
The full command line syntax for CheckStyle (plugin) is:
-d "type=CheckStyle_auto,configFile=[text],xmx=[text],excludedDirectoryPattern=[text]"CheckStyle for SQALE (plugin)
_CheckStyle.png)
Description
CheckStyle is an open source tool that verifies that Java applications adhere to certain coding standards. It produces an XML file which can be imported to generate findings.
For more details, refer to http://checkstyle.sourceforge.net/.
|
This data provider requires an extra download to extract the CheckStyle binary in <SQUORE_HOME>/addons/tools/CheckStyle_auto_for_SQALE/. For more information, refer to the Installation and Administration Guide’s 'Third-Party Plugins and Applications' section. |
Usage
CheckStyle for SQALE (plugin) has the following options:
-
Configuration file (
configFile, default: config_checkstyle_for_sqale.xml): A Checkstyle configuration specifies which modules to plug in and apply to Java source files. Modules are structured in a tree whose root is the Checker module. Specify the name of the configuration file only, and the data provider will try to find it in the CheckStyle_auto folder of your custom configuration. If no custom configuration file is found, a default configuration will be used. -
Xmx (
xmx, default: 1024m): Maximum amount of memory allocated to the java process launching Checkstyle.
The full command line syntax for CheckStyle for SQALE (plugin) is:
-d "type=CheckStyle_auto_for_SQALE,configFile=[text],xmx=[text]"Cobertura format
Description
Cobertura is a free code coverage library for Java. Its XML report file can be imported to generate code coverage metrics for your Java project.
For more details, refer to http://cobertura.github.io/cobertura/.
Usage
Cobertura format has the following options:
-
XML report (
xml): Specify the path to the XML report generated by Cobertura (or by a tool able to produce data in this format).
The full command line syntax for Cobertura format is:
-d "type=Cobertura,xml=[file]"CodeSonar

Description
Codesonar is a static analysis tool for C and C++ code designed for zero tolerance defect environments. It provides an XML output file which is imported to generate findings.
For more details, refer to http://www.grammatech.com/codesonar.
Usage
CodeSonar has the following options:
-
XML results file (
xml): Specify the path to the XML results file generated by Codesonar. The minimum version of Codesonar compatible with this data provider is 3.3.
The full command line syntax for CodeSonar is:
-d "type=CodeSonar,xml=[file]"Compiler
Description
Compiler allows to import information from compiler logs.
Usage
Compiler has the following options:
-
Compiler output file(s) (
txt, mandatory): Specify the path(s) to CSV compiler log file(s). To provide multiple files click on '+'.Each line needs to match the following format: Path;Line;Rule;Descr where Rule is one of COMP_ERR, COMPILER_WARN or COMPILER_INFO.
The full command line syntax for Compiler is:
-d "type=Compiler,txt=[file]"Coverity

Description
Coverity is a static analysis tool for C, C++, Java and C#. It provides an XML output which can be imported to generate findings.
For more details, refer to http://www.coverity.com/.
Usage
Coverity has the following options:
-
XML results file (
xml): Specify the path to the XML file containing Coverity results.
The full command line syntax for Coverity is:
-d "type=Coverity,xml=[file]"ESLint

Description
ESLint is an open source tool that verifies that JavaScript applications adhere to certain coding standards. It produces an XML file which can be imported to generate findings.
For more details, refer to https://eslint.org/.
Usage
ESLint has the following options:
-
ESLint results file (
xml): Point to the XML file that contains ESLint results in Checkstyle format.
The full command line syntax for ESLint is:
-d "type=ESLint,xml=[file]"FindBugs-SpotBugs
Description
Findbugs (and its successor SpotBugs) is an open source tool that looks for bugs in Java code. It produces an XML result file which can be imported to generate findings.
For more details, refer to http://findbugs.sourceforge.net/.
Usage
FindBugs-SpotBugs has the following options:
-
XML results file (
xml): Specify the location of the XML file containing Findbugs results. Note that the minimum supported version for FindBugs is 1.3.9, and 3.1.7 to 3.1.12 for SpotBugs.
The full command line syntax for FindBugs-SpotBugs is:
-d "type=Findbugs,xml=[file]"FindBugs-SpotBugs (plugin)
_Findbugs.png)
Description
FindBugs is an open source tool that looks for bugs in Java code. It produces an XML result file which can be imported to generate findings. Note that the data provider requires an extra download to extract the FindBugs binary in [INSTALLDIR]/addons/tools/Findbugs/. You are free to use FindBugs 3.0 or FindBugs 2.0 depending on what your standard is. For more information, refer to the Installation and Administration Manual’s "Third-Party Plugins and Applications" section.This Data Provider also supports SpotBugs (successor to FindBugs), with the same parameters. If you are using SpotBugs, its binary also has to be accessible, in [INSTALLDIR]/addons/tools/Findbugs/.
For more details, refer to http://findbugs.sourceforge.net/.
|
This data provider requires an extra download to extract the FindBugs or SpotBugs binary in <SQUORE_HOME>/addons/tools/Findbugs_auto/. For more information, refer to the Installation and Administration Guide’s 'Third-Party Plugins and Applications' section. |
Usage
FindBugs-SpotBugs (plugin) has the following options:
-
Classes (
class_dir, mandatory): Specify the folders and/or jar files for your project in classpath format, or point to a text file that contains one folder or jar file per line. -
Auxiliary Class path (
auxiliarypath): Specify a list of folders and/or jars in classpath format, or specify the path to a text file that contains one folder or jar per line. This information will be passed to FindBugs or SpotBugs via the -auxclasspath parameter. -
Memory Allocation (
xmx, default: 1024m): Maximum amount of memory allocated to the java process launching FindBugs or SpotBugs.
The full command line syntax for FindBugs-SpotBugs (plugin) is:
-d "type=Findbugs_auto,class_dir=[file_or_directory],auxiliarypath=[file_or_directory],xmx=[text]"Function Relaxer
Description
Function Relaxer provides a generic import mechanism for relaxing functions in source code.
Usage
Function Relaxer has the following options:
-
CSV File (
csv):
The full command line syntax for Function Relaxer is:
-d "type=Function_Relaxer,csv=[file]"FxCop

Description
FxCop is an application that analyzes managed code assemblies (code that targets the .NET Framework common language runtime) and reports information about the assemblies, such as possible design, localization, performance, and security improvements. FxCop generates an XML results file which can be imported to generate findings.
For more details, refer to https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb429476(v=vs.80).aspx.
Usage
FxCop has the following options:
-
XML results file (
xml): Specify the XML file containing FxCop's analysis results. Note that the minimum supported version of FxCop is 1.35.
The full command line syntax for FxCop is:
-d "type=FxCop,xml=[file]"GCov

Description
GCov is a Code coverage program for C application. GCov generates raw text files which can be imported to generate metrics.
For more details, refer to http://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc/Gcov.html.
Usage
GCov has the following options:
-
Directory containing results files (
dir): Specify the path of the root directory containing the GCov results files. -
Results files extension (
ext, default: *.c.gcov): Specify the file extension of GCov results files.
The full command line syntax for GCov is:
-d "type=GCov,dir=[directory],ext=[text]"GNATcheck

Description
GNATcheck is an extensible rule-based tool that allows developers to completely define a coding standard. The results are output to a log file or an XML file that can be imported to generate findings.
For more details, refer to http://www.adacore.com/gnatpro/toolsuite/gnatcheck/.
Usage
GNATcheck has the following options:
-
Log or XML file (
txt): Specify the path to the log file or the XML file generated by the GNATcheck run.
The full command line syntax for GNATcheck is:
-d "type=GnatCheck,txt=[file]"GNATCompiler

Description
GNATCompiler is a free-software compiler for the Ada programming language which forms part of the GNU Compiler Collection. It supports all versions of the language, i.e. Ada 2012, Ada 2005, Ada 95 and Ada 83. It creates a log file that can be imported to generate findings.
For more details, refer to http://www.adacore.com/gnatpro/toolsuite/compilation/.
Usage
GNATCompiler has the following options:
-
Log file (
log): Specify the path to the log file containing the compiler warnings.
The full command line syntax for GNATCompiler is:
-d "type=GnatCompiler,log=[file]"JSHint

Description
JSHint is an open source tool that verifies that JavaScript applications adhere to certain coding standards. It produces an XML file which can be imported to generate findings.
For more details, refer to http://jshint.com/.
Usage
JSHint has the following options:
-
JSHint results file (Checkstyle formatted): (
xml): Point to the XML file that contains JSHint results Checkstyle formatted.
The full command line syntax for JSHint is:
-d "type=JSHint,xml=[file]"JUnit Format

Description
JUnit is a simple framework to write repeatable tests. It is an instance of the xUnit architecture for unit testing frameworks. JUnit XML result files are imported as test artefacts and links to tested classes are generated in the project.
For more details, refer to http://junit.org/.
Usage
JUnit Format has the following options:
-
Results folder (
resultDir, mandatory): Specify the path to the folder containing the JUnit results (or by a tool able to produce data in this format). The data provider will parse subfolders recursively. Note that the minimum support version of JUnit is 4.10. -
File Pattern (
filePattern, mandatory, default: TEST-.xml)*: Specify the pattern for files to read reports from. -
Root Artefact (
root, mandatory, default: tests[type=TEST_FOLDER]/junit[type=TEST_FOLDER]): Specify the name and type of the artefact under which the test artefacts will be created.
The full command line syntax for JUnit Format is:
-d "type=JUnit,resultDir=[directory],filePattern=[text],root=[text]"JaCoCo

Description
JaCoCo is a free code coverage library for Java. Its XML report file can be imported to generate code coverage metrics for your Java project.
For more details, refer to http://www.eclemma.org/jacoco/.
Usage
JaCoCo has the following options:
-
XML report (
xml, mandatory): Specify the path to the XML report generated by JaCoCo. Note that the folder containing the XML file must also contain JaCoCo's report DTD file, available from http://www.eclemma.org/jacoco/trunk/coverage/report.dtd. XML report files are supported from version 0.6.5.
The full command line syntax for JaCoCo is:
-d "type=Jacoco,xml=[file]"Klocwork

Description
Klocwork is a static analysis tool. Its XML result file can be imported to generate findings.
For more details, refer to http://www.klocwork.com.
Usage
Klocwork has the following options:
-
XML results file (
xml): Specify the path to the XML results file exported from Klocwork. Note that Klocwork version 9.6.1 is the minimum required version.
The full command line syntax for Klocwork is:
-d "type=Klocwork,xml=[file]"Klocwork MISRA

Description
Klocwork is a static analysis tool. Its XML result file can be imported to generate findings.
For more details, refer to http://www.klocwork.com.
Usage
Klocwork MISRA has the following options:
-
XML results file (
xml): Specify the path to the XML results file exported from Klocwork. Note that Klocwork version 9.6.1 is the minimum required version.
The full command line syntax for Klocwork MISRA is:
-d "type=Klocwork_misra,xml=[file]"Rational Logiscope

Description
The Logiscope suite allows the evaluation of source code quality in order to reduce maintenance cost, error correction or test effort. It can be applied to verify C, C++, Java and Ada languages and produces a CSV results file that can be imported to generate findings.
For more details, refer to http://www.kalimetrix.com/en/logiscope.
Usage
Rational Logiscope has the following options:
-
RuleChecker results file (
csv): Specify the path to the CSV results file from Logiscope.
The full command line syntax for Rational Logiscope is:
-d "type=Logiscope,csv=[file]"MSTest

Description
MS-Test automates the process of testing Windows applications. It combines a Windows development language, Basic, with a testing-oriented API.
For more details, refer to https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Visual_Test.
Usage
MSTest has the following options:
-
MSTest results directory (
resultDir): Specify the path to the results directory generated by MSTest. -
Test result file pattern (
filePattern): Specify the pattern of files to extract Test data from.
The full command line syntax for MSTest is:
-d "type=MSTest,resultDir=[directory],filePattern=[text]"MSTest Code Coverage
Description
MSTest is a code coverage library for C#. Its XML report file can be imported to generate code coverage metrics for your C# project.
Usage
MSTest Code Coverage has the following options:
-
XML report (
xml): Specify the path to the XML report generated by MSTest Visual Studio 2017.
The full command line syntax for MSTest Code Coverage is:
-d "type=MSTest_Coverage,xml=[file]"MemUsage
Description
Usage
MemUsage has the following options:
-
Memory Usage excel file (
excel):
The full command line syntax for MemUsage is:
-d "type=MemUsage,excel=[file]"NCover

Description
NCover is a Code coverage program for C# application. NCover generates an XML results file which can be imported to generate metrics.
For more details, refer to http://www.ncover.com/.
Usage
NCover has the following options:
-
XML results file (
xml): Specify the location of the XML results file generated by NCover. Note that the minimum supported version is NCover 3.0.
The full command line syntax for NCover is:
-d "type=NCover,xml=[file]"Oracle PLSQL compiler Warning checker

Description
This data provider reads an Oracle compiler log file and imports the warnings as findings. Findings extracted from the log file are filtered using a prefix parameter.
For more details, refer to http://www.oracle.com/.
Usage
Oracle PLSQL compiler Warning checker has the following options:
-
Compiler log file (
log): -
Prefixes (
prefix): Prefixes and their replacements are specified as pairs using the syntax [prefix1|node1;prefix2|node2]. Leave this field empty to disable filtering.The parsing algorithm looks for lines fitting this pattern:
[PATH;SCHEMA;ARTE_ID;ARTE_TYPE;LINE;COL;SEVERITY_TYPE;WARNING_ID;SEVERITY_ID;DESCR] and keeps lines where [PATH] begins with one of the input prefixes. In each kept [PATH], [prefix] is replaced by [node]. If [node] is empty, [prefix] is removed from [PATH], but not replaced. Some valid syntaxes for prefix:
One prefix to remove: svn://aaaa:12345/valid/path/from/svn
One prefix to replace: svn://aaaa:12345/valid/path/from/svn|node1
Two prefixes to remove: svn://aaaa:12345/valid/path/from/svn|;svn://bbbb:12345/valid/path/from/other_svn|
Two prefixes to remove: svn://aaaa:12345/valid/path/from/svn;svn://bbbb:12345/valid/path/from/other_svn
Two prefixes to replace: svn://aaaa:12345/valid/path/from/svn|node1;svn://bbbb:12345/valid/path/from/other_svn|node2
The full command line syntax for Oracle PLSQL compiler Warning checker is:
-d "type=Oracle_PLSQLCompiler,log=[file],prefix=[text]"MISRA Rule Checking using PC-lint

Description
PC-lint is a static code analyser. The PC-lint data provider reads PC-lint log file(s) and imports MISRA violations as findings.
For more details, refer to http://www.gimpel.com/html/pcl.htm.
Usage
MISRA Rule Checking using PC-lint has the following options:
-
Log file or folder (
logDir): Specify the path to the folder containing the PC-lint log files, or to a single log file. -
Extensions to exclude (
excludedExtensions, default: .h;.H): Specify the file extensions to exclude from the reported violations.
The full command line syntax for MISRA Rule Checking using PC-lint is:
-d "type=PC_Lint_MISRA,logDir=[file_or_directory],excludedExtensions=[text]"PMD

Description
PMD scans Java source code and looks for potential problems like possible bugs, dead code, sub-optimal code, overcomplicated expressions, duplicate code… The XML results file it generates is read to create findings.
For more details, refer to http://pmd.sourceforge.net.
Usage
PMD has the following options:
-
XML results file (
xml): Specify the path to the PMD XML results file. Note that the minimum supported version of PMD for this data provider is 4.2.5.
The full command line syntax for PMD is:
-d "type=PMD,xml=[file]"PMD (plugin)
_Pmd.png)
Description
PMD scans Java source code and looks for potential problems like possible bugs, dead code, sub-optimal code, overcomplicated expressions, duplicate code … The XML results file it generates is read to create findings.
For more details, refer to http://pmd.sourceforge.net.
|
This data provider requires an extra download to extract the PMD binary in <SQUORE_HOME>/addons/tools/PMD_auto/. For more information, refer to the Installation and Administration Guide’s 'Third-Party Plugins and Applications' section. You may also deploy your own version of PMD and make the Data Provider use it by editing <SQUORE_HOME>/configuration/tools/PMD_auto/config.tcl. |
Usage
PMD (plugin) has the following options:
-
Ruleset file (
configFile): Specify the path to the PMD XML ruleset you want to use for this analysis. If you do not specify a ruleset, the default one from INSTALLDIR/addons/tools/PMD_auto will be used.
The full command line syntax for PMD (plugin) is:
-d "type=PMD_auto,configFile=[file]"Polyspace

Description
Polyspace is a static analysis tool which includes a MISRA checker. It produces an XML output which can be imported to generate findings. Polyspace Verifier detects RTE (RunTime Error) such as Division by zero, Illegal Deferencement Pointer, Out of bound array index… Such information is turned into statistical measures at function level. Number of Red (justified/non-justified), Number of Grey (justified/non-justified), Number of Orange (justified/non-justified), Number of Green.
For more details, refer to http://www.mathworks.com/products/polyspace/index.html.
Usage
Polyspace has the following options:
-
DocBook results file (
xml): Specify the path to the DocBook (main XML file) generated by Polyspace. -
Ignore source file path (
ignoreSourceFilePath, default: false): Removes all path elements when doing the mapping between files in Squore project and files in the Pomyspace report. Becareful this can work only if file names in Squore project are unique.
The full command line syntax for Polyspace is:
-d "type=Polyspace,xml=[file],ignoreSourceFilePath=[booleanChoice]"MISRA Rule Checking with QAC

Description
QAC identifies problems in C source code caused by language usage that is dangerous, overly complex, non-portable, difficult to maintain, or simply diverges from coding standards. Its CSV results file can be imported to generate findings.
For more details, refer to http://www.phaedsys.com/principals/programmingresearch/pr-qac.html.
Usage
MISRA Rule Checking with QAC has the following options:
-
Code Folder (
logDir): Specify the path to the folder that contains the annotated files to process.For the findings to be successfully linked to their corresponding artefact, several requirements have to be met:
- The annotated file name should be [Original source file name].txt
e.g. The annotation of file "controller.c" should be called "controller.c.txt"
- The annotated file location in the annotated directory should match the associated source file location in the source directory.
e.g. The annotation for source file "[SOURCE_DIR]/subDir1/subDir2/controller.c" should be located in "[ANNOTATIONS_DIR]/subDir1/subDir2/controller.c.txt"
The previous comment suggests that the source and annotated directory are different.
However, these directories can of course be identical, which ensures that locations of source and annotated files are the same.
-
Extension (
ext, default: html): Specify the extension used by QAC to create annotated files. -
Force import of all QAC violations (not only MISRA) (
force_all_import, default: false): Force the import of all QAC findings ( not only the MISRA violations)
The full command line syntax for MISRA Rule Checking with QAC is:
-d "type=QAC_MISRA,logDir=[directory],ext=[text],force_all_import=[booleanChoice]"Rational Test RealTime

Description
Rational Test RealTime is a cross-platform solution for component testing and runtime analysis of embedded software. This Data Provider extracts coverage results, as well as tests and their status
For more details, refer to http://www-01.ibm.com/software/awdtools/test/realtime/.
Usage
Rational Test RealTime has the following options:
-
.xrd folder (
logDir): Specify the path to the folder containing the .xrd files generated by RTRT. -
Excluded file extensions (
excludedExtensions, default: .h;.H): -
Do you want to include FE (Function and Exit) in MCDC computation? (
include_fe_in_mcdc, default: false): -
Generate Test artefacts and structure from .xrd files? (
generateTests, default: false):
The full command line syntax for Rational Test RealTime is:
-d "type=RTRT,logDir=[directory],excludedExtensions=[text],include_fe_in_mcdc=[booleanChoice],generateTests=[booleanChoice]"ReqIF

Description
RIF/ReqIF (Requirements Interchange Format) is an XML file format that can be used to exchange requirements, along with its associated metadata, between software tools from different vendors.
For more details, refer to http://www.omg.org/spec/ReqIF/.
Usage
ReqIF has the following options:
-
Reqif Directory (
dir): Specify the directory which contains the Reqif files -
Spec Object Type (
objType, default: AUTO): Specify the SPEC_OBJECT_TYPE property LONG-NAME to be used to process the ReqIf file. Using the _AUTO_ value will let the Data Provider extract the value fro the ReqIf file, and assumes that there is only one such definition.
The full command line syntax for ReqIF is:
-d "type=ReqIf,dir=[directory],objType=[text]"SQL Code Guard

Description
SQL Code Guard is a free solution for SQL Server that provides fast and comprehensive static analysis for T-Sql code, shows code complexity and objects dependencies.
For more details, refer to http://www.sqlcodeguard.com.
Usage
SQL Code Guard has the following options:
-
XML results (
xml): Specify the path to the XML file containing SQL Code Guard results.
The full command line syntax for SQL Code Guard is:
-d "type=SQLCodeGuard,xml=[file]"Squan Sources

Description
Squan Sources provides basic-level analysis of your source code.
For more details, refer to https://www.vector.com/squore.
|
The analyser can output info and warning messages in the build logs. Recent additions to those logs include better handling of structures in C code, which will produce these messages:
You can specify the languages for your source code by passing pairs of language and extensions to the In order to launch an analysis using all the available languages by default, do not specify the |
Usage
Squan Sources has the following options:
-
Languages (
languages, default: ada;c;cpp;csharp;cobol;java;fortran77;fortran90;php;python;swift;vbnet): Check the boxes for the languages used in the specified source repositories. Adjust the list of file extensions as necessary. Note that two languages cannot use the same file extension, and that the list of extensions is case-sensitive. Tip: Leave all the boxes unchecked and Squan Sources will auto-detect the language parser to use. -
Force full analysis (
rebuild_all, default: false): Analyses are incremental by default. Check this box if you want to force the source code parser to analyse all files instead of only the ones that have changed since the previous analysis. This is useful if you added new rule files or text parsing rules and you want to re-evaluate all files based on your modifications. -
Generate control graphs (
genCG, default: true): This option allows generating a control graph for every function in your code. The control graph is visible in the dashboard of the function when the analysis completes. -
Use qualified names (
qualified, default: false): Note: This option cannot be modified in subsequent runs after you create the first version of your project. -
Limit analysis depth (
depth, default: false): Use this option to limit the depth of the analysis to file-level only. This means that Squan Sources will not create any class or function artefacts for your project. -
Add a 'Source Code' node (
scnode, default: false): Using this options groups all source nodes under a common source code node instead of directly under the APPLICATION node. This is useful if other data providers group non-code artefacts like tests or requirements together under their own top-level node. This option can only be set when you create a new project and cannot be modified when creating a new version of your project. -
'Source Code' node label (
scnode_name, default: Source Code): Specify a custom label for your main source code node. Note: this option is not modifiable. It only applies to projects where you use the "Add a 'Source Code' node" option. When left blank, it defaults to "Source Code". -
Compact folders (
compact_folder, default: true): When using this option, folders with only one son are aggregates together. This avoids creating many unnecessary levels in the artefact tree to get to the first level of files in your project. This option cannot be changed after you have created the first version of your project. -
Content exclusion via regexp (
pattern): Specify a PERL regular expression to automatically exclude files from the analysis if their contents match the regular expression. Leave this field empty to disable content-based file exclusion. -
File Filtering (
files_choice, default: Exclude): Specify a pattern and an action to take for matching file names. Leave the pattern empty to disable file filtering. -
pattern (
pattern_files): Use a shell-like wildcard e.g. '*-test.c'.-
* Matches any sequence of characters in string, including a null string.
-
? Matches any single character in string.
-
[chars] Matches any character in the set given by chars. If a sequence of the form x-y appears in chars, then any character between x and y, inclusive, will match. On Windows, this is used with the -nocase option, meaning that the end points of the range are converted to lower case first. Whereas [A-z] matches '_' when matching case-sensitively ('_' falls between the 'Z' and 'a'), with -nocase this is considered like [A-Za-z].
-
\x Matches the single character x. This provides a way of avoiding the special interpretation of the characters *?[] in pattern.
Tip: Use ';' to separate multiple patterns.
How to specify a file:
-
By providing its name, containing or not a pattern
-
By providing its name and its path, both containing or not a pattern
e.g.
-
*D??l?g.* : will match MyDialog.java, WinDowlog.c, … anywhere in the project
-
*/[Dd]ialog/*D??l?g.* : will match src/java/Dialog/MyDialog.java, src/c/dialog/WinDowlog.c, but not src/Dlg/c/WinDowlog.c
-
-
Folder Filtering (
dir_choice, default: Exclude): Specify a pattern and an action to take for matching folder names. Leave the pattern empty to disable folder filtering. -
pattern (
pattern_dir): Use a shell-like wildcard e.g. 'Test_*'.-
* Matches any sequence of characters in string, including a null string.
-
? Matches any single character in string.
-
[chars] Matches any character in the set given by chars. If a sequence of the form x-y appears in chars, then any character between x and y, inclusive, will match. On Windows, this is used with the -nocase option, meaning that the end points of the range are converted to lower case first. Whereas [A-z] matches '_' when matching case-sensitively ('_' falls between the 'Z' and 'a'), with -nocase this is considered like [A-Za-z].
-
\x Matches the single character x. This provides a way of avoiding the special interpretation of the characters *?[] in pattern.
Tip: Use ';' to separate multiple patterns.
A directory can be specified:
-
By providing its name, containing or not a pattern
-
By providing its name and its path, both containing or not a pattern. In that case the full path has to match.
e.g.
-
source? : will match directories source, sources, … anywhere in the project
-
src/tests : will not match any directory because the full path can not match
-
*/src/tests : will match java/src/tests, native/c/src/tests, …
To get the root path of the project it is possible to use the nodes variables ($src, $Node1, …). Refers to "Using Data Provider Input Files From Version Control" in the Getting Started to learn more.
e.g. $src/source/tests will match only the directory source/tests if it is a root directory of the project.
-
-
Exclude files whose size exceeds (
size_limit, default: 500000): Provide the size in bytes above which files are excluded automatically from the Squore project (Big files are usually generated files or test files). Leave this field empty to deactivate this option. -
Detect algorithmic cloning (
clAlg, default: true): When checking this box, Squan Sources launches a cloning detection tool capable of finding algorithmic cloning in your code. -
Detect text cloning (
clTxt, default: true): When checking this box, Squan Sources launches a cloning detection tool capable of finding text duplication in your code. -
Ignore blank lines (
clIgnBlk, default: true): When checking this box, blanks lines are ignored when searching for text duplication -
Ignore comment blocks (
clIgnCmt, default: true): When checking this box, blocks of comments are ignored when searching for text duplication -
Minimum size of duplicated blocks (
clRSlen, default: 10): This threshold defines the minimum size (number of lines) of blocks that can be reported as cloned. -
Textual Cloning fault ratio (
clFR, default: 0.1): This threshold defines how much cloning between two artefacts is necessary for them to be considered as clones by the text duplication tool. For example, a fault ratio of 0.1 means that two artefacts are considered clones if less than 10% of their contents differ. -
Algorithmic cloning fault ratio (
clAlgFR, default: 0.1): This threshold defines how much cloning between two artefacts is necessary for them to be considered as clones by the algorithmic cloning detection tool. -
Compute Textual stability (
genTs, default: true): This option allows keeping track of the stability of the code analysed for each version. The computed stability is available on the dashboard as a metric called and can be interpreted as 0% meaning completely changed and 100% meaning not changed at all. -
Compute Algorithmic stability (
genAs, default: true): This option allows keeping track of the stability of the code analysed for each version. The computed stability is available on the dashboard as a metric called Stability Index (SI) and can be interpreted as 0% meaning completely changed and 100% meaning not changed at all. -
Detect artefact renaming (
clRen, default: true): This option allows Squan Sources to detect artefacts that have been moved since the previous version, ensuring that the stability metrics of the previous artefact are passed to the new one. This is typically useful if you have moved a file to a different folder in your source tree and do not want to lose the previous metrics generated for this file. If you do not use this option, moved artefacts will be considered as new artefacts. -
Mark relaxed or confirmed findings as suspicious (
susp, default: MODIFIED_BEFORE): Depending on the choosen option, relaxed findings can be flagged as suspicious in case of changes in and around the finding. In all cases, the following is to be considered:-
Only changes on effective code are considered, comments are ignored.
-
Only changes inside the scope of the artefact containing the finding are considered.
-
-
Accept Relaxation from source code comment (
relax, default: true): Relaxing Violations in CodeSquore interprets comments formatted in one of these three ways:
-
Inline Relaxation
This syntax is used to relax violations on the current line.
some code; /* %RELAX<keys> : Text to justify the relaxation */
-
Relax Next Line
This syntax is used to relax a violation on the first following line that is not a comment. In the example the text of the justification will be: "Text to justify the relaxation the text of the justification continues while lines are made of comments only"
/* >RELAX<keys> : Text to justify the relaxation */
/* the text of the justification continues while */
/* lines are made of comments only */
some code;
-
Block Relaxation
This syntax is used to relax violations in an entire block of code.
/* {{ RELAX<keys> : Text to justify the relaxation */
/* like for format 2 text can be on more than one line */
int my_func() {
/* contains many violations */
…
}
/* }} RELAX<keys> */
<keys> can be one of the following:
-
<*>: relax all violations
-
<MNEMO>: relax violations of the rule MNEMO
-
<MNEMO1,MNEMO2,…,MNEMOn>: relax violations of rules MNEMO1 and MNEMO2 … and MNEMOn
It is possible to relax using a status different from derogation. In that case the keyword RELAX has to be followed by :RELAXATION_STATUS
e.g. RELAX:APPROVED if the status RELAXED_APPOVED is defined in the model.
-
-
Additional parameters (
additional_param): These additional parameters can be used to pass instructions to external processes started by this data provider. This value is generally left empty in most cases.
The full command line syntax for Squan Sources is:
-d "type=SQuORE,languages=[multipleChoice],rebuild_all=[booleanChoice],genCG=[booleanChoice],qualified=[booleanChoice],depth=[booleanChoice],scnode=[booleanChoice],scnode_name=[text],compact_folder=[booleanChoice],pattern=[text],files_choice=[multipleChoice],pattern_files=[text],dir_choice=[multipleChoice],pattern_dir=[text],size_limit=[text],clAlg=[booleanChoice],clTxt=[booleanChoice],clIgnBlk=[booleanChoice],clIgnCmt=[booleanChoice],clRSlen=[text],clFR=[text],clAlgFR=[text],genTs=[booleanChoice],genAs=[booleanChoice],clRen=[booleanChoice],susp=[multipleChoice],relax=[booleanChoice],additional_param=[text]"Squore Import

Description
Squore Import is a data provider used to import the results of another data provider analysis. It is generally only used for debugging purposes.
For more details, refer to support@vector.com.
Usage
Squore Import has the following options:
-
XML folder (
inputDir): Specify the folder that contains the squore_data_*.xml files that you want to import.
The full command line syntax for Squore Import is:
-d "type=SQuOREImport,inputDir=[directory]"Squore Virtual Project
Description
Squore Virtual Project is a data provider that can use the output of several projects to compile metrics in a meta-project composed of the import sub-projects.
For more details, refer to support@vector.com.
Usage
Squore Virtual Project has the following options:
-
Paths to output.xml files (
output): Specify the paths to all the output.xml files you want to include in the virtual project. Separate paths using ';'.
The full command line syntax for Squore Virtual Project is:
-d "type=SQuOREVirtualProject,output=[file]"StyleCop

Description
StyleCop is a C# code analysis tool. Its XML output is imported to generate findings.
For more details, refer to https://stylecop.codeplex.com/.
Usage
StyleCop has the following options:
-
XML results file (
xml): Specify the path to the StyleCop XML results file. The minimum version compatible with this data provider is 4.7.
The full command line syntax for StyleCop is:
-d "type=StyleCop,xml=[file]"StyleCop (plugin)
_StyleCop.png)
Description
StyleCop is a C# code analysis tool. Its XML output is imported to generate findings.
For more details, refer to https://stylecop.codeplex.com/.
|
Note that this data provider is not supported on Linux. On windows, this data provider requires an extra download to extract the StyleCop binary in <SQUORE_HOME>/addons/tools/StyleCop_auto/ and .NET framework 3.5 to be installed on your machine (run Net.SF.StyleCopCmd.Console.exe manually once to install .NET automatically). For more information, refer to the Installation and Administration Guide’s 'Third-Party Plugins and Applications' section. |
Usage
StyleCop (plugin) has the following options:
-
Solution (
sln): Specify the path to the .sln file to analyse. Leave empty to analyse all .sln found in the source repository.
The full command line syntax for StyleCop (plugin) is:
-d "type=StyleCop_auto,sln=[file]"Tessy

Description
Tessy is a tool automating module/unit testing of embedded software written in dialects of C/C++. Tessy generates an XML results file which can be imported to generate metrics. This data provider supports importing files that have a xml_version="1.0" attribute in their header.
For more details, refer to https://www.hitex.com/en/tools/tessy/.
Usage
Tessy has the following options:
-
Results folder (
resultDir): Specify the top folder containing XML result files from Tessy. Note that this data provider will recursively scan sub-folders looking for index.xml files to aggregate results.
The full command line syntax for Tessy is:
-d "type=Tessy,resultDir=[directory]"VectorCAST
Description
The VectorCAST Data Provider extracts coverage results, as well as tests and their status
For more details, refer to https://www.vectorcast.com/.
Usage
VectorCAST has the following options:
-
HTML Report (
html_report): Specify the path to the HTML report which contains the test results. -
Source code file extension (
file_extension, default: .c): Source code file extension -
Create test artefacts from HTML report (
generateTests, default: false): -
Sub Folder for test results (
sub_root): Sub Folder for test results.
The full command line syntax for VectorCAST is:
-d "type=VectorCAST,html_report=[file_or_directory],file_extension=[text],generateTests=[booleanChoice],sub_root=[text]"VectorCAST API
Description
The VectorCAST Data Provider extracts coverage results, as well as tests and their status
For more details, refer to https://www.vectorcast.com/.
Usage
VectorCAST API has the following options:
-
Retrieve the coverage data via vectorCAST API? (
generate_report, mandatory): Squore imports vectorCAST data via ".sqc" files.The sqc files are extracted from vectorCAST API.
If vectorCAST is installed on the Squore server, you can select "Yes" to ask Squore to generate the sqc files.
In that case, make sure the Squore server can access to the vectorCAST results directory.
If vectorCAST is not available on the Squore server, thus, you have to select "No" to import the test and coverage data via sqc files.
-
VectorCAST project configuration files (Path to vcm, vce or vcp) (
project_file_list): Specify the path to your project configuration file.The path should be either:
1) Path to your project ".vcm" file
2) Path to the directory which contains all the vce or vcp (Squore will look for all reccursive folders)
-
Folder of vectorCAST data files (.sqc) (
squore_report_folder)*: Specify the folder which contains all the vectorCAST data files (*.sqc).The .sqc files are generated from vectorCAST API for squore.
-
Root Artefact (
sub_root, default: Tests): Specify the name of the artefact under which the test artefacts will be created. -
Don’t Be "case sensitve" (
case_sensitve_option, default: true): Don't Be "case sensitve" -
Generate a testcase unique id (
create_path_unique_id, default: false): Generate a testcase unique id based on "path + test name"This option is needed if you want to link test objects with external requirements.
The full command line syntax for VectorCAST API is:
-d "type=VectorCAST_API,generate_report=[multipleChoice],project_file_list=[file_or_directory],squore_report_folder=[directory],sub_root=[text],case_sensitve_option=[booleanChoice],create_path_unique_id=[booleanChoice]"Vector Trace Items
Description
Import Trace Items in Vector generic format as Requirements in Squore
For more details, refer to https://www.vector.com/int/en/products/products-a-z/software/vTESTstudio/.
Usage
Vector Trace Items has the following options:
-
Trace Items folder (
dir): Specify the folder containing Trace Items (Requirements) files -
Trace Items file suffix (
suff, default: .vti-tso): Provide the suffix of Trace Items (Requirements) files. -
Default status (
default_status, default: VERIFIED): It is possible to specify the defauls status for Requirements imported in Squore. -
Planned Trace Items folder (
dirPlanned): Specify the folder containing Planned Trace Items files. -
Filter on Requirements (
filter): The filter is a way to keep Requirements which properties match a certain pattern.Syntax:<PROPERTY_NAME>?regex=<REGEX>
Examples:
-
No filters are provided… If no filters are provided, all Requirements from vTESTstudio are shown in Squore (default behavior)
-
Property 1?regex=V_.*… Only keep Requirements where 'Property 1' starts with 'V_'
-
Property 1?regex=V_.*;Property 2?regex=.*VALID.*… Only keep Requirements where 'Property 1' starts with 'V_', AND 'Property 2' contains 'VALID'
-
-
Requirements grouping (
grouping): Grouping is a way to structure Requirements in Squore by the value of given properties, in the order they are provided.Examples:Suppose Requirements have:
-
an 'Origin' property ('Internal', 'External')
-
and a 'Criticity' property ('A', 'B', 'C, 'D')
Possible values for grouping:
-
grouping is empty … If no grouping is provided, Requirement will be shown in Squore with the same structure as in vTESTstudio (default behavior)
-
grouping ='Origin' … In addition to the original structure, Requirements will be broken down by origin ('Internal, 'External', or 'Unknown' if the 'Origin' property is absent or empty)
-
grouping ='Origin;Criticity' … Same as before, but the Requirements will be broken down by Origin, THEN by Criticity ('A', 'B', 'C, 'D', or 'Unknown' if the 'Criticity' property is absent or empty)
-
The full command line syntax for Vector Trace Items is:
-d "type=Vector_TraceItems,dir=[directory],suff=[text],default_status=[multipleChoice],dirPlanned=[directory],filter=[text],grouping=[text]"Axivion

Usage
Axivion has the following options:
-
CSV File (
csv): Specify the CSV file which contains the findings results (MISRA, Coding Style…)
The full command line syntax for Axivion is:
-d "type=bauhaus,csv=[file]"CodeSniffer

Description
CodeSniffer is a rulecker for PHP and Javascript
For more details, refer to http://www.squizlabs.com/php-codesniffer.
Usage
CodeSniffer has the following options:
-
CodeSniffer results file (checkstyle formatted XML) (
xml): Point to the XML file that contains CodeSniffer results.
The full command line syntax for CodeSniffer is:
-d "type=codesniffer,xml=[file]"Configuration Checker
Description
Use this tool to check for duplicated files or XML Elements between a custom configuration and the standard configuration.
Usage
Configuration Checker has the following options:
-
Standard Configuration Path (
s): -
Custom Configurations Path (
p):
The full command line syntax for Configuration Checker is:
-d "type=conf-checker,s=[directory],p=[directory]"CSV Coverage Import
Description
CSV Coverage Import provides a generic import mechanism for coverage results at function level
Usage
CSV Coverage Import has the following options:
-
CSV file (
csv): Enter the path to the CSV containing the coverage data.The expected format of each line contained in the file is PATH;NAME;TESTED_C1;OBJECT_C1;TESTED_MCC;OBJECT_MCC;TESTED_MCDC;OBJECT_MCDC;TCOV_MCC;TCOV_MCDC;TCOV_C1
The full command line syntax for CSV Coverage Import is:
-d "type=csv_coverage,csv=[file]"CSV Findings
Description
CSV Findings is a generic tool that allows importing findings into the project.
Usage
CSV Findings has the following options:
-
CSV File(s) (
csv): Specify the path(s) to your CSV file(s) containing findings. To provide multiple files click on '+'. Each line in the file must use the following format and the file should include the following header:FILE;FUNCTION;RULE_ID;MESSAGE;LINE;COL;STATUS;STATUS_MESSAGE;TOOL
The full command line syntax for CSV Findings is:
-d "type=csv_findings,csv=[file]"CSV Import
Description
Imports artefacts, metrics, findings, textual information and links from one or more CSV files. The expected CSV format for each of the input files is described in the user manuals in the csv_import framework reference.
|
Consult csv_import Reference for more details about the expected CSV format. |
Usage
CSV Import has the following options:
-
CSV Separator (
separator, default: ;): Specify the CSV Separator used in the CSV file. -
CSV Delimiter (
delimiter, default: "): CSV Delimiter is used when the separator is used inside a cell value. If a delimiter is used as a char in a cell it has to be doubled.The ' char is not allowed as a delimiter.
-
Artefact Path Separator (
pathSeparator, default: /): Specify the character used as a separator in an artefact's path in the input CSV file. -
Case-sensitive artefact lookup (
pathAreCaseSensitive, default: true): When this option is turned on, artefacts in the CSV file are matched with existing source code artefacts in a case-sensitive manner. -
Ignore source file path (
ignoreSourceFilePath, default: false): When ignoring source file path it is your responsbility to ensure that file names are unique in the project. -
Create missing files (
createMissingFile, default: false): Automatically creates the artefacts declared in the CSV file if they do not exist. -
Ignore finding if artefact not found (
ignoreIfArtefactNotFound, default: true): If a finding can not be attached to any artefact then it is either ignored (checked) or it is attached to the project node instead (unchecked). -
Unknown rule ID (
unknownRuleId): For findings of a type that is not in your ruleset, set a default rule ID. The value for this parameter must be a valid rule ID from your analysis model. -
Measure ID for orphan artifacts count (
orphanArteCountId): To save the total count of orphan findings as a metric at application level, specify the ID of the measure to use in your analysis model. -
Measure ID for unknown rules count (
orphanRulesCountId): To save the total count of unknown rules as a metric at application level, Specify the ID of the measure to use in your analysis model. -
Information ID receiving the list of unknown rules IDs (
orphanRulesListId): To save the list of unknown rule IDs as textual information at application level, specify the ID of the textual information to use in your analysis model. -
CSV File (
csv): Specify the path to the input CSV file containing artefacts, metrics, findings, textual information, links and keys. -
Metrics CSV File (
metrics): Specify the path to the CSV file containing metrics. -
Infos CSV File (
infos): Specify the path to the CSV file containing textual information. -
Findings CSV File (
findings): Specify the path to the CSV file containing findings. -
Keys CSV File (
keys): Specify the path to the CSV file containing artefact keys. -
Links CSV File (
links): Specify the path to the CSV file containing links. -
Reports artefacts mapping problem as (
level, default: info): When an artefact referenced in the CSV file can not be found in the project, reports the problem as an information or as a warning.
The full command line syntax for CSV Import is:
-d "type=csv_import,separator=[text],delimiter=[text],pathSeparator=[text],pathAreCaseSensitive=[booleanChoice],ignoreSourceFilePath=[booleanChoice],createMissingFile=[booleanChoice],ignoreIfArtefactNotFound=[booleanChoice],unknownRuleId=[text],orphanArteCountId=[text],orphanRulesCountId=[text],orphanRulesListId=[text],csv=[file],metrics=[file],infos=[file],findings=[file],keys=[file],links=[file],level=[multipleChoice]"CSV Tag Import
Description
This data provider allows setting values for attributes in the project.
Usage
CSV Tag Import has the following options:
-
CSV file (
csv): Specify the path to the file containing the metrics.
The full command line syntax for CSV Tag Import is:
-d "type=csv_tag_import,csv=[file]"Generic Findings XML Import
Description
Generic Findings XML Import
Usage
Generic Findings XML Import has the following options:
-
XML File (
xml): Specify the XML file which contains the findings results (MISRA, Coding Style…) -
"Issue" mapping definition (
issue): -
"Rule Id" mapping definition (
id_rule): -
"Message" mapping definition (
message): -
"File" mapping definition (
file): -
"Line" mapping definition (
line): -
"Justification" mapping definition (
justification):
The full command line syntax for Generic Findings XML Import is:
-d "type=findings_xml,xml=[file],issue=[text],id_rule=[text],message=[text],file=[text],line=[text],justification=[text]"GNAThub

Description
Import data from GNAThub. GNAThub integrates and aggregates the results of AdaCore’s various static and dynamic analysis tools (GNATmetric, GNATcheck, GNATcoverage, CodePeer). Compatible with GNAT Pro versions 7.4.2 up to 18.2.
For more details, refer to https://www.adacore.com/gnatpro/toolsuite/gnatdashboard.
|
This Data Provider will only be available after you configure your server or client config.xml with the path to your gnathub executable with a <path name="gnatub" path="C:\tools\GNAThub\gnathub.exe" /> definition. Consult the Configuration Manual for more information about referencing external executables. |
Usage
GNAThub has the following options:
-
Path of the gnathub.db file (
gnatdb): Specify the absolute path of the gnathub.db file.
The full command line syntax for GNAThub is:
-d "type=gnathub,gnatdb=[file]"CPU Data Import
Description
CPU Data Import provides a generic import mechanism for CPU data from a CSV or Excel file.
Usage
CPU Data Import has the following options:
-
Root node name (
root_node, default: Resources): Specify the name of root node in the artefact tree. -
Data File (
xls_file): Specify the path to the file containing CPU information. -
Sheet Name (
xls_sheetname): Specify the name of the Excel sheet that contains the CPU list. -
CPU Column name (
xls_key): Specify the header name of the column which contains the CPU key. -
Grouping Structure (
xls_groups): Specify the headers for Grouping Structure, separated by ";". -
Filtering (
xls_filters): Specify the list of Header for filteringFor example: "column_name_1=regex1;column_name_2=regex2;
-
Specify the CSV separator (
csv_separator, default: ;): Specify the CSV separator -
"CPU Loop Time" Column name (
cpu_loop_column_name, default: Total Loop Time [ms]): Specify the column name of the CPU Loop Time (Ex: "Total Loop Time [ms]") -
"Average Idle Time per loop" Column name (
cpu_idle_column_name, default: Average idle Time per loop [ms]): Specify the column name of the Average Idle Time per loop (Ex: "Average idle Time per loop [ms]") -
"Worst Case Idle Time per loop" Column name (
cpu_worst_column_name, default: Worse case idle Time per loop [ms]): Specify the column name of the Worst Case Idle Time per loop (Ex: "Worse case idle Time per loop [ms]") -
Create an output file (
createOutput, default: true): Create an output file
The full command line syntax for CPU Data Import is:
-d "type=import_cpu,root_node=[text],xls_file=[file],xls_sheetname=[text],xls_key=[text],xls_groups=[text],xls_filters=[text],csv_separator=[text],cpu_loop_column_name=[text],cpu_idle_column_name=[text],cpu_worst_column_name=[text],createOutput=[booleanChoice]"Excel Import
Description
Excel Import
Usage
Excel Import has the following options:
-
Input file (
input_file): Specify the Excel input file -
Sheetname (
sheetname): Sheetname to read data from -
Artefact Type (
artefact_type): Artefact Type used by Squore Analysis model.Example: TEST
-
Artefact Type container (
artefact_type_container): Artefact Type container used by Squore Analysis model.Example: TEST_FOLDER
-
Artefact unique ID (
artefact_uid): Optional unless you want to use links to these artefacts.This is the artefact unique ID, to be used by links, from this Data Provider, or another Data Provider.Examples:
-
${ID}
-
T_${Name}
-
${Name} ${Descr}
Note:${NAME} designates the column called NAME
-
-
Links to this artefact (
artefact_link): Specify how to create links between this artefact and other artefacts with the following format:*<LINK_TYPE>?direction=<IN OR OUT>&column=<COLUMN_NAME>&separator=<SEPARATOR>*Examples:
-
TESTED_BY?column=Test
A 'TESTED_BY' link will be created with the UID found in column 'Test'
-
IMPLEMENTED_BY?direction=IN&column=Implements
An 'IMPLEMENTED_BY' link will be created with the UID found in column 'Implements'. Since the optional 'direction' attribute is provided, it will be set as 'IN' (default value is 'OUT')
-
TESTED_BY?column=Tests&separator=','
'TESTED_BY' links will be created with all UIDs found in column 'Tests', separated by a comma
-
TESTED_BY?column=Tests&separator=',';REFINED_BY?column=DownLinks&separator=','
'TESTED_BY' and 'REFINED_BY' links will be created with UIDs found in columns 'Tests' and 'DownLinks' respectively
-
-
Artefact name (
artefact_name): Artefact name as displayed in Squore. Examples:-
${ID}
-
T_${Name}
-
${Name} ${Descr}
Note:${NAME} designates the column called NAME
-
-
Path to the artefact (
path_list): Optional. If not used, artefacts extracted from the Excel file will be directly added to the Squore root.To specify the path in Squore of artefacts exracted from the Excel file, using the following format:
*<COLUMN_NAME>?map=[<REGEX_1>:<GROUP_NAME_1>,…,<REGEX_N>:<GROUP_NAME_N>]&groupByDate=<YES>&format=<dd-mm-YYYY>*Examples:
-
Area
Artefacts will be regrouped by the value found in the 'Area' column
-
Area?map=[A*:Area A,B*:Area B]
Artefacts will be regrouped into two groups:'Area A', for all values of 'Area' column starting with letter 'A', and 'Area B' for letter 'B'.
-
Started on?groupByDate=Yes&format=YYYY/mm/dd
Artefacts will be regrouped by the date found in column 'Started on', using the format 'YYYY/mm/dd'
Note:Date patterns are based on SimpleDateFormat Java class specifications.
-
-
Textual data to extract (
info_list): Optional.To specify the list of textual data to extract from the Excel file, using the following format:
*<METRIC_ID>?column=<COLUMN_NAME>&map=[<REGEX_1>:<TEXT_1>,…,<REGEX_N>:<TEXT_N>]*Examples:
-
ZONE_ID?column=Zone
Textual data found in column 'Zone' will be associated to metric ZONE_ID
-
ZONE_ID?column=Zone;OWNER?column=Belongs to
Textual data found in columns 'Zone' and 'Belongs to' will be associated to metric ZONE_ID and OWNER respectively
-
ORIGIN?column=Comes from,map=[Cust*:External,Sub-contractor*:External,Support:Internal,Dev:Internal]
_Textual data found in column 'Comes from' will be associated to metric ORIGIN:
-
With value 'External' if the column starts with 'Cust' or 'Sub-contractor'
-
With value 'Internal' if the column equals 'Support' or 'Dev'
_
-
Started on?groupByDate=Yes&format=YYYY/mm/dd
Artefacts will be regrouped by the date found in column 'Started on', using the format 'YYYY/mm/dd'
-
-
Numerical metrics to extract (
metric_list): Optional.To specify the list of numerical data to extract from the Excel file, using the following format:
*<METRIC_ID>?column=<COLUMN_NAME>&extract=<REGEX_EXRACT>&map=[<REGEX_1>:<VALUE_1>,…,<REGEX_N>:<VALUE_N>]*Examples:
-
PRIORITY?column=Priority level
Numerical values found in column 'Priority level' will be associated to metric PRIORITY
-
SEVERITY?column=Severity level,extract=S_
Numerical values found in column 'Severity level' will be associated to metric SEVERITY, after having extracted (removed) the string 'S_', because in this example, column 'Severity level' contains for example 'S_1', 'S_4', etc., and we want to obtain '1', '4', etc.
-
STATUS?column=State&map=[passed:0,Passed:0,Pass:0,*nconclusive*:1,failed:2,Failed:2,FAIL:2]
_Textual values found in column 'State' will be mapped to numerical values using these rules:
-
For values containing 'passed', 'Passed', 'Pass'
-
For values containing 'nconclusive'
-
For values containing 'failed', 'Failed, 'FAIL'
_
-
-
Date metrics to extract (
date_list): Optional.To specify the list of date data to extract from the Excel file, using the following format:
*<METRIC_ID>?column=<COLUMN_NAME>&format=<DATE_FORMAT>*Examples:
-
CREATION_DATE?column=Created on
Date values found in column 'Created on' will be associated to metric CREATION_DATE, using the default dd-MMM-yyyy format
-
LAST_UPDATE?column=Updated on&format=yyyy/mm/dd
Date values found in column 'Created on' will be associated to metric CREATION_DATE, using the yyyy/mm/dd format
Note:Date patterns are based on SimpleDateFormat Java class specifications.
-
-
Filters to set the list of artefacts to keep (
filter_list): Optional.If specified only artefacts complying with the provided filters are kept. Use the following format:
*<COLUMN_NAME>?regex=<REGEX>*Examples:
-
Name?regex=^ST*
Only create artefacts for which column 'Name' starts with 'ST'
-
Name?regex=^ST*;Region?regex=Europe
Same as before, but restrict to artefacts where column 'Region' is 'Europe'
-
-
Import data via UID only (
import_data_via_uid_only, default: 0): Specify this option if you want to add metric/info to an artefact which created in another Data Provider -
Header row index (
initial_row, default: 0): Specify the line number where headers are defined.Note:Indexes start at value '0', e.g. the 4th line has index 3.
The full command line syntax for Excel Import is:
-d "type=import_excel,input_file=[file],sheetname=[text],artefact_type=[text],artefact_type_container=[text],artefact_uid=[text],artefact_link=[text],artefact_name=[text],path_list=[text],info_list=[text],metric_list=[text],date_list=[text],filter_list=[text],import_data_via_uid_only=[text],initial_row=[text]"Memory Data Import
Description
Memory Data Import provides a generic import mechanism for memory data from a CSV or Excel file.
Usage
Memory Data Import has the following options:
-
Root node name (
root_node, default: Resources): Specify the name of root node in the artefact tree. -
Data File (
xls_file): Specify the path to the file containing Memory information. -
Sheet Name (
xls_sheetname): Specify the name of the Excel sheet that contains the Memory list. -
Memory Column name (
xls_key): Specify the header name of the column which contains the Memory key. -
Grouping Structure (
xls_groups): Specify the headers for Grouping Structure, separated by ";". -
Filtering (
xls_filters): Specify the list of Header for filteringFor example: "column_name_1=regex1;column_name_2=regex2;
-
Specify the CSV separator (
csv_separator, default: ;): Specify the CSV separator -
Memory size column name (
memory_size_column_name, default: Total): Specify the header name of the column which contains the memory size. -
Used memory column name (
memory_used_column_name, default: Used): Specify the header name of the column which contains the used memory. -
Memory type column name (
memory_type_column_name, default: Type): Specify the header name of the column which contains the memory type. -
ROM memory type name (
memory_type_rom_name, default: ROM): Specify the name used for ROM memory. -
RAM memory type name (
memory_type_ram_name, default: RAM): Specify the name used for RAM memory. -
NVM memory type name (
memory_type_nvm_name, default: NVM): Specify the name used for NVM memory. -
Create an output file (
createOutput, default: true): Create an output file
The full command line syntax for Memory Data Import is:
-d "type=import_memory,root_node=[text],xls_file=[file],xls_sheetname=[text],xls_key=[text],xls_groups=[text],xls_filters=[text],csv_separator=[text],memory_size_column_name=[text],memory_used_column_name=[text],memory_type_column_name=[text],memory_type_rom_name=[text],memory_type_ram_name=[text],memory_type_nvm_name=[text],createOutput=[booleanChoice]"Requirement Data Import
Description
Requirement Data Import provides a generic import mechanism for requirements from a CSV.
|
Requirement Data Import provides fields so you can map all your requirements and spread them over the following statuses: Proposed, Analyzed, Approved, Implemented, Verified, Postponed, Deleted, Rejected. Overlapping statuses will cause an error, but if a requirement’s status is not declared in the definition, the requirement will still be imported, and a finding will be created. |
Usage
Requirement Data Import has the following options:
-
Root Node (
root_node, default: Requirements): Specify the name of the node to attach requirements to. -
Data File (
input_file): Specify the path to the CSV file containing requirements. -
Sheet Name (
xls_sheetname): Specify the sheet name that contains the requirement list. -
Requirement ID (
artefact_id): Specify the header name of the column which contains the requirement ID. -
Requirement version (
version): Specify the header name of the column which contains the requirement version. -
Linked Requirements IDs which satisfy this requirement (
link_satisfied_by): Specify the header name of the column which contains the requirements IDs which satisfy this requirement. -
Linked Test ID verifying this requirement (
link_tested_by): Specify the header name of the column which contains the linked test ID verifying this requirement. -
Linked Ticket ID associated to this requirement (
link_ticket): Specify the header name of the column which contains the linked Ticket ID corresponding to an issue or enhancement request. -
Requirement Name (
artefact_name): Specify the pattern used to build the name of the requirement. The name can use any information collected from the CSV file as a parameter.Example: ${ID} : ${Summary}
-
Requirement UID (
artefact_uid): Specify the pattern used to build the requirement Unique ID. The UID can use any information collected from the CSV file as a parameter.Example: TK#${ID}
-
Grouping Structure (
artefact_groups): Specify the headers for Grouping Structure, separated by ";".For example: "column_name_1=regex1;column_name_2=regex2;
-
Filtering (
artefact_filters): Specify the list of Header for filteringFor example: "column_name_1=regex1;column_name_2=regex2;
-
Applicable Requirement Pattern (
definition_applicable): Specify the pattern applied to define requirements as Applicable. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Applicable=Yes
-
Proposed Requirement Pattern (
definition_proposed): Specify the pattern applied to define requirements as proposed. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Status=Proposed
-
Analyzed Requirement Pattern (
definition_analyzed): Specify the pattern applied to define requirements as analyzed. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Examples:
-
Status=Analyzed
-
Status=[Analyzed|Introduced]
-
Status=Analyzed;Decision=[final;revised]
-
-
Approved Requirement Pattern (
definition_approved): Specify the pattern applied to define requirements as approved. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Status=Proposed
-
Implemented Pattern (
definition_implemented): Specify the pattern applied to define requirements as Implemented. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Status=Implemented
-
Verified Requirement Pattern (
definition_verified): Specify the pattern applied to define requirements as Verified. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Status=Verified
-
Postponed Requirement Pattern (
definition_postponed): Specify the pattern applied to define requirements as Postponed. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Status=postponed
-
Deleted Requirement Pattern (
definition_deleted): Specify the pattern applied to define requirements as deleted. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Status=Deleted
-
Rejected Requirement Pattern (
definition_rejected): Specify the pattern applied to define requirements as rejected. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Status=Rejected
-
'Very high' Requirement priority Pattern (
definition_priority_very_high): Specify the pattern applied to define requirements priority as 'Very High' (usually associated to value '1'). This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Priority=1
-
'High' Requirement priority Pattern (
definition_priority_high): Specify the pattern applied to define requirements priority as 'High' (usually associated to value '2'). This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Priority=2
-
'Medium' Requirement priority Pattern (
definition_priority_medium): Specify the pattern applied to define requirements priority as 'Medium' (usually associated to value '3'). This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Priority=3
-
'Low' Requirement priority Pattern (
definition_priority_low): Specify the pattern applied to define requirements priority as 'Low' (usually associated to value '4'). This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Priority=4
-
'Met' Compliance Pattern (
definition_met): Specify the pattern applied to define requirement Compliance as 'Met'. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Compliance=Met
-
'Partially Met' Compliance Pattern (
definition_partially_met): Specify the pattern applied to define requirement Compliance as 'Partially Met'. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Compliance=Partially Met
-
'Not Met' Compliance Pattern (
definition_not_met): Specify the pattern applied to define requirement Compliance as 'Not Met'. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Compliance=Not Met
-
'Inspection' Test Method Pattern (
definition_inspection): Specify the pattern applied to define requirement Test method as 'Inspection'. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: IADT Method=Inspection
-
'Analysis' Test Method Pattern (
definition_analysis): Specify the pattern applied to define requirement Test method as 'Analysis'. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: IADT Method=Analysis
-
'Demonstration' Test Method Pattern (
definition_demonstration): Specify the pattern applied to define requirement Test method as 'Demonstration'. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: IADT Method=Demonstration
-
'Test' Test Method Pattern (
definition_test): Specify the pattern applied to define requirement Test method as 'Test'. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: IADT Method=Test
-
Creation Date Column (
creation_date): Enter the name of the column containing the creation date of the requirement.Accepted formats are detailed here.
-
Last Update Column (
last_updated): Enter the name of the column containing the last modification date of the requirement.Accepted formats are detailed here.
-
URL (
url): Specify the pattern used to build the requirement URL. The URL can use any information collected from the CSV file as a parameter.Example: https://example.com/bugs/${ID}
-
Description Column (
description): Specify the header of the column containing the description of the requirement. -
Priority Column (
priority): Specify the header of the column containing priority data. -
'A' critical factor Pattern (
definition_crit_factor_A): Specify the pattern applied to define requirement critical factor as 'A' (low). This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Criticity=A.
-
'B' critical factor Pattern (
definition_crit_factor_B): Specify the pattern applied to define requirement critical factor as 'B' (medium). This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Criticity=B.
-
'C' critical factor Pattern (
definition_crit_factor_C): Specify the pattern applied to define requirement critical factor as 'C' (high). This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Criticity=C.
-
'D' critical factor Pattern (
definition_crit_factor_D): Specify the pattern applied to define requirement critical factor as 'D' (highest). This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Criticity=D.
-
CSV Separator (
csv_separator): Specify the character used in the CSV file to separate columns. -
Information Fields (
informations): Specify the list of extra textual information to import from the CSV file. This parameter expects a list of headers separated by ";" characters.For example: Company;Country;Resolution
-
Save Output (
createOutput):
The full command line syntax for Requirement Data Import is:
-d "type=import_req,root_node=[text],input_file=[file],xls_sheetname=[text],artefact_id=[text],version=[text],link_satisfied_by=[text],link_tested_by=[text],link_ticket=[text],artefact_name=[text],artefact_uid=[text],artefact_groups=[text],artefact_filters=[text],definition_applicable=[text],definition_proposed=[text],definition_analyzed=[text],definition_approved=[text],definition_implemented=[text],definition_verified=[text],definition_postponed=[text],definition_deleted=[text],definition_rejected=[text],definition_priority_very_high=[text],definition_priority_high=[text],definition_priority_medium=[text],definition_priority_low=[text],definition_met=[text],definition_partially_met=[text],definition_not_met=[text],definition_inspection=[text],definition_analysis=[text],definition_demonstration=[text],definition_test=[text],creation_date=[text],last_updated=[text],url=[text],description=[text],priority=[text],definition_crit_factor_A=[text],definition_crit_factor_B=[text],definition_crit_factor_C=[text],definition_crit_factor_D=[text],csv_separator=[text],informations=[text],createOutput=[booleanChoice]"Requirement ASIL via Excel Import
Description
Requirement ASIL via Excel Import
Usage
Requirement ASIL via Excel Import has the following options:
-
Input file (
input_file): Specify the Excel input file -
Sheetname (
sheetname): Sheetname to read data from -
Artefact name (
artefact_name): Artefact name as displayed in Squore. Examples:-
${ID}
-
T_${Name}
-
${Name} ${Descr}
Note:${NAME} designates the column called NAME
-
-
Path to the artefact (
path_list): Optional. If not used, artefacts extracted from the Excel file will be directly added to the Squore root.To specify the path in Squore of artefacts exracted from the Excel file, using the following format:
*<COLUMN_NAME>?map=[<REGEX_1>:<GROUP_NAME_1>,…,<REGEX_N>:<GROUP_NAME_N>]&groupByDate=<YES>&format=<dd-mm-YYYY>*Examples:
-
Area
Artefacts will be regrouped by the value found in the 'Area' column
-
Area?map=[A*:Area A,B*:Area B]
Artefacts will be regrouped into two groups:'Area A', for all values of 'Area' column starting with letter 'A', and 'Area B' for letter 'B'.
-
Started on?groupByDate=Yes&format=YYYY/mm/dd
Artefacts will be regrouped by the date found in column 'Started on', using the format 'YYYY/mm/dd'
Note:Date patterns are based on SimpleDateFormat Java class specifications.
-
-
Textual data to extract (
info_list): Optional.To specify the list of textual data to extract from the Excel file, using the following format:
*<METRIC_ID>?column=<COLUMN_NAME>&map=[<REGEX_1>:<TEXT_1>,…,<REGEX_N>:<TEXT_N>]*Examples:
-
ZONE_ID?column=Zone
Textual data found in column 'Zone' will be associated to metric ZONE_ID
-
ZONE_ID?column=Zone;OWNER?column=Belongs to
Textual data found in columns 'Zone' and 'Belongs to' will be associated to metric ZONE_ID and OWNER respectively
-
ORIGIN?column=Comes from,map=[Cust*:External,Sub-contractor*:External,Support:Internal,Dev:Internal]
_Textual data found in column 'Comes from' will be associated to metric ORIGIN:
-
With value 'External' if the column starts with 'Cust' or 'Sub-contractor'
-
With value 'Internal' if the column equals 'Support' or 'Dev'
_
-
Started on?groupByDate=Yes&format=YYYY/mm/dd
Artefacts will be regrouped by the date found in column 'Started on', using the format 'YYYY/mm/dd'
-
-
Numerical metrics to extract (
metric_list): Optional.To specify the list of numerical data to extract from the Excel file, using the following format:
*<METRIC_ID>?column=<COLUMN_NAME>&extract=<REGEX_EXRACT>&map=[<REGEX_1>:<VALUE_1>,…,<REGEX_N>:<VALUE_N>]*Examples:
-
PRIORITY?column=Priority level
Numerical values found in column 'Priority level' will be associated to metric PRIORITY
-
SEVERITY?column=Severity level,extract=S_
Numerical values found in column 'Severity level' will be associated to metric SEVERITY, after having extracted (removed) the string 'S_', because in this example, column 'Severity level' contains for example 'S_1', 'S_4', etc., and we want to obtain '1', '4', etc.
-
STATUS?column=State&map=[passed:0,Passed:0,Pass:0,*nconclusive*:1,failed:2,Failed:2,FAIL:2]
_Textual values found in column 'State' will be mapped to numerical values using these rules:
-
For values containing 'passed', 'Passed', 'Pass'
-
For values containing 'nconclusive'
-
For values containing 'failed', 'Failed, 'FAIL'
_
-
-
Artefact unique ID (
artefact_uid): Optional unless you want to use links to these artefacts.This is the artefact unique ID, to be used by links, from this Data Provider, or another Data Provider.Examples:
-
${ID}
-
T_${Name}
-
${Name} ${Descr}
Note:${NAME} designates the column called NAME
-
The full command line syntax for Requirement ASIL via Excel Import is:
-d "type=import_req_asil,input_file=[file],sheetname=[text],artefact_name=[text],path_list=[text],info_list=[text],metric_list=[text],artefact_uid=[text]"Stack Data Import
Description
Stack Data Import provides a generic import mechanism for stack data from a CSV or Excel file.
Usage
Stack Data Import has the following options:
-
Root node name (
root_node, default: Resources): Specify the name of root node in the artefact tree. -
Data File (
xls_file): Specify the path to the file containing Stack information. -
Sheet Name (
xls_sheetname): Specify the sheetname that contains the Stack list. -
Stack Column name (
xls_key): Specify the header name of the column which contains the Stack key. -
Grouping Structure (
xls_groups): Specify the headers for Grouping Structure, separated by ";". -
Filtering (
xls_filters): Specify the list of Header for filteringFor example: "column_name_1=regex1;column_name_2=regex2;
-
Specify the CSV separator (
csv_separator, default: ;): Specify the CSV separator -
Stack size column (
stack_size_column_name, default: Stack Size [Bytes]): Specify the name of the column of Stack Size -
Stack Average column (
stack_average_column_name, default: Average Stack Size used [Bytes]): Specify the name of the column of Stack Average -
Stack Worst column (
stack_worst_column_name, default: Worse Case Stack Size used [Bytes]): Specify the name of the column of Stack Worst -
Create an output file (
createOutput, default: true): Create an output file
The full command line syntax for Stack Data Import is:
-d "type=import_stack,root_node=[text],xls_file=[file],xls_sheetname=[text],xls_key=[text],xls_groups=[text],xls_filters=[text],csv_separator=[text],stack_size_column_name=[text],stack_average_column_name=[text],stack_worst_column_name=[text],createOutput=[booleanChoice]"Test Data Import
Description
Test Data Import provides a generic import mechanism for tests from a CSV, Excel or JSON file. Additionnally, it generates findings when the imported tests have an unknown status or type.
|
This Data Provider provides fields so you can map all your tests and spread them over the following statuses: Failed, Inconclusive, Passd. Overlapping statuses and types will cause an error, but if a test status is not declared in the definition, the test will still be imported, and a finding will be created. |
Usage
Test Data Import has the following options:
-
Root Node (
root_node, default: Tests): Specify the name of the node to attach tests to. -
Data File (
input_file): Specify the path to the CSV, Excel or JSON file containing tests. -
Excel Sheet Name (
xls_sheetname): Specify the sheet name that contains the test list if your import file is in Excel format. -
TestID (
artefact_id): Specify the header name of the column which contains the test ID. -
Linear Index Column (
linear_idx): Specify the column name of the Linear Index (=Linear Index is used to order unit or integration tests in matrix graph). -
Test Name (
artefact_name): Specify the pattern used to build the name of the test. The name can use any information collected from the CSV file as a parameter.Example: ${ID} : ${Summary}
-
Test UID (
artefact_uid): Specify the pattern used to build the test Unique ID. The UID can use any information collected from the CSV file as a parameter.Example: TST#${ID}
-
Grouping Structure (
artefact_groups): Specify the headers for Grouping Structure, separated by ";".For example: "column_name_1=regex1;column_name_2=regex2;
-
Filtering (
artefact_filters): Specify the list of Header for filteringFor example: "column_name_1=regex1;column_name_2=regex2;
-
Failed Test Pattern (
definition_failed): Specify the pattern applied to define tests as failed. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Status=Failed
-
Inconcusive Test Pattern (
definition_inconclusive): Specify the pattern applied to define tests as inconclusive. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Status=[Inconclusive|Unfinished]
-
Passed Test Pattern (
definition_passed): Specify the pattern applied to define tests as passed. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Status=Passed
-
Date when the test was executed (
execution_date): Enter the name of the column containing the execution date of the test.Accepted formats are detailed here.
-
Unit of test duration (
execution_duration_unit, default: ms): Enter the unit used for the test duration. Possible values are 's' (seconds) or 'ms' (milliseconds), default is 'ms') -
Duration of the test (
execution_duration): Enter duration of the test, in milliseconds. -
TODO Pattern (
in_todo_list): Specify the pattern applied to include tests in the TODO list. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Active=Yes
-
Creation Date Column (
creation_date): Enter the name of the column containing the creation date of the test.Accepted formats are detailed here.
-
Last Updated Date Column (
last_updated_date): Enter the name of the column containing the last updated date of the test.Accepted formats are detailed here.
-
URL (
url): Specify the pattern used to build the test URL. The URL can use any information collected from the CSV file as a parameter.Example: https://example.com/tests/${ID}
-
Description Column (
description): Specify the header of the column containing the description of the test. -
Category Column (
category): Specify the header of the column containing the category of the test. -
Priority Column (
priority): Specify the header of the column containing priority data. -
CSV Separator (
csv_separator): Specify the character used in the CSV file to separate columns. -
Information Fields (
informations): Specify the list of extra textual information to import from the CSV file. This parameter expects a list of headers separated by ";" characters.For example: Architecture;Responsible;Target
-
Save Output (
createOutput):
The full command line syntax for Test Data Import is:
-d "type=import_test,root_node=[text],input_file=[file],xls_sheetname=[text],artefact_id=[text],linear_idx=[text],artefact_name=[text],artefact_uid=[text],artefact_groups=[text],artefact_filters=[text],definition_failed=[text],definition_inconclusive=[text],definition_passed=[text],execution_date=[text],execution_duration_unit=[multipleChoice],execution_duration=[text],in_todo_list=[text],creation_date=[text],last_updated_date=[text],url=[text],description=[text],category=[text],priority=[text],csv_separator=[text],informations=[text],createOutput=[booleanChoice]"Test Excel Import
Description
Test Excel Import
Usage
Test Excel Import has the following options:
-
Input file (
input_file): Specify the Excel input file -
Sheetname (
sheetname): Sheetname to read data from -
Artefact name (
artefact_name): Artefact name as displayed in Squore. Examples:-
${ID}
-
T_${Name}
-
${Name} ${Descr}
Note:${NAME} designates the column called NAME
-
-
Path to the artefact (
path_list): Optional. If not used, artefacts extracted from the Excel file will be directly added to the Squore root.To specify the path in Squore of artefacts exracted from the Excel file, using the following format:
*<COLUMN_NAME>?map=[<REGEX_1>:<GROUP_NAME_1>,…,<REGEX_N>:<GROUP_NAME_N>]&groupByDate=<YES>&format=<dd-mm-YYYY>*Examples:
-
Area
Artefacts will be regrouped by the value found in the 'Area' column
-
Area?map=[A*:Area A,B*:Area B]
Artefacts will be regrouped into two groups:'Area A', for all values of 'Area' column starting with letter 'A', and 'Area B' for letter 'B'.
-
Started on?groupByDate=Yes&format=YYYY/mm/dd
Artefacts will be regrouped by the date found in column 'Started on', using the format 'YYYY/mm/dd'
Note:Date patterns are based on SimpleDateFormat Java class specifications.
-
-
Textual data to extract (
info_list): Optional.To specify the list of textual data to extract from the Excel file, using the following format:
*<METRIC_ID>?column=<COLUMN_NAME>&map=[<REGEX_1>:<TEXT_1>,…,<REGEX_N>:<TEXT_N>]*Examples:
-
ZONE_ID?column=Zone
Textual data found in column 'Zone' will be associated to metric ZONE_ID
-
ZONE_ID?column=Zone;OWNER?column=Belongs to
Textual data found in columns 'Zone' and 'Belongs to' will be associated to metric ZONE_ID and OWNER respectively
-
ORIGIN?column=Comes from,map=[Cust*:External,Sub-contractor*:External,Support:Internal,Dev:Internal]
_Textual data found in column 'Comes from' will be associated to metric ORIGIN:
-
With value 'External' if the column starts with 'Cust' or 'Sub-contractor'
-
With value 'Internal' if the column equals 'Support' or 'Dev'
_
-
Started on?groupByDate=Yes&format=YYYY/mm/dd
Artefacts will be regrouped by the date found in column 'Started on', using the format 'YYYY/mm/dd'
-
-
Numerical metrics to extract (
metric_list): Optional.To specify the list of numerical data to extract from the Excel file, using the following format:
*<METRIC_ID>?column=<COLUMN_NAME>&extract=<REGEX_EXRACT>&map=[<REGEX_1>:<VALUE_1>,…,<REGEX_N>:<VALUE_N>]*Examples:
-
PRIORITY?column=Priority level
Numerical values found in column 'Priority level' will be associated to metric PRIORITY
-
SEVERITY?column=Severity level,extract=S_
Numerical values found in column 'Severity level' will be associated to metric SEVERITY, after having extracted (removed) the string 'S_', because in this example, column 'Severity level' contains for example 'S_1', 'S_4', etc., and we want to obtain '1', '4', etc.
-
STATUS?column=State&map=[passed:0,Passed:0,Pass:0,*nconclusive*:1,failed:2,Failed:2,FAIL:2]
_Textual values found in column 'State' will be mapped to numerical values using these rules:
-
For values containing 'passed', 'Passed', 'Pass'
-
For values containing 'nconclusive'
-
For values containing 'failed', 'Failed, 'FAIL'
_
-
-
Date metrics to extract (
date_list): Optional.To specify the list of date data to extract from the Excel file, using the following format:
*<METRIC_ID>?column=<COLUMN_NAME>&format=<DATE_FORMAT>*Examples:
-
CREATION_DATE?column=Created on
Date values found in column 'Created on' will be associated to metric CREATION_DATE, using the default dd-MMM-yyyy format
-
LAST_UPDATE?column=Updated on&format=yyyy/mm/dd
Date values found in column 'Created on' will be associated to metric CREATION_DATE, using the yyyy/mm/dd format
Note:Date patterns are based on SimpleDateFormat Java class specifications.
-
-
Filters to set the list of artefacts to keep (
filter_list): Optional.If specified only artefacts complying with the provided filters are kept. Use the following format:
*<COLUMN_NAME>?regex=<REGEX>*Examples:
-
Name?regex=^ST*
Only create artefacts for which column 'Name' starts with 'ST'
-
Name?regex=^ST*;Region?regex=Europe
Same as before, but restrict to artefacts where column 'Region' is 'Europe'
-
-
Artefact unique ID (
artefact_uid): Optional unless you want to use links to these artefacts.This is the artefact unique ID, to be used by links, from this Data Provider, or another Data Provider.Examples:
-
${ID}
-
T_${Name}
-
${Name} ${Descr}
Note:${NAME} designates the column called NAME
-
-
Links to this artefact (
artefact_link): Specify how to create links between this artefact and other artefacts with the following format:*<LINK_TYPE>?direction=<IN OR OUT>&column=<COLUMN_NAME>&separator=<SEPARATOR>*Examples:
-
TESTED_BY?column=Test
A 'TESTED_BY' link will be created with the UID found in column 'Test'
-
IMPLEMENTED_BY?direction=IN&column=Implements
An 'IMPLEMENTED_BY' link will be created with the UID found in column 'Implements'. Since the optional 'direction' attribute is provided, it will be set as 'IN' (default value is 'OUT')
-
TESTED_BY?column=Tests&separator=','
'TESTED_BY' links will be created with all UIDs found in column 'Tests', separated by a comma
-
TESTED_BY?column=Tests&separator=',';REFINED_BY?column=DownLinks&separator=','
'TESTED_BY' and 'REFINED_BY' links will be created with UIDs found in columns 'Tests' and 'DownLinks' respectively
-
The full command line syntax for Test Excel Import is:
-d "type=import_test_excel,input_file=[file],sheetname=[text],artefact_name=[text],path_list=[text],info_list=[text],metric_list=[text],date_list=[text],filter_list=[text],artefact_uid=[text],artefact_link=[text]"Ticket Data Import
Description
Ticket Data Import provides a generic import mechanism for tickets from a CSV, Excel or JSON file. Additionnally, it generates findings when the imported tickets have an unknown status or type.
|
This Data Provider provides fields so you can map all your tickets as Enhancements and defects and spread them over the following statuses: Open, In Implementation, In Verification, Closed. Overlapping statuses and types will cause an error, but if a ticket’s type or status is not declared in the definition, the ticket will still be imported, and a finding will be created. |
Usage
Ticket Data Import has the following options:
-
Root Node (
root_node, default: Tickets): Specify the name of the node to attach tickets to. -
Data File (
input_file): Specify the path to the CSV, Excel or JSON file containing tickets. -
Excel Sheet Name (
xls_sheetname): Specify the sheet name that contains the ticket list if your import file is in Excel format. -
Ticket ID (
artefact_id): Specify the header name of the column which contains the ticket ID. -
Ticket Name (
artefact_name): Specify the pattern used to build the name of the ticket. The name can use any information collected from the CSV file as a parameter.Example: ${ID} : ${Summary}
-
Ticket UID (
artefact_uid): Specify the pattern used to build the ticket Unique ID. The UID can use any information collected from the CSV file as a parameter.Example: TK#${ID}
-
Grouping Structure (
artefact_groups): Specify the headers for Grouping Structure, separated by ";".For example: "column_name_1=regex1;column_name_2=regex2;
-
Filtering (
artefact_filters): Specify the list of Header for filteringFor example: "column_name_1=regex1;column_name_2=regex2;
-
Open Ticket Pattern (
definition_open): Specify the pattern applied to define tickets as open. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Status=[Open|New]
-
In Development Ticket Pattern (
definition_rd_progress): Specify the pattern applied to define tickets as in development. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Status=Implementing
-
Fixed Ticket Pattern (
definition_vv_progress): Specify the pattern applied to define tickets as fixed. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Status=Verifying;Resolution=[fixed;removed]
-
Closed Ticket Pattern (
definition_close): Specify the pattern applied to define tickets as closed. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Status=Closed
-
Defect Pattern (
definition_defect): Specify the pattern applied to define tickets as defects. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Type=Bug
-
Enhancement Pattern (
definition_enhancement): Specify the pattern applied to define tickets as enhancements. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Type=Enhancement
-
TODO Pattern (
in_todo_list): Specify the pattern applied to include tickets in the TODO list. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Sprint=2018-23
-
Creation Date Column (
creation_date): Enter the name of the column containing the creation date of the ticket.Accepted formats are detailed here.
-
Due Date Column (
due_date): Enter the name of the column containing the due date of the ticket.Accepted formats are detailed here.
-
Last Updated Date Column (
last_updated_date): Enter the name of the column containing the last updated date of the ticket.Accepted formats are detailed here.
-
Closure Date Column (
closure_date): Enter the name of the column containing the closure date of the ticket.Accepted formats are detailed here.
-
URL (
url): Specify the pattern used to build the ticket URL. The URL can use any information collected from the CSV file as a parameter.Example: https://example.com/bugs/${ID}
-
Description Column (
description): Specify the header of the column containing the description of the ticket. -
Category Column (
category): Specify the header of the column containing the category of the ticket. -
Reporter Column (
reporter): Specify the header of the column containing the reporter of the ticket. -
Handler Column (
handler): Specify the header of the column containing the handler of the ticket. -
Priority Column (
priority): Specify the header of the column containing priority data. -
Severity Column (
severity): Specify the header of the column containing severity data. -
CSV Separator (
csv_separator): Specify the character used in the CSV file to separate columns. -
Information Fields (
informations): Specify the list of extra textual information to import from the CSV file. This parameter expects a list of headers separated by ";" characters.For example: Company;Country;Resolution
-
Save Output (
createOutput):
The full command line syntax for Ticket Data Import is:
-d "type=import_ticket,root_node=[text],input_file=[file],xls_sheetname=[text],artefact_id=[text],artefact_name=[text],artefact_uid=[text],artefact_groups=[text],artefact_filters=[text],definition_open=[text],definition_rd_progress=[text],definition_vv_progress=[text],definition_close=[text],definition_defect=[text],definition_enhancement=[text],in_todo_list=[text],creation_date=[text],due_date=[text],last_updated_date=[text],closure_date=[text],url=[text],description=[text],category=[text],reporter=[text],handler=[text],priority=[text],severity=[text],csv_separator=[text],informations=[text],createOutput=[booleanChoice]"Jira
Description
This Data Provider extracts tickets and their attributes from a Jira instance to create ticket artefacts in your project.
For more details, refer to https://www.atlassian.com/software/jira.
|
The extracted JSON from Jira is then passed to the Ticket Data Import Data Provider (described in Ticket Data Import). Finer configuration of the data passed from this Data Provider to Ticket Data Import is available by editing (or overriding) <SQUORE_HOME>/addons/tools/jira/jira_config.xml. |
Usage
Jira has the following options:
-
Jira REST API URL (
url, mandatory): The URL used to connect to yout Jira instance's REST API URL (e.g: https://jira.domain.com/rest/api/2) -
Jira User login (
login, mandatory): Specyfy your Jira User login. -
Jira User password (
pwd, mandatory): Specify your Jira User password. -
Number of queried tickets (
max_results, mandatory, default: -1): Maximum number of queried tickets returned by the query (default is -1, meaning 'retrieve all tickets'). -
Additional Fields (
additional_fields, default: environment,votes): List additional fields to be exported from Jira.This field accepts a comma-separated list of field names that are added to the export request URL, for example fixVersions,versions
-
Grouping Structure (
artefact_groups, default: fields/components[0]/name): Specify the headers for Grouping Structure, separated by ";".For example: "column_name_1=regex1;column_name_2=regex2;
-
Creation Date Field (
creation_date, default: fields/created): Enter the name of the column containing the creation date of the ticket.For example: column_name{format="dd/mm/yyyy"}).
If format is not specified, the following is used by default: dd/mm/yyyy.
-
Closure Date Field (
closure_date, default: fields/resolutiondate): Enter the name of the column containing the closure date of the ticket.For example: column_name{format="dd/mm/yyyy"}).
If format is not specified, the following is used by default: dd/mm/yyyy.
-
Due Date Field (
due_date, default: fields/duedate): Enter the name of the column containing the due date of the ticket.For example: column_name{format="dd/mm/yyyy"}).
If format is not specified, the following is used by default: dd/mm/yyyy.
-
Last Updated Date Field (
last_updated_date, default: fields/updated): Enter the name of the column containing the last updated date of the ticket.For example: column_name{format="dd/mm/yyyy"}).
If format is not specified, the following is used by default: dd/mm/yyyy.
-
Category (
category, default: fields/components[0]/name): Specify the path to the field that will contain the ticket category. -
Priority (
priority, default: fields/priority/name): Specify the path to the field that will contain the ticket priority. -
JQL Request (
jql_request): Specify a JQL request (see JIRA documentation) in order to limit the number of elements sent by the JIRA server.For example: project=MyProject.This parameter is optional.
-
Filtering (
artefact_filters, default: fields/issuetype/name=(Task|Bug|Improvement|New Feature)): Specify the list of Header for filteringFor example: "column_name_1=regex1;column_name_2=regex2;
-
Information Fields (
informations, default: fields/environment;fields/votes/votes): Specify a semicolon-separated list of paths to fields you want to extract from the Jira JSON export to be added as textual information for the ticket artefacts.For example: fields/fixVersions[0]/name;fields/versions[0]/name
-
Open Ticket Pattern (
definition_open, default: fields/status/name=[To Do|Open|Reopened]): Specify the pattern applied to define tickets as open. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Status=[Open|New]
-
In Development Ticket Pattern (
definition_rd_progress, default: fields/status/name=[In Progress|In Review]): Specify the pattern applied to define tickets as in development. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Status=Implementing
-
Fixed Ticket Pattern (
definition_vv_progress, default: fields/status/name=[Verified]): Specify the pattern applied to define tickets as fixed. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Status=Verifying;Resolution=[fixed;removed]
-
Closed Ticket Pattern (
definition_close, default: fields/status/name=[Resolved|Closed|Done]): Specify the pattern applied to define tickets as closed. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Status=Closed
-
Defect Pattern (
definition_defect, default: fields/issuetype/name=[Bug]): Specify the pattern applied to define tickets as defects. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Type=Bug
-
Enhancement Pattern (
definition_enhancement, default: fields/issuetype/name=[Improvement|New Feature]): Specify the pattern applied to define tickets as enhancements. This field accepts a regular expression to match one or more column headers with a list of possible values.Example: Type=Enhancement
-
Todo list regex (
in_todo_list, default: fields/status/name=.)*: Todo list regex (ticket which fit the regex will be considered as part of the TODO list for the analysis)
The full command line syntax for Jira is:
-d "type=jira,url=[text],login=[text],pwd=[password],max_results=[text],additional_fields=[text],artefact_groups=[text],creation_date=[text],closure_date=[text],due_date=[text],last_updated_date=[text],category=[text],priority=[text],jql_request=[text],artefact_filters=[text],informations=[text],definition_open=[text],definition_rd_progress=[text],definition_vv_progress=[text],definition_close=[text],definition_defect=[text],definition_enhancement=[text],in_todo_list=[text]"Mantis
Description
The Mantis Data Provider extracts tickets and their attributes from a Mantis installation and creates ticket artefacts.
Prerequisites:
-
This Data Provider queries Mantis tickets using the Mantis BT REST API. An API token is required to access this API.
-
The Mantis server should be configured to avoid filtering 'Authorization' headers.
See http://docs.php.net/manual/en/features.http-auth.php#114877 for further details.
For more details, refer to https://www.mantisbt.com.
|
The extracted JSON from Mantis BT is then passed to the Ticket Data Import Data Provider (described in Ticket Data Import). Finer configuration of the data passed from this Data Provider to Ticket Data Import is available by editing (or overriding) <SQUORE_HOME>/addons/tools/mantis/mantis_config.xml. |
Usage
Mantis has the following options:
-
Mantis URL (
url, mandatory): Specify the URL of the Mantis instance (e.g: https://www.mantisbt.org/bugs/api/rest) -
Mantis API Token (
api_token, mandatory): Copy the Mantis API Token generated from your Account Settings in Mantis. -
Number of queried tickets (
max_results, mandatory, default: 50): Maximum number of queried tickets returned by the query (default is 50. value=-1 means 'retrieve all tickets').
The full command line syntax for Mantis is:
-d "type=mantis,url=[text],api_token=[text],max_results=[text]"OSLC
Description
OSLC-CM allows retrieving information from Change Management systems following the OSLC standard. Metrics and artefacts are created by connecting to the OSLC system and retrieving issues with the specified query.
For more details, refer to http://open-services.net/.
Usage
OSLC has the following options:
-
Change Server (
server): Specify the URL of the project you want to query on the OSLC server. Typically the URL will look like this: http://myserver:8600/change/oslc/db/3454a67f-656ddd4348e5/role/User/ -
Query (
query): Specify the query to send to the OSLC server (e.g.: release="9TDE/TDE_00_01_00_00"). It is passed to the request URL via the ?oslc_cm.query= parameter. -
Query Properties (
properties, default: request_type,problem_number,crstatus,severity,submission_area,functionality…): Specify the properties to add to the query. They are passed to the OSLC query URL using the ?oslc_cm.properties= parameter. -
Login (
login): -
Password (
password):
The full command line syntax for OSLC is:
-d "type=oslc_cm,server=[text],query=[text],properties=[text],login=[text],password=[password]"pep8
Description
pep8 is a tool to check your Python code against some of the style conventions in PEP 88. Its CSV report file is imported to generate findings.
For more details, refer to https://pypi.python.org/pypi/pep8.
Usage
pep8 has the following options:
-
CSV results file (
csv): Specify the path to the CSV report file created by pep8.
The full command line syntax for pep8 is:
-d "type=pep8,csv=[file]"pycodestyle / pep8 (plugin)
Description
Style Guide for Python Code. Pep8 results are imported to produce findings on Python code. This data provider requires having pycodestyle or pep8 installed on the machine running the analysis and the pycodestyle or pep8 command to be available in the path. It is compatible with pycodestyle 2.4 or pep8 1.7 and may also work with older versions.
For more details, refer to https://pypi.org/project/pycodestyle.
Usage
pycodestyle / pep8 (plugin) has the following options:
-
Source code directory to analyse (
dir): Leave this field empty to analyse all sources.
The full command line syntax for pycodestyle / pep8 (plugin) is:
-d "type=pep8_auto,dir=[directory]"PHP Code Coverage
Description
Library that provides collection, processing, and rendering functionality for PHP code coverage information.
For more details, refer to https://github.com/sebastianbergmann/php-code-coverage.
Usage
PHP Code Coverage has the following options:
-
Report file or folder (
html_report): Specify the path to the HTML report folder or file which contains the coverage results.
The full command line syntax for PHP Code Coverage is:
-d "type=phpcodecoverage,html_report=[file_or_directory]"pylint
Description
Pylint is a Python source code analyzer which looks for programming errors, helps enforcing a coding standard and sniffs for some code smells (as defined in Martin Fowler’s Refactoring book). Pylint results are imported to generate findings for Python code.
For more details, refer to http://www.pylint.org/.
Usage
pylint has the following options:
-
CSV results file (
csv): Specify the path to the CSV file containing pylint results. Note that the minimum version supported is 1.1.0.
The full command line syntax for pylint is:
-d "type=pylint,csv=[file]"pylint (plugin)
Description
Coding Guide for Python Code. Pylint results are imported to produce findings on Python code. This data provider requires having pylint installed on the machine running the analysis and the pylint command to be available in the path. It is known to work with pylint 1.7.0 and may also work with older versions.
Usage
pylint (plugin) has the following options:
-
Source code directory to analyse (
dir): Leave this field empty to analyse all sources.
The full command line syntax for pylint (plugin) is:
-d "type=pylint_auto,dir=[directory]"QAC 8.2

Description
QA-C is a static analysis tool for MISRA checking.
For more details, refer to http://www.programmingresearch.com/static-analysis-software/qac-qacpp-static-analyzers/.
Usage
QAC 8.2 has the following options:
-
QAC output file(s) (
txt, mandatory): Specify the path(s) to the .tab file(s) to extract findings from. To provide multiple files click on '+' -
Eliminate duplicated findings (
eliminate_duplicate, default: false): When 2 occurences of the same finding (same rule, same file, same line, same description) is found, only one is reported.
The full command line syntax for QAC 8.2 is:
-d "type=qac,txt=[file],eliminate_duplicate=[booleanChoice]"QAC 8.2 CERT Import

Description
QA-C is a static analysis tool for MISRA and CERT checking.
For more details, refer to http://www.programmingresearch.com/static-analysis-software/qac-qacpp-static-analyzers/.
Usage
QAC 8.2 CERT Import has the following options:
-
QAC CERT output file(s) (
txt, mandatory): Specify the path(s) to the .tab file(s) to extract findings from. To provide multiple files click on '+' -
Eliminate duplicated findings (
eliminate_duplicate, default: false): When 2 occurences of the same finding (same rule, same file, same line, same description) is found, only one is reported.
The full command line syntax for QAC 8.2 CERT Import is:
-d "type=qac_cert,txt=[file],eliminate_duplicate=[booleanChoice]"SonarQube

Description
This data provider imports findings from SonarQube. Note that versions prior to 6.2 may not be supported.
For more details, refer to https://www.sonarqube.org/.
Usage
SonarQube has the following options:
-
SonarQube Location (
sonar, default: http://127.0.0.1:9000): Specify the URL of the SonarQube installation to work with (for example: http://localhost:9000) -
SonarQube Component Key (
key): -
Version Name (
version): -
Login (
login): -
Password (
password):
The full command line syntax for SonarQube is:
-d "type=sonarqube,sonar=[text],key=[text],version=[text],login=[text],password=[password]"Testwell CTC++

Description
Import data from Testwell CTC++ XML results
For more details, refer to http://www.testwell.fi/ctcdesc.html.
Usage
Testwell CTC++ has the following options:
-
Results folder (
dir): Specify the folder containing XML test results files from Testwell CTC++. -
Instrumented files extension (
extension, default: .test.runner.c): Instrumented files extension (Extension of the instrumented files generated by ctc++)
The full command line syntax for Testwell CTC++ is:
-d "type=testwell_ctc,dir=[directory],extension=[text]"vTESTstudio Traceability
Description
Import vTESTstudio traeability Matrix information
For more details, refer to https://www.vector.com/int/en/products/products-a-z/software/vTESTstudio/.
Usage
vTESTstudio Traceability has the following options:
-
Traceability matrix file path (
file): Specify the absolute path to the vTESTstudio traceability matrix file (.vti-tso format) -
Test path (
testPath, default: Tests): Define test path (for example Test/HIL Test), by default the value is Tests.
The full command line syntax for vTESTstudio Traceability is:
-d "type=vTestStudio_Traceability,file=[file],testPath=[text]"PC Lint MISRA 2012
Description
PC Lint MISRA 2012 (via XML import)
Usage
PC Lint MISRA 2012 has the following options:
-
XML File (
xml): Specify the XML file which contains the findings results (MISRA, Coding Style…)
The full command line syntax for PC Lint MISRA 2012 is:
-d "type=vectorCAST_Lint,xml=[file]"Adding More Languages to Squan Sources
Squan Sources can handle files written in languages that are not officially supported with a bit of extra configuration. In this mode, only a basic analysis of the file is carried out so that an artefact is created in the project and findings can be attached to it. A subset of the base metrics from Squan Sources is optionally recorded for the artefact so that line counting, stability and text duplication metrics are available at file level for the new language.
The example below shows how you can add TypeScript files to your analysis:
-
Copy <SQUORE_HOME>/configuration/tools/SQuORE/form.xml and its .properties files into your own configuration
-
Edit form.xml to add a new language key and associated file extensions:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <tags baseName="SQuORE" ...> <tag type="multipleChoice" key="languages" ... defaultValue="...;typescript"> ... <value key="typescript" option=".ts,.TS" /> </tag> </tags>Files with extensions matching the typescript language will be added to your project as TYPESCRIPT_FILE artefacts
-
Edit the
defaultValueof theadditional_paramfield to specify how Squan Sources should count source code lines and comment lines in the new language, based on another language officially supported by Squore. This step is optional, and is only needed if you want the to record basic line counting metrics for the artefacts.<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <tags baseName="SQuORE" ...> ... <tag type="text" key="additional_param" defaultValue="typescript=javascript" /> ... </tags>Lines in TypeScript files will be counted as they would for Javascript code.
-
Add translations for the new language key to show in the web UI in Squan Sources’s form_en.properties
OPT.typescript.NAME=TypeScript -
Add translations for the new artefact type and new LANGUAGE information value in one of the properties files imported by your Description Bundle:
T.TYPESCRIPT_FILE.NAME=TypeScript File INFO_VALUE.LANGUAGE.TYPESCRIPT.NAME=Typescript INFO_VALUE.LANGUAGE.TYPESCRIPT.COLOR=#2b7489 -
The new artefact type should also be declared as a type in your model. The easiest way to do this is to add it to the GENERIC_FILE alias in your analysis model, which is pre-configured to record the line counting metrics for new artefacts. You should also define a root indicator for you new artefact type. The following snippet shows a minimal configuration using a dummy indicator:
<!-- <configuration>/MyModel/Analysis/Bundle.xml --> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <Bundle> ... <ArtefactType id="GENERIC_FILE" heirs="TYPESCRIPT_FILE" /> <RootIndicator artefactTypes="TYPESCRIPT_FILE" indicatorId="DUMMY" /> <Indicator indicatorId="DUMMY" scaleId="SCALE_INFO" targetArtefactTypes="TYPESCRIPT_FILE" displayTypes="IMAGE" /> <Measure measureId="DUMMY"> <Computation targetArtefactTypes="TYPESCRIPT_FILE" result="0" /> </Measure> ... </Bundle>Make sure that this declaration appears in your analysis model before the inclusion of import.xml so it overrides the default analysis model.
Don’t forget to add translations for your dummy indicator to avoid warnings in the Model Validator:
DUMMY.NAME= Generic Indicator DUMMY.DESCR= This is an indicator for additional languages in Squan Sources. It does not rate files in any way. -
Reload your configuration and analyse a project, checking the box for TypeScript in Squan Sources’s options to get Typescrypt artefacts in your project.
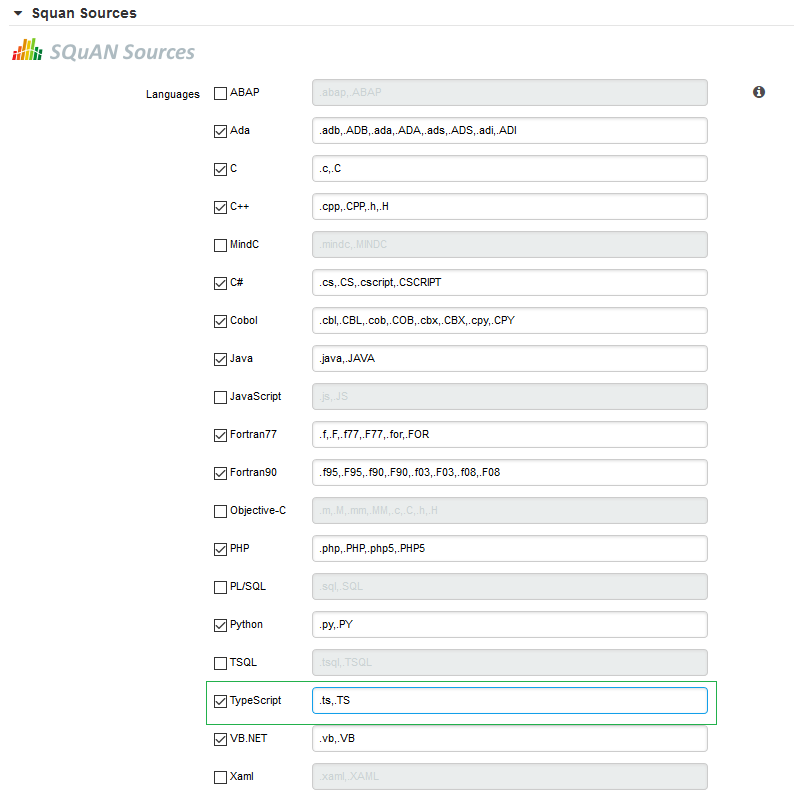 The new option for TypeScript files in Squan Sources
The new option for TypeScript files in Squan SourcesIf you are launchin an analysis from the command line, use the language key defined in step 2 to analyse TypeScript files:
-d "type=SQuORE,languages=typescript,additional_param=typescript=javascript" -
After the analysis finishes and you can see your artefacts in the tree, use the Dashboard Editor to build a dashboard for your new artefact type.
-
Finally, create a handler for the source code viewer to display your new file type into your configuration folder, by copying <SQUORE_HOME>/configuration/sources/javascript_file.properties into your own configuration as <SQUORE_HOME>/configuration/sources/typescript_file.properties.
Advanced COBOL Parsing
By default, Squan Sources generates artefacts for all PROGRAMs in COBOL source files. It is possible to configure the parser to also generate artefacts for all SECTIONs and PARAGRAPHs in your source code. This feature can be enabled with the following steps:
-
Open <SQUORE_HOME>/configuration/tools/SQuORE/Analyzer/artifacts/cobol/ArtifactsList.txt
-
Edit the list of artefacts to generate and add the section and paragraph types:
program section paragraph -
Save your changes
If you create a new project, you will see the new artefacts straight away. For already-existing projects, make sure to launch a new analysis and check Squan Sources’s Force full analysis option to parse the entire code again and generate the new artefacts.
Using Data Provider Input Files From Version Control
Input files for Squore’s Data Providers, like source code, can be located in your version control system. When this is the case, you need to specify a variable in the input field for the Data Provider instead of an absolute path to the input file.
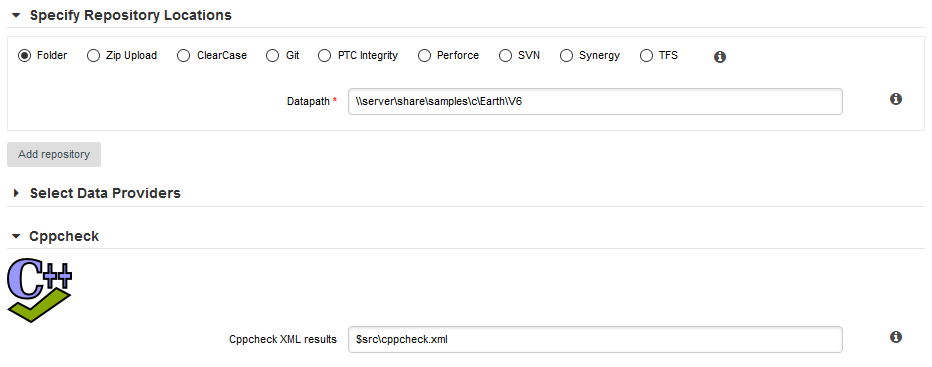
The variable to use varies depending on your scenario:
-
You have only one node of source code in your project
In this case, the variable to use is $src.
-
You have more than one node of source code in your project
In this case, you need to tell Squore in which node the input file is located. This is done using a variable that has the same name as the alias you defined for the source code node in the previous step of the wizard. For example, if your nodes are labelled Node1 and Node2 (the default names), then you can refer to them using the $Node1 and $Node2 variables.
|
When using these variables from the command line on a linux system, the $ symbol must be escaped: |
Providing a catalog file to a Data Provider for Offline XSL Transformations
When transforming an XML results file with an XSL stylesheet, the XML parser used by Squore will try to validate the XML file against the DTD declared in the XML header. In cases where the XSL transformation is running on a machine with no internet access, this can result in the execution of the Data Provider failing with a No route to host error message.
You can fix this issue by modifying the data provider to use a catalog file that will provide an alternate location for the DTD used to validate the XML. This feature can be used by all Data Providers that include an XSL transformation [1] .
The following example adds this functionality to the Cobertura Data Provider:
-
Add a catalog.xml file in the Data Provider’s configuration folder:
<configuration>/tools/cobertura/catalog.xml: <?xml version="1.0"?> <catalog xmlns="urn:oasis:names:tc:entity:xmlns:xml:catalog"> <rewriteSystem systemIdStartString="http://cobertura.sourceforge.net/xml" rewritePrefix="./DTD"/> </catalog> -
Copy the dtd that the XML needs to validate again inside a DTD folder in <configuration>/tools/cobertura/.
The catalog file will be used the next time the Data Provider is executed and the DTD declaration will dynamically be changed from:
<!DOCTYPE coverage SYSTEM "http://cobertura.sourceforge.net/xml/coverage-04.dtd">to:
<!DOCTYPE coverage SYSTEM "<configuration>/tools/cobertura/DTD/coverage-04.dtd">">For more information about how to write your catalog file, refer to https://xerces.apache.org/xerces2-j/faq-xcatalogs.html.
Creating a form.xml for your own Data Providers, Repository Connectors and Export Definitions
All Data Providers are utilities that run during an analysis. They usually take an input file to parse or parameters specified by the user to generate output files containing violations or metrics to add to your project. Here is a non-exhaustive list of what some of them do:
-
Use XSLT files to transform XML files
-
Read information from Microsoft Excel files
-
Parse HTML test results
-
Query web services
-
Export data from OSLC systems
-
Launch external processes
|
Repository Connectors are based on the same model and are used to specifically retrieve source code and other data from source code management systems. Export Definitions use the same form.xml specification to offer custom export formats to users from the web interface, dumping data from highlight definitions into a specified, custom format. |
Read on to learn about how to configure your Data Provider, make it available in the web interface, and then understand how to implement the scripted part of a Data Provider that is executed during an analysis.
After you understand how to build a a Data Provider using a form.xml file, you can apply this knowledge to building Repository Connectors and Export Definitions, as described in Creating Repository Connectors and Creating Export Definitions.
|
You can find the XML schema for form.xml in form.xsd. |
Defining Data Provider Parameters
A Data Provider’s parameters are defined in a file called form.xml. The following is an example of form.xml for a Data Provider extending the GenericPerl framework:
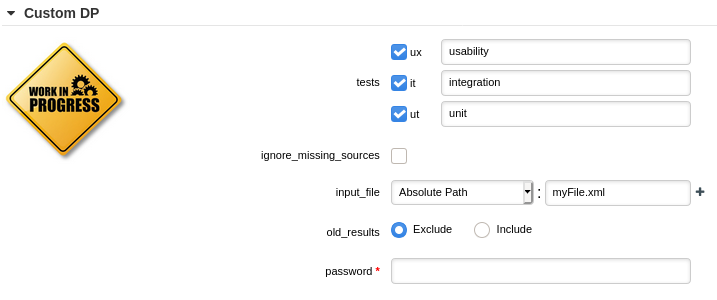
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<tags baseName="GenericPerl" needSources="true" image="CustomDP.png" projectStatusOnFailure="ERROR">
<tag type="multipleChoice" displayType="checkbox" key="tests" optionTitle=" ">
<value key="ux" option="usability"/>
<value key="it" option="integration"/>
<value key="ut" option="unit"/>
</tag>
<tag type="booleanChoice" key="ignore_missing_sources" defaultValue="false" />
<tag type="file" key="input_file" defaultValue="myFile.xml" multi="true"/>
<tag type="multipleChoice" key="old_results" style="margin-left:10px" displayType="radioButton" defaultValue="Exclude">
<value key="Exclude" />
<value key="Include" />
</tag>
<tag type="text" key="java_path" defaultValue="/usr/bin/java" hide="true" />
<tag type="password" required="true" key="password" />
</tags>The tags element accepts the following attributes:
-
baseName(mandatory if you are not using anexec-phase) indicates on which framework you are basing this Data Provider. The value of this attribute must match a folder from the addons folder of your installation. -
needSources(optional, default: false) allows specifying whether the Data Provider requires sources or not. When set to true, an error will be displayed if you try to select this Data Provider without adding any Repository Connector location to your project. -
image(optional, default: none) allows displaying a logo in the web UI for the Data Provider -
projectStatusOnFailure(optional, default: ERROR) defines what status the project ends in when this Data Provider produces an error. The following values are allowed:-
IGNORE
-
WARNING
-
ERROR
-
-
projectStatusOnWarning(optional, default: WARNING) defines what status the project ends in when this Data Provider produces a warning. The following values are allowed:-
IGNORE
-
WARNING
-
ERROR
-
Each tag element is a Data Provider option and allows the following attributes:
-
key(mandatory) is the option’s key that will be passed to the perl script, or can be used to specify the parameter’s value from the command line -
type(mandatory) defines the type of the parameter. The following values are accepted:-
text for free text entry
-
file for file path with native permission and validity checks
-
directory for directory path with native permission and validity checks
-
file_or_directory for file or directory path with native permission and validity checks
-
password for password fields
-
booleanChoice for a boolean
-
multipleChoice for offering a selection of predefined values
Predefined values are specified with a
valueelement with a mandatorykeyattribute and an optionaloptionattribute that allows modifying the value of the option from the UI. The input field for eachoptionattribute is only displayed if the parenttagcontains anoptionTitleattribute.
-
-
displayType(optional) allows specifying how to display amultipleChoiceparameter by using one of:-
comboBox
-
radioButton
-
checkbox
-
-
multi(optional, default: false) allows for dynamic addition/removal of multiple files or directories path -
defaultValue(optional, default: empty) is the value used for the parameter when not specified -
hide(optional, default: false) allows hiding a parameter from the web UI, which is useful when combining it with a default value -
changeable(optional, default: true) allows making a parameter configurable only when creating the project but read-only for following analyses when set to true -
style(optional, default: empty) allows setting basic css for the attribute in the web UI -
required(optional, default: false) allows showing a red asterisk next to the field in the web UI to make it visibly requiredYou can use a required
tagof type booleanchoice to ensure that users must check a box in the web UI or set its value to true when building from the command line in order to proceed with the analysis.<tag type="booleanChoice" required="true" key="accept_privacy_policy" />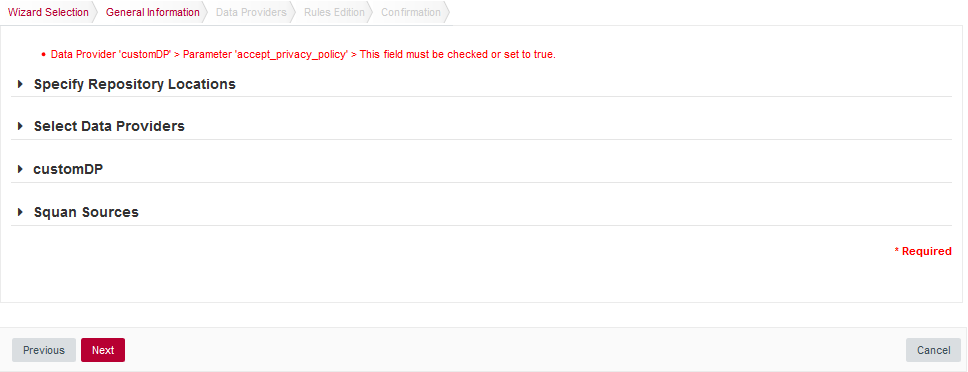 Clicking the Next button without checking a required checkbox displays an error
Clicking the Next button without checking a required checkbox displays an error
Hiding your Data Provider elements in the web UI
You can associate to your tag element the displayIf element:
The displayIf (optional)* This element allows the user to define conditions on the tagged field to make it visible in the web UI.
The displayIf element accepts logical conditions. These conditions are designed as containers that can contains the following elements:
-
and(optional, applied by default) all conditions defined in the "and" container must be true in order to display tagged items of the data-provider -
or(optional) one condition defined in the "or" container must be true in order to hide tagged items of the data-provider
The displayIf elements and conditionnal containers can accepts the following elements:
-
equals(optional) this element is associated to a tag element defined in the "key" and "value" attributes. The tagged element must contains the value specified in the value attribute in order to be displayed in the web UI -
notEmpty(optional) the tag element defined in the "key" attribute has to be filed in order to display the data-provider element in the web UI
|
You can use the displayIf condition in a Syntax example: |
Localising your Data Provider
In order to display your Data Provider parameters in different languages in the web UI, yout Data Provider’s form.xml does not contain any hard-coded strings.
Instead, Squore uses each parameter’s key attribute to dynamically retrieve a translation from a form_xx.properties file located next to form.xml.
When you create a Data Provider, it is mandatory to include at least an English version of the strings in a file called form_en.properties. You are free to add other languages as needed. Here is a sample .properties for for the CustomDP you created in the previous section:
FORM.GENERAL.NAME = CustomDP
FORM.DASHBOARD.NAME = Test Status
FORM.GENERAL.DESCR = CustomDP imports test results for my project
FORM.GENERAL.URL = http://example.com/CustomDP
TAG.tests.NAME = Test Types
TAG.tests.DESCR = Check the boxes next to the types of test results contained in the results
TAG.ignore_missing_sources.NAME = Ignore Missing Sources
TAG.input_file.NAME = Test Results
TAG.input_file.DESCR = Specify the absolute path to the file containing the test results
TAG.old_results.NAME = Old Test Results
TAG.old_results.DESCR = If the previous analysis contained results that are not in this results file, what do you want to do with the old results?
OPT.Exclude.NAME = discard
OPT.Include.NAME = keep
TAG.password.NAME = File Password
TAG.password.DESCR = Specify the password to decrypt the test results fileThe syntax for the .properties file is as follows:
-
FORM.GENERAL.NAME is the display name of the Data Provider in the project wizard
-
FORM.DASHBOARD.NAME is the display name of the Data Provider in the Explorer
-
FORM.GENERAL.DESCR is the description displayed in the Data Provider’s tooltip in the web UI
-
FORM.GENERAL.URL is a reference URL for the Data Provider. Note that it is not displayed in ther web UI yet.
-
TAG.tag_name.NAME allows setting the display name of a parameter
-
TAG.tag_name.DESCR is a help text displayed in a tooltip next to the Data Provider option in the web UI
-
OPT.option_name.NAME allows setting the display name of an option
Using the form_en.properties above for CustomDP results in the following being displayed in the web UI when launching an analysis:
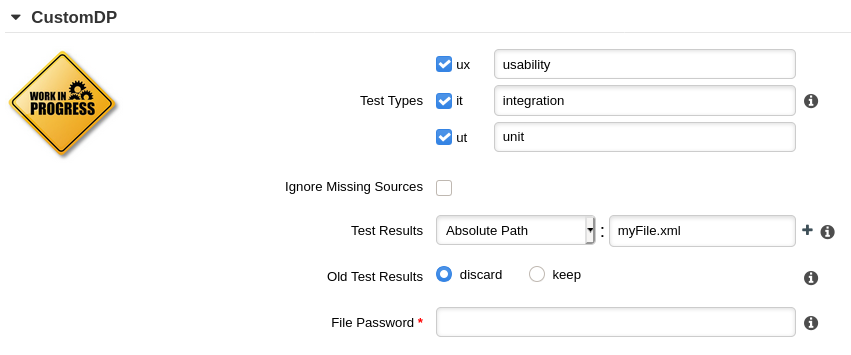
|
Not all wizards display all Data Providers by default.
If your Data Provider does not appear after refreshing your configuration, make sure that your wizard bundle allows displaying all Data Providers by reviewing the For more information about the wizard bundle, consult the the chapter called "Project Wizards" in the Configuration Guide. If you have made this change and your Data Provider still does not appear in your wizard, consult the Validator to find out if it was disabled because of an error in its configuration. 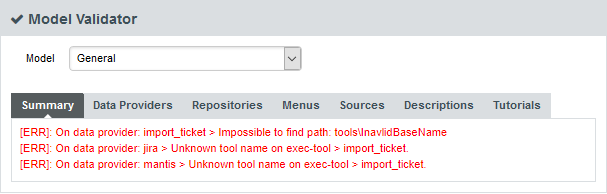
The General section of the Validator shows errors in your Data Providers
|
Running your Data Provider
Now that you have a new Data Provider available in the web interface (and the command line), this section will show you how to use these parameters and pass them to one or more scripts or executables in order to eventually write data in the format that Squore expects to import during the analysis.
At the end of a Data Provider execution, Squore expects a file named input-data.xml to be written in a specific location. The syntax of the XML file to generate is as follows:
<!-- input-data.xml syntax -->
<bundle version="2">
<artifact [local-key=""] [local-parent=""|parent=""] >
<artifact [id="<guid-stable-in-time-also-used-as-a-key>"] name="Component" type="REQ" [location=""] >
<info name|n="DESCR" value="The description of the object"/>
<key value="3452-e89b-ff82"/>
<metric name="TEST_KO" value="2"/>
<finding name="AR120" loc="xxx" p0="The message" />
<link name="TEST" local-src=""|src=""|local-dst=""|dst="" />
<artifact id="" name="SubComponent" type="REQ">
...
</artifact>
</artifact>
</artifact>
<artifact id="" local-key="" name="" type="" local-parent=""|parent="" [location=""] />
...
<link name="" local-src=""|src="" local-dst=""|dst="" />
...
<info local-ref=""|ref="" name="" value=""/>
...
<metric local-ref=""|ref="" name="" value=""/>
...
<finding local-ref=""|ref="" [location=""] p0="" />
<finding local-ref=""|ref="" [location=""] p0="">
<location local-ref=""|ref="" [location=""] />
...
<relax status="RELAXED_DEROGATION|RELAXED_LEGACY|RELAXED_FALSE_POSITIVE"><![CDATA[My Comment]]></relax>
</finding>
...
</bundle>|
You can find the XML schema for input-data.xml in input-data-2.xsd. |
Your Data Provider is configured by adding an exec-phase element with a mandatory id="add-data" attribute in form.xml.
The basic syntax of an exec-phase can be seen below:
<exec-phase id="add-data">
<exec name="tcl|perl|java" | executable="/path/to/bin" | executable="executable_name" failOnError="true|false" failOnStdErr="true|false" warn="[WARN]" error="[ERROR|ERR]" fatal="[FATAL]">
<arg value="${<function>(<args>)}"/>
<arg value="-freeText" />
<arg value="${<predefinedVars>}" />
<arg value="versions" />
<arg value="-myTag"/>
<arg tag="myTag"/>
<env key="MY_VAR" value="SOME_VALUE"/>
</exec>
<exec ... />
<exec-tool name="another_data_provider">
<param key="<tagName>" value="<value>" />
<param key="<tagName>" tag="<tag>" />
<param ... />
</exec-tool>
<exec-tool ... >
...
</exec-tool>
</exec-phase>You can also use Groovy in order to configure your Data Provider.
The basic syntax of a Groovy exec name is indicated below:
<exec name="java">
<arg value="${javaClasspath(poi,groovy,jackson)}"/>
<arg value="groovy.lang.GroovyShell" />
<arg value="${getConfigFile(to_excel.groovy)}"/>
<arg value="${getSharedAddonsFile(GroovyScriptUtils.groovy)}"/>
...|
Only the |
Executables
The exec-phase element accepts one or more launches of scripts or executables specified in an exec child element, that can receive arguments and environment variables specified via arg and env elements.
There are four built-in languages for executables:
-
tcl
-
perl
-
java
-
Groovy
The scripts are launched using the tcl, perl, or java runtimes defined in your Squore installation. This is also the case for Groovy, which is handled by Java engine.
The following attributes of the exec element allow you to control error handling:
-
failOnError(optional, default: true) marks the Data Provider execution as failed if the executable returns an error code -
failOnStdErr(optional, default: true) marks the Data Provider execution as failed if the executable prints something to stdErr during the execution -
warn,errorandfatal(optional, default: see code block above) allow you to define patterns to look for in the executable’s standard output to fine-tune the result of the execution.
Other executables can be called, as long as they are available on the system’s PATH, or configured in config.xml
Given the following config.xml:
<!-- config.xml (server or cli) -->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<squore type="server" version="1.3">
<paths>
<path name="python" path="C:\Python\python.exe" />
<path name="git" path="C:\Git\bin\git.exe" />
</paths>
...
</squore>git and python can be called in your Data Provider as follows:
<exec-phase id="add-data">
<exec name="git">
...
</exec>
<exec name="python">
...
</exec>
</exec-phase>Arguments
Argument values can be:
-
Free text passed in a
valuetag, useful to specify a parameter for your script<exec name="perl"> <arg value="-V" /> </exec> -
A tag key declared in form.xml passed as a `tag ` attribute to retrieve the input specified by the user. If no input was specified, you can define a
defaultValue:<arg tag="maxValue" defaultValue="50" /> <arg tag="configFile" defaultValue="${getConfigFile(default.xml)}" /> -
One of the predefined functions
-
${getOutputFile(<relative/path/to/file>,<abortIfMissing>)} returns the absolute path of an input-data.xml file output by an
exec-phase. failIfMissing is an optional boolean which aborts the execution when set to true if the file is missing. -
${getTemporaryFile(<relative/path/to/file>)} returns the absolute path of a temporary file created by an
exec(only for add-data and repo-add-data phases) -
${getAddonsFile(<relative/path/to/file>)} returns the absolute path of a file in the Data Provider’s addons folder
-
${getConfigFile(<relative/path/to/file>)} returns the absolute path of a file in the Data Provider’s configuration folder
-
${getSharedAddonsFile(<relative/path/to/file>)} returns the absolute path of a file in Data Provider’s addons/shared folder, if not returns the absolute path of a file in addons/shared folder
-
${path(<executable_name>)} returns the absolute path of an executable configured in config.xml, or just the executable name if the executable is available from the system’s PATH.
<exec name="..."> <arg value="-git_path" /> <arg value="${path(git)}" /> -
${javaClasspath(poi,groovy,jackson,abc.jar,xyz.jar)} adds the specified list of jars to the classpath for java execution.
Squore will look for the jars in the addons/lib folder of your configuration and return a classpath parameter for the desired runtime environment (-cp="…" for java)
poi is a shortcut for poi-ooxml-3.17.jar,poi-3.17.jar,poi-ooxml-schemas-3.17.jar,xmlbeans-2.6.0.jar,commons-collections4-4.1.jar and configures the environment necessary to use Apache POI when creating custom Export Definitions, as described in Creating Export Definitions.
groovy is a shortcut for groovy-3.0.1.jar, groovy-json-3.0.1.jar and groovy-xml-3.0.1.jar libraries needed to run Groovy scripts
jackson is a shortcut for jackson-core-2.6.3.jar, jackson-databind-2.6.3.jar and jackson-annotations-2.6.0.jar libraries needed to parse Json file
-
-
One of the predefined variables
-
${tmpDirectory} to get an absolute path to a temp folder to create files
-
${sourcesList} to get a list of the aliases and locations containing the data extracted by the repository connectors used in the analysis
-
${outputDirectory} to get the absolute path of folder where the Data Provider needs to write the final input-data.xml
-
Conditions
You can use condition statements in the exec and exec-tool elements in order to parametrize the execution of your Data Providers.
The execute-if element is used as follow :
<exec-phase id="add-data">
<exec name="java">
<executeIf>
<equals key="outputFile" value="" /> <!-- Execute this Java process only if the output file is not provided. -->
</executeIf>
...
</exec>
</exec-phase>The execute-if element uses the same syntax as the displayIf element : Hiding your Data Provider elements in the web UI.
Calling Other Data Providers
You can call and pass parameters to other Data Providers after your exec-phase using an exec-tool element.
The exec-tool element uses a mandatory name which is the name of the folder containing the other Data Provider to launch in your configuration folder and supports passing the parameters expected by the other Data Provider via one or more param elements where:
-
keyis the name of the parameter expected by the other Data Provider (as defined in its form.xml) -
valueallows passing free text -
tagallows passing the value of your own Data Provider’s tag value to the other Data Provider and can be combined with adefaultValueattribute in case no value was specified by the user for the tag
As an example, the following Data Provider generates a CSV file that is then passed to the pep8 Data Provider:
<exec-phase id="add-data">
<exec name="python">
<arg value="consolidate-reports-recursive.py" />
<arg value="-folders" />
<arg tag="root_folder" />
<arg value="-outputFile" />
<arg value="output.csv" />
</exec>
<exec-tool name="pep8">
<param key="csv" value="${getOutputFile(output.csv)}" />
<param key="separator" tag="separator" defaultValue=";" />
</exec-tool>
</exec-phase>In this other example, a perl script is launched to retrieves issues from a ticketing system and the export data is passed to the import_ticket Data Provider:
<exec-phase id="add-data">
<exec name="perl">
<arg value="${getConfigFile(export_ticket.pl)}" />
<arg value="-url" />
<arg tag="url" />
<arg value="-login" />
<arg tag="login" />
<arg value="-pwd" />
<arg tag="pwd" />
<arg value="-outputFile" />
<arg value="${getOutputFile(exportdata.csv,false)}" />
</exec>
<exec-tool name="import_ticket">
<param key="input_file" value="${getOutputFile(exportdata.csv)}" />
<param key="csv_separator" value=";" />
</exec-tool>
</exec-phase>|
If your Data Provider uses a perl script, Squore provides a small library that makes it easy to retrieve script arguments called SQuORE::Args. Using it as part of your script, you can retrieve arguments using the get_tag_value() function, as shown below: |
Using the Squore toolkit
If you want your Data Provider to use the Squore toolkit to retrieve references to artefacts, the following variables are available (in the add-data and repo-add-data phases only):
-
${tclToolkitDirectory}: the directory of the toolkit tcl code to execute
-
${squanOutputDirectory}: the directory of containing the results of the execution of Squan Sources
In order to use the toolkit, your exec must use the tcl language.
As an example, here is a sample exec-phase and associated tcl file to get you started:
<!-- form.xml -->
<exec-phase id="repo-add-data">
<exec name="tcl">
<arg value="${getAddonsFile(repo-add-data.tcl)}" />
<arg value="${tclToolkitFile}" />
<arg value="${squanOutputDirectory}" />
<arg value="${outputDirectory}" />
<arg tag="xxx" />
</exec>
</exec-phase>#repo-add-data.tcl:
set toolkitFile [lindex $argv 0]
set sqOutputDir [lindex $argv 1]
set outputDir [lindex $argv 2]
set xxx [lindex $argv 3]
# Initialise the toolkit
puts "Initializing toolkit"
source $toolkitFile
toolkit::initialize $sqOutputDir $outputDir
# Execute your code
puts "Main execution"
# yout code here
# ...
# Generate xml files (artefacts)
puts "Generating xml files"
toolkit::generate $outputDir {artefacts}Finding More Examples
If you want to find more examples of working Data Providers that use this syntax, check the following Data Providers in Squore’s default configuration folder:
-
conf-checker calls a jar file to write an XML file in Squore’s exchange format
-
import_ticket parses a file to translate it into a format that can then be passed to csv_import to import the tickets into Squore
-
jira retrieves data from Jira and passes it to import_ticket
Built-in Data Provider Frameworks
In order to help you import data into Squore, the following Data Provider frameworks are provided and can write a valid input-data.xml file for you:
-
csv_import
The csv_import framework allows you to write Data Providers that produce CSV files and then pass them on to the framework to be converted to an XML format that Squore understands. This framework allows you to import metrics, findings, textual information and links as well as generate your own artefacts. It is fully linked to the source code parser and therefore allows to locate existing source code artefacts generated by the source code parser. Refer to the full csv_import Reference for more information.
-
xml
The xml framework is a sample implementation of a Data Provider that allows you to directly import an XML file or run it through an XSL transformation to that it matches the input format expected by Squore (input-data.xml). This framework therefore allows you to import metrics, findings, textual information and links as well as generate your own artefacts. Refer to the full xml Reference for more information.
|
If you are looking for the legacy Data Provider frameworks from previous versions of Squore, consult Legacy Frameworks. The legacy Data Provider frameworks are still supported, however using the new frameworks is recommended for developping new Data Providers, as they are more flexible and provide more functionality to interact with source code artefacts. |
Creating Repository Connectors
The same syntax used to create Data Providers can be used to create Repository Connectors, and therefore instruct Squore to get source code from SCMs.
Instead of using an exec-phase with the id="add-data", your Repository Connector should define the following phases:
-
id="import"defines how you extract source code and make it available to Squan Sources so it can be analysed. This phase is expected to return a path to a folder containing the sources to analyse or a data.properties file listing the path to the folder containing source and various other properties to be used in other executions:directory=/path/to/sources-to-analyse data.<key1>=<value1> data.<key2>=<value2>This phase is executed once per source code node in the project and allows you to use the following additional variables: ${outputSourceDirectory} is the folder containing the sources to analyse ${alias} is the alias used for the source code node (empty if there is only one source code node)
-
id="repo-add-data"is similar to the add-data phase described for Data Providers in Running your Data Provider and is expected to produce an input-data.xml. The only difference in the case of a Repository Connector is that this phase is executed once per source code node in the analysis. -
id="display"is the phase that is called when users request to view the source code for an artefact from the web UI. This phase is expected to return a data.properties file with the following keys:filePath=/path/to/source/file displayPath=<Artefact Display Path (optional)>The contents of filePath will be loaded in the source code viewer, while the value of displayPath will be used as the file path displayed in the header of the source code viewer.
This phase allows you to use the following additional variables:
-
${scaInfo} is text to display in the title bar of the source code viewer in the web interface
-
${artefactName} is the name of the file to display
-
${artefactPath} is the path (without the alias) of the file to display
During the display phase, you can retrieve any data set during the import phase for the repository using the ${getImportData(<key1>)} function
Additional attributes are available for the tags element of a Repository Connector:
-
deleteTmpSrc(optional, default: false) indicates whether or not the content of sources folder coming from this Repository Connector will be deleted upon Squore Server restart. -
useCredentialsForSCA(optional, default: true) allows specifying whether credentials dialog will be prompted in View Source Code or not.
|
Consult SVN’s form.xml in <SQUORE_HOME>/configuration/repositoryConnectors/SVN for a working example of a Repository Connector that uses all the phases described above. Please note, as data-provider, you can use the <exec-tool> parameter in order to call other elements while processing, like Data Provider or Scripts. For more informations about <exec-tool> parameter, please refer to Running your Data Provider. |
Creating Export Definitions
The form.xml specification can also be used to create Export Definitions that allow users to export data based on one or more highlight categories from the web interface.
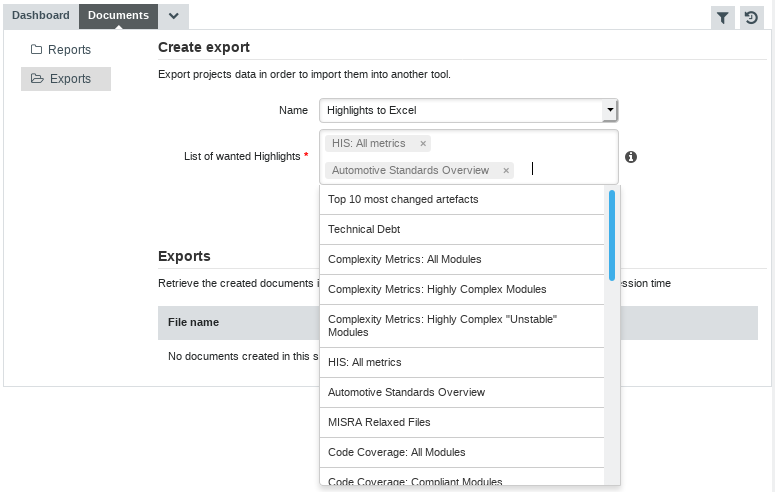
The Highlights to Excel Export Definition uses the following form.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<tags>
<tag type="multipleChoice" displayType="multi-autocomplete" required="true" key="highlights">
<values type="highlights" />
</tag>
<exec-phase id="export">
<exec name="java">
<arg value="${javaClasspath(poi,groovy,jackson)}"/>
<arg value="groovy.lang.GroovyShell" />
<arg value="${getConfigFile(to_excel.groovy)}"/>
<arg value="${getSharedAddonsFile(GroovyScriptUtils.groovy)}"/>
<arg value="-importScript"/>
<arg value="${getSharedAddonsFile(exports_utils.groovy)}" />
<arg value="-squoreApiUtils"/>
<arg value="${getSharedAddonsFile(SquoreApiUtils.groovy)}" />
<arg value="-excelUtilsScript"/>
<arg value="${getSharedAddonsFile(ExcelUtils.groovy)}" />
<arg value="-highlights"/>
<arg tag="highlights" />
<arg value="-outputDirectory" />
<arg value="${outputDirectory}" />
<arg value="-idArtefact" />
<arg value="${idArtefact}"/>
<arg value="-idVersion"/>
<arg value="${idVersion}"/>
<arg value="-idModel"/>
<arg value="${idModel}"/>
<arg value="-group"/>
<arg value="${group}"/>
<arg value="-serverUrl"/>
<arg value="${localUrl}"/>
<arg value="-token"/>
<arg value="${token}"/>
<arg value="-template"/>
<arg value="${getConfigFile(template.xlsx)}" />
</exec>
</exec-phase>
</tags>|
Data is exported from the server as a JSON file, which your Export Definition can modify as needed before sending it to the end-user who launched the export. You can consult the format of the JSON file in the Data Exchange Formats appendix for more information. |
In order to create an Export Definition, the syntax described in Defining Data Provider Parameters and Running your Data Provider is augmented to include the extra additional capabilities:
-
A multi-autocomplete
displayTypefor multipleChoicetagelements.The
tagelement accepts avaluessub-element with a mandatorytypeattributes. When set to highlights, the widget automatically displays all the available highlight definitions for the currently selected artefact. -
A mandatory
exec-phasewithid="export"that contains one or moreexecs.This
exec-phaseis expected to return a data.properties file with the following keys:filename=/path/to/export/file -
Variables that can be used in the
exec-phaseto pass the context of the currently selected artefact to the Export Definition:-
${idUser} is the ID of the user generating the export
-
${token} is the auto-generated token for on the fly authentification to the API REST
-
${idArtefact} is the ID of the currently selected artefact
-
${idVersion} is the ID of the version of the project that is currently selected
-
${idApplication} is the ID of the project that currently selected
-
${idModel} is the ID of the analysis model used for the project that is currently selected
-
${group} is the path of the current selected group portfolio
-
${serverUrl} is the Squore Server URL, as defined in Administration > System
-
${localUrl} is the Squore Local URL
-
You can add your own Export Definition by following these steps:
-
Create a folder in configuration/exports called my_export_definition.
-
Create a form.xml and form_en.properties in my_export_definition
-
Define the
exec-phasethat your Export Definition will run -
Add your Export Definition to your model’s Export Bundle for the desired project role and artefact type, using the folder name (my_export_definition) as the
ExportDef'snameattribute:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <Bundle> <Role name="DEFAULT"> <Export type="..."> <ExportDef name="my_export_definition" /> ... </Export> ... </Role> </Bundle> -
Reload the Squore configuration and your Export Definition should appear in the Documents tab of the Explorer.
For more examples of custom Export Definitions, consult the configuration/exports and addons/exports folders of the default Squore configuration.
|
Please note, as data-provider, you can use the <exec-tool> parameter in order to call other elements while processing, like Data Provider or Scripts. For more informations about <exec-tool> parameter, please refer to Running your Data Provider. |
5. Cloning Detection
This chapter lists the various metrics collected in Squore when running the cloning detection tool, as well as the violations presented in the Findings tab of the web interface.
Note that the concepts used for cloning detection in Squore are based on the notions of longest common subsequence problem (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Longest_common_subsequence_problem) and longest repeated substring problem (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Longest_repeated_substring_problem).
Cloning Metrics
None of the metrics below are set by the cloning detection tool if thresholds are not met. That is, if an artefact has no CC measure in the output file, that does NOT mean that it has no line in common with other artefacts. In models, metrics default to 0 though.
The two main thresholds are:
-
A minimum size, to skip small artefacts
-
A minimum cloning ratio, to keep only similar artefacts
CCLC - Code Cloning Line Counting
Number of lines taken into account by the cloning detection tool. This metric is impacted by parameters like "Ignore blank lines", or "Ignore comments blocks".
CC - Code Cloned
Length of the highest Longest Common Substring (LCS) among all cloned artefacts.
Clones are looked in the whole application, in artefacts with the same language and the same type.
-
Textual detection, using lines, with trailing spaces removed
-
Two artefacts are cloned if they have 90% of lines in common, for LC >= 10
Scope: all artefacts but the root node.
CFTC - Control Flow Token (CFT) Cloned
Length of the highest LCS among all cloned CFT.
Clones are looked in the whole application, in artefacts with the same language and the same type.
-
Algorithmic detection, using CFT characters
-
Two artefacts are cloned if they have 90% of characters in common, for CFT >= 50
Scope: all artefacts but the root node.
CAC - Children Artefact Cloned
Number of clones in direct children of an artefact.
Parent clones are looked in the whole application, in artefacts with the same language and the same type.
Two classes may have two methods in common, for example, without being cloned. The CAC metric for these two classes will be two (assuming that they only have these two methods in common). Such artefacts should be re-factored (using inheritance for example).
-
Use both textual (CC > 0) and algorithmic (CFTC > 0) cloning when counting
-
Two parent artefacts are cloned if 25% of their direct children are cloned
-
Small children artefacts (LC < 10) are taken in account, using exact comparison
Scope: all artefacts but the root node.
CN - Clones Number
Number of cloned artefacts.
Clones are looked in the whole application, in artefacts with the same language and the same type.
-
Use both textual (CC > 0) and algorithmic (CFTC > 0) cloning when counting
Scope: all artefacts but the root node.
RS - Repeated Substrings (Repeated Code Blocks)
Length of all Repeated Substrings in the artefact definition.
That is, duplicated blocks in a function for example.
-
Textual detection, using lines, with trailing spaces removed
-
The metric is triggered if blocks longer than 10 are found, for LC >= 10
Scope: files and all children artefacts.
CFTRS - Repeated Substrings in Control Flow Token
Length of all Repeated Substrings in the artefact CFT.
That is, duplicated algorithmic blocks in a function for example.
-
Algorithmic detection, using CFT characters
-
The metric is triggered if blocks longer than 20 are found, for CFT >= 50
Scope: artefacts with a CFT, like functions.
ICC - Inner Code Cloned
Number of duplicated lines in an artefact.
Clones are looked in all descendants of the artefact. This basically sums all duplicated lines in descendants.
-
Use textual cloning (CC > 0) when counting
Scope: all artefacts.
ICFTC - Inner Control Flow Token Cloned
Number of duplicated tokens in an artefact.
Clones are looked in all descendants of the artefact. This basically sums all cloned tokens in descendants.
-
Use algorithmic cloning (CFTC > 0) when counting
Scope: all artefacts.
Cloning Violations
This section lists all the findings that are reported by Squore cloning detection tool.
CC (R_NOCC)
Avoid code duplication.
-
Similar artefacts (transitive closure) are part of the same violation
-
Use artefacts with textual cloning (CC > 0) when grouping
Scope: files and all children artefacts.
CFTC (R_NOCFTC)
Avoid algorithmic cloning.
-
Similar artefacts (transitive closure) are part of the same violation
-
Use artefacts with algorithmic cloning (CFTC > 0) when grouping
Scope: artefacts with a CFT, like functions.
CAC (R_NOCAC)
Consider refactorisation.
-
Similar artefacts (transitive closure) are part of the same violation
-
Use "refactorable" artefacts (CAC > 0) when grouping
Scope: files and all children artefacts.
RS (R_NORS)
Consider refactorisation.
-
One violation per "refactorable" artefact (RS > 0)
Scope: files and all children artefacts.
CFTRS (R_NOCFTRS)
Consider algorithmic refactorisation.
-
One violation per "refactorable" artefact (CFTRS > 0)
Scope: artefacts with a CFT, like functions.
6. Glossary
Acceptance Testing
Formal testing conducted to enable a user, customer, or other authorised entity to determine whether to accept a system or component. [ SIGIST ]
Other Definitions
Acceptance Testing [ IEEE 610.12 ]: Formal testing conducted to determine whether or not a system satisfies its acceptance criteria and to enable the customer to determine whether or not to accept the system.
Accessibility
Usability of a product, service, environment or facility by people with the widest range of capabilities. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765, ISO/IEC 25062 ]
Notes
Accuracy
The capability of the software product to provide the right or agreed results or effects with the needed degree of precision. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Other Definitions
Accuracy [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]:
-
A qualitative assessment of correctness, or freedom from error.
-
A quantitative measure of the magnitude of error
Accuracy of Measurement
The closeness of the agreement between the result of a measurement and the true value of the measurand. [ ISO/IEC 14143-3, ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Acquirer
Individual or organisation that procures a system, software product, or software service from a supplier. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1, ISO/IEC 15939 ]
Other Definitions
Acquirer [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765, ISO/IEC 12207 ]: Stakeholder that acquires or procures a product or service from a supplier.
Acquirer [ IEEE 1058, ISO/IEC 15288 ]: The individual or organization that specifies requirements for and accepts delivery of a new or modified software product and its documentation.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Action
Element of a step that a user performs during a procedure. [ ISO/IEC 26514 ]
Activity
Any step taken or function performed, both mental and physical, toward achieving some objective. Activities include all the work the managers and technical staff do to perform the tasks of the project and organization. [ CMMi ]
Other Definitions
Activity [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15288 ]: Set of cohesive tasks of a process.
Activity [ IEEE 1490 ]: A component of work performed during the course of a project.
Activity [ ISO/IEC 14756 ]: An order submitted to the system under test (SUT) by a user or an emulated user demanding the execution of a data processing operation according to a defined algorithm to produce specific output data from specific input data and (if requested) stored data.
Activity [ IEEE 1074 ]: A defined body of work to be performed, including its required input information and output information
Activity [ ISO/IEC 90003 ]: Collection of related tasks.
Activity [ IEEE 829 ]: Element of work performed during the implementation of a process.
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Actor
A role (with respect to that action) in which the enterprise object fulfilling the role participates in the action. [ ISO/IEC 15414 ]
Adaptability
The capability of the software product to be adapted for different specified environments without applying actions or means other than those provided for this purpose for the software considered. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Agreement
Mutual acknowledgement of terms and conditions under which a working relationship is conducted. [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15288 ]
Analysability
The capability of the software product to be diagnosed for deficiencies or causes of failures in the
software, or for the parts to be modified to be identified. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
See also
Analysis Model
Algorithm or calculation combining one or more base and/or derived measures with associated decision criteria. [ ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Architecture
Fundamental organization of a system embodied in its components, their relationships to each other, and to the environment, and the principles guiding its design and evolution. [ ISO/IEC 15288 ]
Attractiveness
The capability of the software product to be attractive to the user. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Other Definitions
Other definitions of this word are..
See also
Attribute
A measurable physical or abstract property of an entity. [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 14598 ]
Other Definitions
Attribute [ IEEE 610.12 ]: A characteristic of an item; for example, the item’s color, size, or type.
Attribute [ ISO/IEC 15939, ISO/IEC 25000 ]: Inherent property or characteristic of an entity that can be distinguished quantitatively or qualitatively by human or automated means.
Attribute for Quality Measure [ ISO/IEC 25000 ]: Attribute that relates to software product itself, to the use of the software product or to its development process.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Availability
The degree to which a system or component is operational and accessible when required for use. [ ISO/IEC 20000 ]
Other Definitions
Availability [ ISO/IEC 20000 ]: Ability of a component or service to perform its required function at a stated instant or over a stated period of time.
Notes
Base Measure
Measure defined in terms of an attribute and the method for quantifying it. [ ISO/IEC 99, ISO/IEC 15939, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Baseline
Formally approved version of a configuration item, regardless of media, formally designated and fixed at a specific time during the configuration item’s life cycle. [ ISO/IEC 19770-1 ]
Other Definitions
Baseline [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15288 ]: Specification or product that has been formally reviewed and agreed upon, that thereafter serves as the basis for further development, and that can be changed only through formal change control procedures.
Baseline [ ISO/IEC 20000 ]: Snapshot of the state of a service or individual configuration items at a point in time.
Baseline [ IEEE 1490 ]: An approved plan (for a project), plus or minus approved changes. It is compared to actual performance to determine if performance is within acceptable variance thresholds. Generally refers to the current baseline, but may refer to the original or some other baseline. Usually used with a modifier (e.g., cost performance baseline, schedule baseline, performance measurement baseline, technical baseline).
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Branch
A Branch is either:
Other Definitions
Branch [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]:
-
a computer program construct in which one of two or more alternative sets of program statements is selected for execution.
-
a point in a computer program at which one of two or more alternative sets of program statements is selected for execution.
-
to perform the selection in (1).
-
any of the alternative sets of program statements in (1).
-
a set of evolving source file versions.
Notes
Branch Coverage
The percentage of branches that have been exercised by a test case suite. [ SIGIST ]
Branch Testing
Testing designed to execute each outcome of each decision point in a computer program. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Budget
The approved estimate for the project or any work breakdown structure component or any schedule activity. [ IEEE 1490 ]
Notes
Build
An operational version of a system or component that incorporates a specified subset of the capabilities that the final product will provide. [ IEEE 610.12, ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Call Graph
A diagram that identifies the modules in a system or computer program and shows which modules call one another. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Capability Maturity Model
Model that contains the essential elements of effective processes for one or more disciplines and describes an evolutionary improvement path from ad hoc, immature processes to disciplined, mature processes with improved quality and effectiveness. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Capability Maturity Model [ CMMi ]: A description of the stages through which software organizations evolve as they define, implement, measure, control, and improve their software processes. This model provides a guide for selecting process improvement strategies by facilitating the determination of current process capabilities and the identification of the issues most critical to software quality and process improvement.
Certification
A formal demonstration that a system or component complies with its specified requirements and is acceptable for operational use. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Certification [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]:
-
A written guarantee that a system or component complies with its specified requirements and is acceptable for operational use.
-
The process of confirming that a system or component complies with its specified requirements and is acceptable for operational use.
Example
Certification Criteria
A set of standards, rules, or properties to which an asset must conform in order to be certified to a certain level. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Change Control Board
A formally constituted group of stakeholders responsible for reviewing, evaluating, approving, delaying, or rejecting changes to a project, with all decisions and recommendations being recorded. [ IEEE 1490 ]
Change Control System
A collection of formal documented procedures that define how project deliverables and documentation will be controlled, changed, and approved. [ IEEE 1490, ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Change Management
Judicious use of means to effect a change, or a proposed change, to a product or service. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Changeability
The capability of the software product to enable a specified modification to be implemented. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Notes
Co-existence
The capability of the software product to co-exist with other independent software in a common environment sharing common resources. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Code
In software engineering, computer instructions and data definitions expressed in a programming language or in a form output by an assembler, compiler, or other translator. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Code (verb) [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: To express a computer program in a programming language.
Code Coverage
An analysis method that determines which parts of the software have been executed (covered) by the test case suite and which parts have not been executed and therefore may require additional attention. [ SIGIST ]
Code Freeze
A period during which non-critical changes to the code are not allowed. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Code Review
A meeting at which software code is presented to project personnel, managers, users, customers, or other interested parties for comment or approval. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Code Verification
Ensures by static verification methods the conformance of source code to the specified design of the
software module, the required coding standards, and the safety planning requirements. [ IEC 61508-3 ]
See also
Coding
In software engineering, the process of expressing a computer program in a programming language. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Coding [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The transforming of logic and data from design specifications (design descriptions) into a programming language.
Cohesion
In software design, a measure of the strength of association of the elements within a module. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Cohesion [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The manner and degree to which the tasks performed by a single software module are related to one another.
Notes
Commercial-Off-The-Shelf (COTS)
Software defined by a market-driven need, commercially available, and whose fitness for use has been demonstrated by a broad spectrum of commercial users. [ ISO/IEC 25051 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Commit
To integrate the changes made to a developer’s private view of the source code into a branch accessible through the version control system’s repository. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Commitment
An action resulting in an obligation by one or more of the participants in the act to comply with a rule or perform a contract. [ ISO/IEC 15414 ]
Other Definitions
Commitment [ CMMi ]: A pact that is freely assumed, visible, and expected to be kept by all parties.
Notes
Compatibility
The ability of two or more systems or components to perform their required functions while sharing the same hardware or software environment. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Compatibility [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The ability of two or more systems or components to exchange information.
Compatibility [ ISO/IEC 2382-1 ]: The capability of a functional unit to meet the requirements of a specified interface without appreciable modification.
Complexity
The degree to which a system's design or code is difficult to understand because of numerous components or relationships among components. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Complexity [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The degree to which a system or component has a design or implementation that is difficult to understand and verify.
Component
An entity with discrete structure, such as an assembly or software module, within a system considered at a particular level of analysis. [ ISO/IEC 15026 ]
Other Definitions
Component [ SIGIST ]: A minimal software item for which a separate specification is available.
Component [ IEEE 829 ]: One of the parts that make up a system.
Component [ ISO/IEC 29881 ]: Set of functional services in the software, which, when implemented, represents a well-defined set of functions and is distinguishable by a unique name.
Software Component [ IEEE 1061 ]: A general term used to refer to a software system or an element, such as module, unit, data, or document.
Software Component [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A functionally or logically distinct part of a software configuration item, distinguished for the purpose of convenience in designing and specifying a complex SCI as an assembly of subordinate elements.
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Conciseness
Software attributes that provide implementation of a function with a minimum amount of code. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Condition
A boolean expression containing no boolean operators. For instance A<B is a condition but A and B is not. [ RTCA/EUROCAE ]
Other Definitions
Condition [ ISO 5806, ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: a description of a contingency to be considered in the representation of a problem, or a reference to other procedures to be considered as part of the condition.
Configuration
The arrangement of a computer system or component as defined by the number, nature, and interconnections of its constituent parts. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Configuration [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: In configuration management, the functional and physical characteristics of hardware or software as set forth in technical documentation or achieved in a product.
Configuration [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The arrangement of a system or network as defined by the nature, number, and chief characteristics of its functional units.
Configuration [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The requirements, design, and implementation that define a particular version of a system or system component.
Configuration [ ISO/IEC 2382-1 ]: The manner in which the hardware and software of an information processing system are organized and interconnected.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Configuration Control
An element of configuration management, consisting of the evaluation, coordination, approval or disapproval, and implementation of changes to configuration items after formal establishment of their configuration identification. [ IEEE 610.12, ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Configuration Item
Entity within a configuration that satisfies an end use function and that can be uniquely identified at a given reference point. [ ISO/IEC 12207 ]
Other Definitions
Configuration Item [ ISO/IEC 19770 ]: Item or aggregation of hardware or software or both that is designed to be managed as a single entity.
Configuration Item [ ISO/IEC 20000-1 ]: Component of an infrastructure or an item which is, or will be, under the control of configuration management.
Configuration Item [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: An aggregation of hardware, software, or both, that is designated for configuration management and treated as a single entity in the configuration management process.
Configuration Item [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Aggregation of work products that is designated for configuration management and treated as a single entity in the configuration management process.
Software Configuration Item [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A software entity that has been established as a configuration item.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Configuration Management
A discipline applying technical and administrative direction and surveillance to
-
identify and document the functional and physical characteristics of a configuration item,
-
control changes to those characteristics, record and report change processing and implementation status, and
Other Definitions
Configuration Management <ref name="sting">Software Technology Interest Group On-line Glossary, http: //www.apl.jhu.edu/Notes/Hausler/web/glossary.html .</ref>: The process of identifying, defining, recording and reporting the configuration items in a system and the change requests. Controlling the releases and change of the items throughout the life-cycle.
Configuration Management [ ISO/IEC 29881 ]: Technical and organizational activities comprising configuration identification, control, status accounting, and auditing.
Software Configuration Management [ ISO/IEC 15846 ]: The process of applying configuration management throughout the software life cycle to ensure the completeness and correctness of Software Configuration Items.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
External Links:
Configuration Management System
The discipline of identifying the components of a continually evolving system to control changes to those components and maintaining integrity and traceability throughout the life cycle. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
-
A subsystem of the overall project management system. It is a collection of formal documented procedures used to apply technical and administrative direction and surveillance to:
-
* identify and document the functional and physical characteristics of a product, result, service, or component;
-
* control any changes to such characteristics;
-
* record and report each change and its implementation status; and
-
* support the audit of the products, results, or components to verify conformance to requirements.
:It includes the documentation, tracking systems, and defined approval levels necessary for authorizing and controlling changes. [ IEEE 1490 ]
Conflict
A change in one version of a file that cannot be reconciled with the version of the file to which it is applied. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Conformance
The fulfillment by a product, process or service of specified requirements. [ ISO/IEC 12207 ]
Connectivity
The capability of a system or device to be attached to other systems or devices without modification. [ ISO/IEC 2382-1 ]
Consistency
The degree of uniformity, standardization, and freedom from contradiction among the documents or parts of a system or component. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Consistency [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Software attributes that provide uniform design and implementation techniques and notations.
Constraint
A restriction on the value of an attribute or the existence of any object based on the value or existence of one or more others. [ ISO/IEC 15474-1 ]
Other Definitions
Constraint [ IEEE 1362 ]: An externally imposed limitation on system requirements, design, or implementation or on the process used to develop or modify a system.
Constraint [ IEEE 1490 ]: The state, quality, or sense of being restricted to a given course of action or inaction. An applicable restriction or limitation, either internal or external to a project, which will affect the performance of the project or a process. For example, a schedule constraint is any limitation or restraint placed on the project schedule that affects when a schedule activity can be scheduled and is usually in the form of fixed imposed dates.
Constraint [ IEEE 1233 ]: A statement that expresses measurable bounds for an element or function of the system.
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Content Coupling
A type of coupling in which some or all of the contents of one software module are included in the contents of another module. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Context of Use
Users, tasks, equipment (hardware, software and materials), and the physical and social environments in which a product is used. [ ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Contract
Binding agreement between two parties, especially enforceable by law, or a similar internal agreement wholly within an organization. [ ISO/IEC 12207 ]
Other Definitions
Contract [ IEEE 1490 ]: A mutually binding agreement that obligates the seller to provide the specified product or service or result and obligates the buyer to pay for it.
Control Coupling
A type of coupling in which one software module communicates information to another module for the explicit purpose of influencing the latter module’s execution. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Control Flow
The sequence in which operations are performed during the execution of a computer program. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Control Flow Diagram
A diagram that depicts the set of all possible sequences in which operations may be performed during the execution of a system or program. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Convention
Requirement employed to prescribe a disciplined, uniform approach to providing consistency in a software product, that is, a uniform pattern or form for arranging data. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Correctability
The degree of effort required to correct software defects and to cope with user complaints. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Correctness
The degree to which a system or component is free from faults in its specification, design, and implementation. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Correctness [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The degree to which software, documentation, or other items meet specified requirements.
Correctness [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The degree to which software, documentation, or other items meet user needs and expectations, whether specified or not.
Coupling
The manner and degree of interdependence between software modules. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Coupling [ ISO/IEC 19759 ]: The strength of the relationships between modules.
Coupling [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A measure of how closely connected two routines or modules are.
Coupling [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: In software design, a measure of the interdependence among modules in a computer program
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Coverage
The degree, expressed as a percentage, to which a specified coverage item has been exercised by a test case suite. [ SIGIST ]
Other Definitions
Test Coverage [ ISO/IEC 12207 ]: Extent to which the test cases test the requirements for the system or software product.
test Coverage [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The degree to which a given test or set of tests addresses all specified requirements for a given system or
component.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Criteria
Specific data items identified as contents of information items for appraising a factor in an evaluation, audit, test or review. [ ISO/IEC 15289 ]
Other Definitions
Criteria [ ISO/IEC 15289 ]: standards, rules, or tests on which a judgment or decision can be based, or by which a product, service, result, or process can be evaluated.
Criticality
Custom Software
Software product developed for a specific application from a user requirements specification. [ ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Customer
Organization or person that receives a product or service. [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15288 ]
Other Definitions
Customer [ IEEE 1233 ]: The entity or entities for whom the requirements are to be satisfied in the system being defined and developed.
Customer [ IEEE 1362 ]: An individual or organization who acts for the ultimate user of a new or modified hardware or software product to acquire the product and its documentation.
Customer [ IEEE 830 ]: The person, or persons, who pay for the product and usually (but not necessarily) decide the requirements.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Data
Collection of values assigned to base measures, derived measures, and/or indicators. [ ISO/IEC 15939, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Other Definitions
Data [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A representation of facts, concepts, or instructions in a manner suitable for communication, interpretation, or processing by humans or by automatic means.
Data [ ISO/IEC 2382-1 ]: A reinterpretable representation of information in a formalized manner suitable for communication, interpretation, or communication, or processing.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Data Coupling
A type of coupling in which output from one software module serves as input to another module. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Data Flow
The sequence in which data transfer, use, and transformation are performed during the execution of a computer program. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Data Flow Diagram
A diagram that depicts data sources, data sinks, data storage, and processes performed on data as nodes, and logical flow of data as links between the nodes. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Data Management
In a data processing system, the functions that provide access to data, perform or monitor the storage of data, and control input-output operations. [ ISO/IEC 2382-1 ]
Other Definitions
Data Management [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The disciplined processes and systems that plan for, acquire, and provide stewardship for business and technical data, consistent with data requirements, throughout the data lifecycle.
Data Model
A model about data by which an interpretation of the data can be obtained in the modeling tool industry. [ ISO/IEC 15474-1 ]
Notes
Data Processing
The systematic performance of operations upon data. [ ISO/IEC 2382-1 ]
Data Provider
Individual or organisation that is a source of data. [ ISO/IEC 15939 ]
Data Store
Organised and persistent collection of data and information that allows for its retrieval. [ ISO/IEC 15939 ]
Data Type
A class of data, characterized by the members of the class and the operations that can be applied to them. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Database
A collection of data organized according to a conceptual structure describing the characteristics of the data and the relationships among their corresponding entities, supporting one or more application areas. [ ISO/IEC 2382-1 ]
Other Definitions
Database [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A collection of interrelated data stored together in one or more computerized files.
Database [ ISO/IEC 29881 ]: Collection of data describing a specific target area that is used and updated by one or more applications.
Decision Criteria
Thresholds, targets, or patterns used to determine the need for action or further investigation, or to describe the level of confidence in a given result. [ ISO/IEC 15939, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Decoupling
The process of making software modules more independent of one another to decrease the impact of changes to, and errors in, the individual modules. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Defect
A flaw in a system or system component that causes the system or component to fail to perform its required function. A defect, if encountered during execution, may cause a failure of the system. [ CMMi ]
Other Definitions
Defect [ IEEE 1490 ]: An imperfection or deficiency in a project component where that component does not meet its requirements or specifications and needs to be either repaired or replaced.
Notes
Degree of Confidence
The degree of confidence that software conforms to its requirements. [ ISO/IEC 15026 ]
Deliverable
Items whose delivery to the customer is a requirement of the contract. [ ISO/IEC 15910 ]
Other Definitions
Deliverable [ IEEE 1490 ]: Any unique and verifiable product, result, or capability to perform a service that must be produced to complete a process, phase, or project. Often used more narrowly in reference to an external deliverable, which is a deliverable that is subject to approval by the project sponsor or customer.
Deliverable [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Item[3] to be provided to an acquirer or other designated recipient as specified in an agreement.
Deliverables [ ISO/IEC 15910 ]: Items whose delivery to the customer is a requirement of the contract.
Delivery
Release of a system or component to its customer or intended user. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Dependability
Measure of the degree to which an item is operable and capable of performing its required function at any (random) time during a specified mission profile, given item availability at the start of the mission. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Dependability [ IEEE 982 ]: Trustworthiness of a computer system such that reliance can be justifiably placed on the service it delivers.
Deployment
Phase of a project in which a system is put into operation and cutover issues are resolved. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Derived Measure
Measure that is defined as a function of two or more values of base measures. [ ISO/IEC 99, ISO/IEC 15939, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Design
The process of defining the architecture, components, interfaces, and other characteristics of a system or component. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Design [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The result of the process of defining the architecture, components, interfaces, and other characteristics of a system or component.
Design [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The process of defining the software architecture, components, modules, interfaces, and data for a software system to satisfy specified requirements.
Design [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The process of conceiving, inventing, or contriving a scheme for turning a computer program specification into an operational program.
Design [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Activity that links requirements analysis to coding and debugging.
Design [ ISO/IEC 26514 ]: Stage of documentation development that is concerned with determining what documentation will be provided in a product and what the nature of the documentation will be.
Design Pattern
A description of the problem and the essence of its solution to enable the solution to be reused in different settings. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Developer
Individual or organisation that performs development activities (including requirements analysis, design, testing through acceptance) during the software lifecycle process. [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Notes
Development
Software life cycleprocess that contains the activities of requirements analysis, design, coding, integration, testing, installation and support for acceptance of software products. [ ISO/IEC 90003, ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15939 ]
Other Definitions
Development [ ISO/IEC 26514 ]: Activity of preparing documentation after it has been designed.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Development Testing
Formal or informal testing conducted during the development of a system or component, usually in the development environment by the developer. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Direct Measure
A measure of an attribute that does not depend upon a measure of any other attribute. [ ISO/IEC 14598, ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
See also
Glossary:
Papers:
Standards:
Direct Metric
Document
Uniquely identified unit of information for human use, such as a report, specification, manual or book, in printed or electronic form. [ ISO/IEC 9294 ]
Other Definitions
Document (verb) [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: To add comments to a computer program.
Document [ ISO/IEC 15910 ]: An item of documentation.
Document [ ISO/IEC 20000 ]: Information and its supporting medium.
Document [ ISO/IEC 26514 ]: Separately identified piece of documentation which could be part of a documentation set.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Documentation
Collection of related documents that are designed, written, produced and maintained. [ ISO/IEC 9294 ]
Other Definitions
Documentation [ ISO/IEC 26514 ]: Information that explains how to use a software product.
Documentation [ IEEE 829 ]:
Examples
Notes
Dynamic Analysis
The process of evaluating a system or component based on its behavior during execution. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Earned Value
The value of work performed expressed in terms of the approved budget assigned to that work for a schedule activity or work breakdown structure component. [ IEEE 1490 ]
Effectiveness
The capability of the software product to enable users to achieve specified goals with accuracy and completeness in a specified context of use. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Other Definitions
Effectiveness [ ISO/IEC 25062 ]: The accuracy and completeness with which users achieve specified goals.
See also
Efficiency
Resources expended in relation to the accuracy and completeness with which users achieve goals. [ ISO/IEC 25062 ]
Other Definitions
Efficiency [ IEEE 610.12, ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The degree to which a system or component performs its designated functions with minimum consumption of resources.
Efficiency [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]: The capability of the software product to provide appropriate performance, relative to the amount of resources used, under stated conditions.
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Efficiency Compliance
The capability of the software product to adhere to standards or conventions relating to efficiency. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Effort
The number of labor units required to complete a schedule activity or work breakdown structure component. Usually expressed as staff hours, staff days, or staff weeks. [ IEEE 1490 ]
Encapsulation
A software development technique that consists of isolating a system function or a set of data and operations on those data within a module and providing precise specifications for the module. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Encapsulation [ IEEE 1320 ]: The concept that access to the names, meanings, and values of the responsibilities of a class is entirely separated from access to their realization.
Encapsulation [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The idea that a module has an outside that is distinct from its inside, that it has an external interface and an internal implementation.
End User
Individual person who ultimately benefits from the outcomes of the system. [ ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Other Definitions
End User [ IEEE 1233 ]: The person or persons who will ultimately be using the system for its intended purpose. [ IEEE 1233 ]
End User [ ISO 9127 ]: The person who uses the software package.
End User [ ISO/IEC 29881 ]: Any person that communicates or interacts with the software at any time.
Entity
Object[4] that is to be characterised by measuring its attributes. [ ISO/IEC 15939, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Other Definitions
Entity [ IEEE 1320 ]: The representation of a set of real or abstract things that are recognized as the same type because they share the same characteristics and can participate in the same relationships.
Entity [ ISO/IEC 15474 ]: An object (i.e., thing, event or concept) that occurs in a model (i.e., transfer).
Entity [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: In computer programming, any item that can be named or denoted in a program.
Entity [ ISO/IEC 29881 ]: Logical component of the data store, representing fundamental things of relevance to the user, and about which persistent information is stored.
Examples
See also
Standards:
Entry Point
A point in a software module at which execution of the module can begin. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Environment
The configuration(s) of hardware and software in which the software operates. [ ISO 9127 ]
Other Definitions
Environment [ IEEE 1362 ]: The circumstances, objects, and conditions that surround a system to be built.
Environment [ IEEE 1233 ]: The circumstances, objects, and conditions that will influence the completed system.
Environment [ IEEE 1320 ]: A concept space, i.e., an area in which a concept has an agreed-to meaning and one or more agreed-to names that are used for the concept.
Error
A human action that produces an incorrect result, such as software containing a fault. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Error [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]:
-
An incorrect step, process, or data definition.
-
An incorrect result
-
The difference between a computed, observed, or measured value or condition and the true, specified, or theoretically correct value or condition.
Notes
-
Example: omission or misinterpretation of user requirements in a software specification, incorrect translation, or
omission of a requirement in the design specification. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Error Tolerance
The ability of a system or component to continue normal operation despite the presence of erroneous inputs. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Evaluation
Systematic determination of the extent to which an entity meets its specified criteria. [ ISO/IEC 12207 ]
Other Definitions
Evaluation [ ISO/IEC 15414 ]: An action that assesses the value of something.
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Evaluation Activity
Assessment of a software product against identified and applicable quality characteristics performed using applicable techniques or methods. [ ISO/IEC 25001 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Evaluation Group
Organization responsible for specifying the software qualityrequirements as well as managing and implementing the software quality evaluation activities through the provision of technology, tools, experiences, and management skills. [ ISO/IEC 25001 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Evaluation Method
Procedure describing actions to be performed by the evaluator in order to obtain results for the specified measurement applied to the specified product components or on the product as a whole. [ ISO/IEC 25000 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Evaluation Module
A package of evaluation technology for a specific software quality characteristic or sub-characteristic. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1, ISO/IEC 14598 ]
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Evaluation Technology
Technique, processes, tools, measures and relevant technical information used for evaluation. [ ISO/IEC 25001 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Evaluation Tool
An instrument that can be used during evaluation to collect data, to perform interpretation of data or to automate part of the evaluation. [ ISO/IEC 14598-5 ]
Execute
To carry out an instruction, process, or computer program. [ IEEE 1490 ]
Other Definitions
Execute [ IEEE 1490 ]: Directing, managing, performing, and accomplishing the project work, providing the deliverables, and providing work performance information.
Execution Efficiency
The degree to which a system or component performs its designated functions with minimum consumption of time. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Execution Time
The time which elapses between task submission and completion. [ ISO/IEC 14756 ]
Notes
Exit
A point in a software module at which execution of the module can terminate. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Expandability
The degree of effort required to improve or modify software functions' efficiency. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Extendability
The ease with which a system or component can be modified to increase its storage or functional capacity. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
External Attribute
A measurable property of an entity which can only be derived with respect to how it relates to its environment. [ ISO/IEC 14598-3 ]
Notes
External Measure
An indirect measure of a product derived from measures of the behaviour of the system of which it is a part. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1, ISO/IEC 14598 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
External Quality
The extent to which a product satisfies stated and implied needs when used under specified conditions. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1, ISO/IEC 14598 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
External Software Quality
Capability of a software product to enable the behavior of a system to satisfy stated and implied needs when the system is used under specified conditions. [ ISO/IEC 25000 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Facility
Physical means or equipment for facilitating the performance of an action. [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15288 ]
Notes
Failure
The termination of the ability of a product to perform a required function or its inability to perform within previously specified limits. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1, ISO/IEC 14598-5, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Other Definitions
Failure [ SIGIST ]: Deviation of the software from its expected delivery or service.
Failure [ IEEE 610.12 ]: The inability of a system or component to perform its required functions within specified performance requirements.
Failure [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: An event in which a system or system component does not perform a required function within specified limits.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Failure Rate
The ratio of the number of failures of a given category to a given unit of measure. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Fault
An incorrect step, process or data definition in a computer program. [ IEEE 610.12, ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Other Definitions
Fault [ RTCA/EUROCAE ]: A manifestation of an error in software. A fault, if encountered may cause a failure.
Fault [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]:
-
a manifestation of an error in software.
-
an incorrect step, process, or data definition in a computer program.
-
a defect in a hardware device or component.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Fault Tolerance
The capability of the software product to maintain a specified level of performance in cases of software faults or of infringement of its specified interface. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Other Definitions
Fault Tolerance [ IEEE 610.12 ]:
-
The ability of a system or component to continue normal operation despite the presence of hardware or software faults.
-
The number of faults a system or component can withstand before normal operation is impaired.
-
Pertaining to the study of errors, faults, and failures, and of methods for enabling systems to continue normal operation in the presence of faults.
Notes
Feasibility
The degree to which the requirements, design, or plans for a system or component can be implemented under existing constraints. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Feature
Distinguishing characteristic of a system item. [ IEEE 829 ]
Feature Freeze
Notes
Finite State Machine
A computational model consisting of a finite number of states and transitions between those states, possibly with accompanying actions. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Flexibility
The ease with which a system or component can be modified for use in applications or environments other than those for which it was specifically designed. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765, IEEE 610.12 ]
Frozen Branch
A branch where no development takes place, either in preparation for a release or because active development has ceased on it. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Function
A software module that performs a specific action, is invoked by the appearance of its name in an expression, may receive input values, and returns a single value. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Function [ IEEE 1233 ]: A task, action, or activity that must be accomplished to achieve a desired outcome.
Function [ IEEE 1320 ]: A transformation of inputs to outputs, by means of some mechanisms, and subject to certain controls, that is identified by a function name and modeled by a box.
Function [ ISO/IEC 26514 ]: Part of an application that provides facilities for users to carry out their tasks.
Function [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A defined objective or characteristic action of a system or component.
Functional Analysis
A systematic investigation of the functions of a real or planned system. [ ISO/IEC 2382-1 ]
Other Definitions
Functional Analysis [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Examination of a defined function to identify all the sub-functions necessary to accomplish that function, to identify functional relationships and interfaces (internal and external) and capture these in a functional architecture, to flow down upper-level performance requirements and to assign these requirements to lower-level sub-functions.
Functional Requirement
A statement that identifies what a product or process must accomplish to produce required behavior and/or results. [ IEEE 1220 ]
Other Definitions
Model [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A requirement that specifies a function that a system or system component must be able to perform.
Functional Size
A size of the software derived by quantifying the functional user requirements. [ ISO/IEC 14143-1 ]
Functional Testing
Testing that ignores the internal mechanism of a system or component and focuses solely on the outputs generated in response to selected inputs and execution conditions. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Functional Unit
An entity of hardware or software, or both, capable of accomplishing a specified purpose. [ ISO/IEC 2382-1 ]
Functionality
The capability of the software product to provide functions which meet stated and implied needs when the software is used under specified conditions. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Other Definitions
Functionality Compliance
The capability of the software product to adhere to standards, conventions or regulations in laws and similar prescriptions relating to functionality. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Generality
The degree to which a system or component performs a broad range of functions. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Generic Practice
An activity that, when consistently performed, contributes to the achievement of a specific process attribute. [ ISO/IEC 15504 ]
Glossary
The collection of the names and narrative descriptions of all terms that may be used for defined concepts within an environment. [ IEEE 1320 ]
Goal
Intended outcome of user interaction with a product. [ ISO/IEC 25062 ]
Other Definitions
Goal [ ISO/IEC 9126-4 ]: An intended outcome.
Granularity
The depth or level of detail at which data is collected. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Historical Information
Documents and data on prior projects including project files, records, correspondence, closed contracts, and closed projects. [ IEEE 1490 ]
Hybrid Coupling
A type of coupling in which different subsets of the range of values that a data item can assume are used for different and unrelated purposes in different software modules. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Impact Analysis
Identification of all system and software products that a change request affects and development of an estimate of the resources needed to accomplish the change. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Implementation
The process of translating a design into hardware components, software components, or both. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Implementation ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The installation and customization of packaged software.
Implementation ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Construction.
Implementation ISO/IEC 2382 ]: The system development phase at the end of which the hardware, software and procedures of the system considered become operational.
Implementation ISO/IEC 26514 ]: Phase of development during which user documentation is created according to the design, tested, and revised.
Implied Needs
Needs that may not have been stated but are actual needs. [ ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Other Definitions
Implied Needs [ ISO/IEC 9126-1, ISO/IEC 14598-1 ]: Needs that may not have been stated but are actual needs when the entity is used in particular conditions.
Notes
Incremental Development
A software development technique in which requirements definition, design, implementation, and testing occur in an overlapping, iterative (rather than sequential) manner, resulting in incremental completion of the overall software product. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Indicator
Measure that provides an estimate or evaluation of specified attributes derived from a model with respect to defined information needs. [ ISO/IEC 15939, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Other Definitions
Indicator [ ISO/IEC 9126-1, ISO/IEC 14598-1 ]: A measure that can be used to estimate or predict another measure.
Indicator Value
Numerical or categorical result assigned to an indicator. [ ISO/IEC 15939 ]
Indirect Measure
A measure of an attribute that is derived from measures of one or more other attributes. [ ISO/IEC 14598 ]
See also
Glossary:
Papers:
Standards:
Indirect Metric
Information
An information processing, knowledge concerning objects, such as facts, events, things, processes, or ideas, including concepts, that within a certain context has a particular meaning. [ ISO/IEC 2382-1 ]
Notes
Information Analysis
A systematic investigation of information and its flow in a real or planned system. [ ISO/IEC 2382-1 ]
Information Management
In an information processing system, the functions of controlling the acquisition, analysis, retention, retrieval, and distribution of information. [ ISO/IEC 2382-1 ]
Information Need
Insight necessary to manage objectives, goals, risks, and problems. [ ISO/IEC 15939 ]
See also
Information Product
One or more indicators and their associated interpretations that address an information need. [ ISO/IEC 15939, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Example
Inspection
A static analysis technique that relies on visual examination of development products to detect errors, violations of development standards, and other problems. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Inspection [ IEEE 1490 ]: Examining or measuring to verify whether an activity, component, product, result, or service conforms to specified requirements.
Notes
Installability
The capability of the software product to be installed in a specified environment. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
See also
Installation Manual
A document that provides the information necessary to install a system or component, set initial parameters, and prepare the system or component for operational use. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Integration
The process of combining software components, hardware components, or both into an overall system. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Integration Test
The progressive linking and testing of programs or modules in order to ensure their proper functioning in the complete system. [ ISO/IEC 2382 ]
Integrity
The degree to which a system or component prevents unauthorized access to, or modification of, computer programs or data. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Interface Testing
Testing conducted to evaluate whether systems or components pass data and control correctly to one another. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Intermediate Software Product
A product of the software development process that is used as input to another stage of the software development process. [ ISO/IEC 14598, ISO/IEC 9126-1, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Internal Attribute
A measurable property of an entity which can be derived purely in terms of the entity itself. [ ISO/IEC 14598, ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Internal Measure
A measure of the product itself, either direct or indirect. [ ISO/IEC 14598, ISO/IEC 9126-1, ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Internal Quality
The totality of attributes of a product that determine its ability to satisfy stated and implied needs when used under specified conditions. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1, ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Internal Software Quality
Capability of a set of static attributes of a software product to satisfy stated and implied needs when the software product is used under specified conditions. [ ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Examples
Interoperability
The capability of the software product to interact with one or more specified systems. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
See also
Interoperability Testing
Testing conducted to ensure that a modified system retains the capability of exchanging information with systems of different types, and of using that information. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Interval Scale
Scale in which the measurement values have equal distances corresponding to equal quantities of the attribute. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Item
An entity such as a part, component, subsystem, equipment or system that can be individually considered. An item may consist of hardware, software or both. [ ISO/IEC 15026 ]
Iteration
-
The process of performing a sequence of steps repeatedly.
Key Practices
The infrastructures and activities that contribute most to the effective implementation and institutionalization of a key process area. [ CMMi ]
Notes
In the CMMi process, each key process area is described in terms of the key practices that contribute to satisfying its goals. The key practices describe the infrastructure and activities that contribute most to the effective implementation and institutionalization of the key process area.
Each key practice consists of a single sentence, often followed by a more detailed description, which may include examples and elaboration. These
key practices, also referred to as the top-level key practices, state the fundamental policies, procedures, and activities for the key process area.
The components of the detailed description are frequently referred to as sub-practices.
The key practices describe "what" is to be done, but they should not be interpreted as mandating "how" the goals should be achieved. Alternative practices may accomplish the goals of the key process area. The key practices should be interpreted rationally to judge whether the goals of the key
process area are effectively, although perhaps differently, achieved.
See also
Key Process Area
A cluster of related activities that, when performed collectively, achieve a set of goals considered important for establishing process capability. [ CMMi ]
Notes
The key process areas have been defined to reside at a single maturity level. They are the areas identified by the SEI to be the principal building blocks to help determine the software process capability of an organization and understand the improvements needed to advance to higher maturity levels.
-
-
The Level 4 key process areas are Quantitative Process Management and Software Quality Management.
-
The Level 5 key process areas are Defect Prevention, Technology Change Management, and Process Change Management.
-
See also
Knowledge Base
A database that contains inference rules and information about human experience and expertise in a domain. [ ISO/IEC 2382-1 ]
Learnability
The capability of the software product to enable the user to learn its application. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Lessons Learned
The learning gained from the process of performing the project. Lessons learned may be identified at any point. Also considered a project record, to be included in the lessons learned knowledge base. [ IEEE 1490 ]
Level of Performance
The degree to which the needs are satisfied, represented by a specific set of values for the quality characteristics. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Life Cycle
Evolution of a system, product, service, project or other human-made entity from conception through retirement. [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15288 ]
Other Definitions
Life Cycle [ IEEE 1220 ]: The system or product evolution initiated by a perceived stakeholder need through the disposal of the products.
Life Cycle Model
Framework of processes and activities concerned with the life cycle that may be organized into stages, which also acts as a common reference for communication and understanding. [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15288 ]
Maintainability
The capability of the software product to be modified. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1, ISO/IEC 14764 ]
Other Definitions
Maintainability [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The ease with which a software system or component can be modified to change or add capabilities, correct faults or defects, improve performance or other attributes, or adapt to a changed environment.
Maintainability [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The average effort required to locate and fix a software failure.
Maintainability [ IEEE 982 ]: Speed and ease with which a program can be corrected or changed.
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Maintainability Compliance
The capability of the software product to adhere to standards or conventions relating to maintainability. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Maintainer
Individual or organization that performs maintenance activities. [ ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Other Definitions
Maintainer [ ISO/IEC 9126-1, ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 14598 ]: An organisation that performs maintenance activities.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Maintenance
The process of modifying a software system or component after delivery to correct faults, improve performance or other attributes, or adapt to a changed environment. [ IEEE 610.12, ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Software Maintenance [ ISO/IEC 14764 ]: The totality of activities required to provide cost-effective support to a software system.
Notes
+[6]
+ * * Perfective maintenance - Changes which improve the system in some way without changing its functionality; * * Adaptive maintenance - Maintenance which is required because of changes in the environment of a program; * * Corrective maintenance - The correction of previously undiscovered system errors.
+[7]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Maintenance Manual
A software engineering project-deliverable document that enables a system’s maintenance personnel (rather than users) to maintain the system. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Maturity
The capability of the software product to avoid failure as a result of faults in the software. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Measurable Concept
Abstract relationship between attributes of entities and information needs. [ ISO/IEC 15939 ]
See also
Measure
Variable to which a value is assigned as the result of measurement. [ ISO/IEC 15939, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Other Definition
Measure (verb) [ ISO/IEC 14598, ISO/IEC 15939 ]: To make a measurement.
Measure [ IEEE 1061 ]: A way to ascertain or appraise value by comparing it to a norm.
Measure (verb) [ IEEE 1061 ]: To apply a metric.
Measure [ ISO/IEC 14598 ]: The number or category assigned to an attribute of an entity by making a measurement.
Measure [ IEEE 982 ]: The number or symbol assigned to an entity by a mapping from the empirical world to the formal, relational world in order to characterize an attribute.
Measure [ IEEE 982 ]: The act or process of measuring.
Measurement
Set of operations having the object of determining a value of a measure. [ ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Other Definitions
Measurement [ ISO/IEC 99, ISO/IEC 15939 ]: Set of operations having the object of determining a value of a measure.
Measurement [ IEEE 1061 ]: Act or process of assigning a number or category to an entity to describe an attribute of that entity.
Measurement [ ISO/IEC 19759 ]: The assignment of numbers to objects in a systematic way to represent properties of the object.
Measurement [ ISO/IEC 9126-1, ISO/IEC 14598 ]: The use of a metric to assign a value (which may be a number or category) from a scale to an attribute of an entity.
Measurement [ ISO/IEC 19759 ]: the assignment of values and labels to aspects of software engineering (products, processes, and resources) and the models that are derived from them, whether these models are developed using statistical, expert knowledge or other techniques.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Measurement Analyst
Individual or organisation that is responsible for the planning, performance, evaluation, and improvement of measurement. [ ISO/IEC 15939 ]
See also
Measurement Experience Base
Data store that contains the evaluation of the information products and the measurement process as well as any lessons learned during the measurement process. [ ISO/IEC 15939 ]
See also
Measurement Function
Algorithm or calculation performed to combine two or more base measures. [ ISO/IEC 15939, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Measurement Method
Logical sequence of operations, described generically, used in quantifying an attribute with respect to a specified scale. [ ISO/IEC 99, ISO/IEC 15939, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Notes
-
-
* subjective — quantification involving human judgement,
-
Measurement Procedure
Set of operations, described specifically, used in the performance of a particular measurement according to a given method. [ ISO/IEC 99, ISO/IEC 15939, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Measurement Process
The process for establishing, planning, performing and evaluating software measurement within an overall project or organisational measurement structure. [ ISO/IEC 15939 ]
See also
Measurement Process Owner
Individual or organisation responsible for the measurement process. [ ISO/IEC 15939 ]
Measurement Sponsor
Individual or organisation that authorises and supports the establishment of the measurement process. [ ISO/IEC 15939 ]
Measurement User
Individual or organisation that uses the information products. [ ISO/IEC 15939 ]
Metric
The defined measurement method and the measurement scale. [ ISO/IEC 14598, ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Milestone
A significant point or event in the project. [ IEEE 1490 ]
Other Definitions
Milestone [ IEEE 1058 ]: A scheduled event used to measure progress.
Notes
-
Major milestones for software projects may include an acquirer or managerial sign-off, baselining of a specification, completion of system integration, and product delivery. Minor milestones might include baselining of a software module or completion of a chapter of the user manual
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Mock Object
Temporary dummy objects created to aid testing until the real objects become available. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Model
A semantically closed abstraction of a system or a complete description of a system from a particular perspective. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Model [ IEEE 1233 ]: A representation of a real world process, device, or concept.
Model [ ISO/IEC 15474 ]: A related collection of instances of meta-objects, representing (describing or prescribing) an information system, or parts thereof, such as a software product.
Modifiability
The ease with which a system can be changed without introducing defects. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Modifiable
Structured and has a style such that changes can be made completely, consistently, and correctly while retaining the structure. [ ISO/IEC 12207 ]
Modularity
The degree to which a system or computer program is composed of discrete components such that a change to one component has minimal impact on other components. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Modularity [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Software attributes that provide a structure of highly independent components.
Modularity [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The extent to which a routine or module is like a black box
Module
A program unit that is discrete and identifiable with respect to compiling, combining with other units, and loading. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Module [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]:
-
A logically separable part of a program.
-
A set of source code files under version control that can be manipulated together as one.
-
A collection of both data and the routines that act on it.
Notes
-
The terms 'module', 'component,' and 'unit' are often used interchangeably or defined to be sub-elements of one another in different ways depending upon the context. The relationship of these terms is not yet standardized.
Moke Object
Temporary dummy objects created to aid testing until the real objects become available. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Multidimensional Analysis
Multidimensional analysis is a measurement function that weights different base measures to give a more relevant insight of the final goal of the measure.
It was primarily developed by Kaner and Bond in Software Engineering Metrics: What Do They Measure And How Do We Know.
Network
An arrangement of nodes and interconnecting branches. [ ISO/IEC 2382-1 ]
Nonfunctional Requirement
A software requirement that describes not what the software will do but how the software will do it. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Nontechnical Requirement
Requirement affecting product and service acquisition or development that is not a property of the product or service. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Object
An encapsulation of data and services that manipulate that data. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Object [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A specific entity that exists in a program at runtime in object-oriented programming.
Object [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Pertaining to the outcome of an assembly or compilation process.
Object [ IEEE 1320 ]: A member of an object set and an instance of an object type.
Object Model
An integrated abstraction that treats all activities as performed by collaborating objects and encompassing both the data and the operations that can be performed against that data. [ ISO/IEC 12207 ]
Notes
Object Oriented Design
A software development technique in which a system or component is expressed in terms of objects and connections between those objects. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Observation
Instance of applying a measurement procedure to produce a value for a base measure. [ ISO/IEC 15939, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Observation Period
The time interval, where the measurement procedure is observed for collecting (logging) measurement results for rating or validation, consisting of the rating interval and the supplementary run. [ ISO/IEC 14756 ]
Operability
The capability of the software product to enable the user to operate and control it. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Notes
Operand
A variable, constant, or function upon which an operation is to be performed. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Operational Testing
Testing conducted to evaluate a system or component in its operational environment. [ ISO/IEC 15504 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Operator
Individual or organisation that operates the system. [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15939, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Other Definitions
Operator [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A mathematical or logical symbol that represents an action to be performed in an operation.
Operator [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15288 ]: Entity that performs the operation of a system.
Operator [ IEEE 1220 ]: An individual or an organization that contributes to the functionality of a system and draws on knowledge, skills, and procedures to contribute the function.
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Operator Manual
A document that provides the information necessary to initiate and operate a system or component. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Optional Attribute
Optional Requirement
Requirement of a normative document that must be fulfilled in order to comply with a particular option permitted by that document. [ ISO/IEC 14143 ]
Organisational Unit
The part of an organisation that is the subject of measurement. [ ISO/IEC 15504-9, ISO/IEC 15939 ]
Notes
Path
In software engineering, a sequence of instructions that may be performed in the execution of a computer program. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Path [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: In file access, a hierarchical sequence of directory and subdirectory names specifying the storage location of a file.
Path Analysis
Analysis of a computer program to identify all possible paths through the program, to detect incomplete paths, or to discover portions of the program that are not on any path. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Path Testing
Testing designed to execute all or selected paths through a computer program. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Pathological Coupling
A type of coupling in which one software module affects or depends upon the internal implementation of another. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Peer Review
A review of a software work product, following defined procedures, by peers of the producers of the product for the purpose of identifying defects and improvements. [ CMMi ]
Other Definitions
Peer Review [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Review of work products performed by peers during development of the work products to identify defects for removal.
Performance
The degree to which a system or component accomplishes its designated functions within given constraints, such as speed, accuracy, or memory usage. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Performance Indicator
An assessment indicator that supports the judgment of the process performance of a specific process. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Performance Testing
Testing conducted to evaluate the compliance of a system or component with specified performance requirements. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Pilot Project
A project designed to test a preliminary version of an information processing system under actual but limited operating conditions and which will then be used to test the definitive version of the system. [ ISO/IEC 2382 ]
Portability
The capability of the software product to be transferred from one environment to another. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Other Definitions
Portability [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The ease with which a system or component can be transferred from one hardware or software environment to another.
Portability [ ISO/IEC 2382 ]: The capability of a program to be executed on various types of data processing systems without converting the program to a different language and with little or no modification.
Notes
See also
Portability Compliance
The capability of the software product to adhere to standards or conventions relating to portability. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Practice
An activity that contributes to the purpose or outcomes of a process or enhances the capability of a process. [ ISO/IEC 15504 ]
Other Definitions
Practice [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Requirements employed to prescribe a disciplined uniform approach to the software development process.
Practice [ IEEE 1490 ]: A specific type of professional or management activity that contributes to the execution of a process and that may employ one or more techniques and tools.
Precision
The degree of exactness or discrimination with which a quantity is stated. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Predictive Metric
A metric applied during development and used to predict the values of a software quality factor. [ IEEE 1061 ]
Procedure
Ordered series of steps that specify how to perform a task. [ ISO/IEC 26514 ]
Other Definitions
Procedure [ ISO/IEC 19770 ]: Specified way to carry out an activity or process.
Procedure [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A portion of a computer program that is named and that performs a specific action.
Procedure [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A routine that does not return a value.
Process
System of activities, which use resources to transform inputs into outputs. [ ISO/IEC" 25000 ]
Other Definitions
Process [ ISO/IEC 15504-9, ISO/IEC 15939 ]: Set of interrelated activities that transform inputs into outputs.
Process [ ISO/IEC 2382 ]: Predetermined course of events defined by its purpose or by its effect, achieved under given conditions.
Process (verb) [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: To perform operations on data.
Process [ ISO/IEC 15414 ]: A collection of steps taking place in a prescribed manner and leading to an objective.
Process [ ISO/IEC 2382 ]: In data processing, the predetermined course of events that occur during the execution of all or part of a program.
Notes
Process Assessment
A disciplined evaluation of an organizational unit’s processes against a Process Assessment Model. [ ISO/IEC 15504 ]
Process Assessment Model
A model suitable for the purpose of assessing process capability, based on one or more process reference models. [ ISO/IEC 15504 ]
Process Capability
A characterization of the ability of a process to meet current or projected business goals. [ ISO/IEC 15504 ]
Process Capability Determination
A systematic assessment and analysis of selected processes within an organization against a target capability, carried out with the aim of identifying the strengths, weaknesses and risks associated with deploying the processes to meet a particular specified requirement. [ ISO/IEC 15504 ]
Process Capability Level
A point on the six-point ordinal scale (of process capability) that represents the capability of the process; each level builds on the capability of the level below. [ ISO/IEC 15504 ]
Process Context
The set of factors, documented in the assessment input, that influence the judgment, comprehension and comparability of process attribute ratings. [ ISO/IEC 15504 ]
Process Improvement
Actions taken to change an organization’s processes so that they more effectively and/or efficiently meet the organization’s business goals. [ ISO/IEC 15504 ]
Process Improvement Objective
Set of target characteristics established to guide the effort to improve an existing process in a specific, measurable way, either in terms of resultant product or service characteristics, such as quality, performance, and conformance to standards, or in the way in which the process is executed, such as elimination of redundant process steps, combination of process steps, and improvement of cycle time. [ ISO/IEC 15504 ]
Process Improvement Program
The strategies, policies, goals, responsibilities and activities concerned with the achievement of specified improvement goals. [ ISO/IEC 15504 ]
Notes
Process Improvement Project
A subset of the Process Improvement Program that forms a coherent set of actions to achieve a specific improvement. [ ISO/IEC 15504 ]
Process Metric
Process Outcome
An observable result of a process. [ ISO/IEC 15504 ]
Other Definitions
Process Outcome [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15288 ]: Observable result of the successful achievement of the process purpose.
Notes
Process Performance
The extent to which the execution of a process achieves its purpose. [ ISO/IEC 15504 ]
Process Purpose
High-level objective of performing the process and the likely outcomes of effective implementation of the process. [ ISO/IEC 15504, ISO/IEC 15288 ]
Notes
Product
An artifact that is produced, is quantifiable, and can be either an end item in itself or a component item. [ IEEE 1490 ]
Other Definitions
Product [ ISO/IEC 26514 ]: Complete set of software and documentation.
Product [ IEEE 1074 ]: Output of the software development activities (e.g., document, code, or model).
Product [ ISO/IEC 15939 ]: Result of a process.
Software Product [ ISO/IEC 9126, ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15939 ]: Set of computer programs, procedures, and associated documentation and data.
Notes
-
In ISO 9000 there are four agreed generic product categories:
-
* hardware (e.g., engine mechanical part);
-
* software (e.g., computer program);
-
* services (e.g., transport); and
-
* processed materials (e.g., lubricant).
:Hardware and processed materials are generally tangible products, while software or services are generally intangible. Most products comprise elements belonging to different generic product categories. Whether the product is then called hardware, processed material, software, or service depends on the dominant element. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Product Line
Group of products or services sharing a common, managed set of features that satisfy specific needs of a selected market or mission. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Product Metric
Productivity
The capability of the software product to enable users to expend appropriate amounts of resources in relation to the effectiveness achieved in a specified context of use. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Notes
See also
Programmer Manual
A document that provides the information necessary to develop or modify software for a given computer system. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Project
Endeavor with defined start and finish dates undertaken to create a product or service in accordance with specified resources and requirements. [ ISO/IEC 15288, ISO/IEC 15939 ]
Other Definitions
Project [ ISO/IEC 2382 ]: An undertaking with pre-specified objectives, magnitude and duration.
Project [ IEEE 1490 ]: A temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result.
Notes
Project Management
The application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet the project requirements. [ IEEE 1490 ]
Other Definitions
Project Management [ ISO/IEC 2382 ]: The activities concerned with project planning and project control.
Project Phase
A collection of logically related project activities, usually culminating in the completion of a major deliverable. [ IEEE 1490 ]
Notes
Prototype
Model or preliminary implementation of a piece of software suitable for the evaluation of system design, performance or production potential, or for the better understanding of the software requirements. [ ISO/IEC 15910 ]
Other Definitions
Prototype [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A preliminary type, form, or instance of a system that serves as a model for later stages or for the final, complete version of the system.
Notes
Qualification
Process of demonstrating whether an entity is capable of fulfilling specified requirements. [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15288 ]
Other Definitions
Qualification [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The process of determining whether a system or component is suitable for operational use.
Qualification Testing
Testing, conducted by the developer and witnessed by the acquirer (as appropriate), to demonstrate that a software product meets its specifications and is ready for use in its target environment or integration with its containing system. [ ISO/IEC 12207 ]
Other Definitions
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Quality
The totality of characteristics of an entity that bear on its ability to satisfy stated and implied needs. [ ISO 8402, ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Other Definitions
Quality [ IEEE 829 ]: The degree to which a system, component, or process meets specified requirements.
Quality [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Ability of a product,service, system, component, or process to meet customer or user needs, expectations, or requirements.
Quality [ IEEE 1490 ]: The degree to which a set of inherent characteristics fulfils requirements.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Quality Assurance
The planned and systematic activities implemented within the quality system, and demonstrated as needed, to provide adequate confidence that an entity will fulfil requirements for quality. [ ISO/IEC 12207 ]
Other Definitions
Quality Assurance [ IEEE 610.12, ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A planned and systematic pattern of all actions necessary to provide adequate confidence that an item or product conforms to established technical requirements.
Quality Assurance [ IEEE 610.12, ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A set of activities designed to evaluate the process by which products are developed or manufactured.
Quality Assurance [ ISO/IEC 15288 ]: Part of quality management focused on providing confidence that quality requirements will be fulfilled.
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Quality Control
A set of activities designed to evaluate the quality of developed or manufactured products. [ IEEE 610.12 ]
Notes
Quality Evaluation
Systematic examination of the extent to which an entity is capable of fulfilling specified requirements. [ ISO 8402, ISO/IEC 9126-1, ISO/IEC 14598 ]
Notes
Quality Factor
Quality Management
Coordinated activities to direct and control an organization with regard to quality. [ ISO/IEC 19759 ]
Quality Measure Element
Base measure or derived measure that is used for constructing software quality measures. [ ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Notes
Quality Metric
a quantitative measure of the degree to which an item possesses a given quality attribute. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Quality Metric [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A function whose inputs are software data and whose output is a single numerical value that can be interpreted as the degree to which the software possesses a given quality attribute.
Quality Model
Defined set of characteristics, and of relationships between them, which provides a framework for specifying quality requirements and evaluating quality. [ ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Other Definitions
Quality Model [ ISO/IEC 9126-1, ISO/IEC 14598-1 ]: The set of characteristics and the relationships between them which provide the basis for specifying quality requirements and evaluating quality.
Quality in Use
The capability of the software product to enable specified users to achieve specified goals with effectiveness, productivity, safety and satisfaction in specified contexts of use. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1, ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Rating
The action of mapping the measured value to the appropriate rating level. Used to determine the rating level associated with the software for a specific quality characteristic. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1, ISO/IEC 14598-1, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Rating Level
A scale point on an ordinal scale which is used to categorise a measurement scale. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1, ISO/IEC 14598, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Readability
The ease with which a system’s source code can be read and understood, especially at the detailed, statement level. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Recoverability
The capability of the software product to re-establish a specified level of performance and recover the data directly affected in the case of a failure. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Recovery
The restoration of a system, program, database, or other system resource to a state in which it can perform required functions. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Reengineering
The examination and alteration of software to reconstitute it in a new form, including the subsequent implementation of the new form. [ ISO/IEC 19759 ]
Regression Testing
Selective retesting of a system or component to verify that modifications have not caused unintended effects and that the system or component still complies with its specified requirements. [ ISO/IEC 90003 ]
Other Definitions
Regression Testing [ ISO/IEC 90003 ]: Testing required to determine that a change to a system component has not adversely affected functionality, reliability or performance and has not introduced additional defects.
Release
Collection of new and/or changed configuration items which are tested and introduced into the live environment together. [ ISO/IEC 20000 ]
Other Definitions
Release [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A software version that is made formally available to a wider community.
Release [ IEEE 829, ISO/IEC 12207 ]: Particular version of a configuration item that is made available for a specific purpose.
Release [ IEEE 829 ]: The formal notification and distribution of an approved version.
Notes
Reliability
The capability of the software product to maintain a specified level of performance in cases of software faults or of infringement of its specified interface. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Other Definitions
Reliability [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The ability of a system or component to perform its required functions under stated conditions for a specified period of time.
Software Reliability [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The probability[8] that software will not cause the failure of a system for a specified time under specified conditions.
Notes
Reliability Compliance
The capability of the software product to adhere to standards, conventions or regulations relating to reliability. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Repeatability of Results of Measurements
Closeness of the agreement between the results of successive measurements of the same measurand carried out under the same conditions of measurement. [ ISO/IEC 14143 ]
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Replaceability
The capability of the software product to be used in place of another specified software product for the same purpose in the same environment. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Reproducibility of Results of Measurements
Closeness of the agreement between the results of measurements of the same measurand carried out under changed conditions of measurement. [ ISO/IEC 14143 ]
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Request For Change
Form or screen used to record details of a request for a change to any configuration item within a service or infrastructure. [ ISO/IEC 20000 ]
Request For Information
A type of procurement document whereby the buyer requests a potential seller to provide various pieces of information related to a product or service or seller capability. [ IEEE 1490 ]
Request For Proposal
A document used by the acquirer as a means to announce intention to potential bidders to acquire a specified system, product, or service. [ ISO/IEC 15288 ]
Other Definitions
Request for Proposal [ IEEE 1362 ]: A request for services, research, or a product prepared by a customer and delivered to prospective developers with the expectation that prospective developers will respond with their proposed cost, schedule, and development approach.
Request for Proposal [ IEEE 1490 ]: A type of procurement document used to request proposals from prospective sellers of products or services. In some application areas, it may have a narrower or more specific meaning.
Request for Proposal [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A collection of formal documents that includes a description of the desired form of response from a potential supplier, the relevant statement of work for the supplier, and required provisions in the supplier agreement.
Requirement
A condition or capability that must be met or possessed by a system, system component, product, or service to satisfy an agreement, standard, specification, or other formally imposed documents. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Requirement [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A condition or capability needed by a user to solve a problem or achieve an objective.
Requirement [ IEEE 1490 ]: A condition or capability that must be met or possessed by a system, product, service, result, or component to satisfy a contract, standard, specification, or other formally imposed document. Requirements include the quantified and documented needs, wants, and expectations of the sponsor, customer, and other stakeholders.
Software Requirement [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A software capability needed by a user to solve a problem to achieve an objective.
Software Requirement [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A software capability that must be met or possessed by a system or system component to satisfy a contract, standard, specification, or other formally imposed document.
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Requirements Analysis
The process of studying user needs to arrive at a definition of system, hardware, or software requirements. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Requirements Analysis [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The process of studying and refining system, hardware, or software requirements.
Requirements Analysis [ ISO/IEC 2382 ]: A systematic investigation of user requirements to arrive at a definition of a system.
Requirements Analysis [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Determination of product- or service-specific performance and functional characteristics based on analyses of customer needs, expectations, and constraints; operational concept; projected utilization environments for people, products, services, and processes; and measures of effectiveness
Requirements Derivation
The changing or translation of a requirement through analysis into a form that is suitable for low-level analysis or design. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Requirements Document
Document containing any combination of requirements or regulations to be met by a COTS software product. [ ISO/IEC 25051 ]
Example
Requirements Engineering
The science and discipline concerned with analyzing and documenting requirements. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Requirements Partitioning
The separation or decomposing of a top-level requirement or design into successively lower-level detailed requirements or design. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Requirements Review
A process or meeting during which the requirements for a system, hardware item, or software item are presented to project personnel, managers, users, customers, or other interested parties for comment or approval. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Requirements Specification
A document that specifies the requirements for a system or component. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Requirements Traceability
Discernible association between a requirement and related requirements, implementations, and verifications. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Requirements Traceability [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: the identification and documentation of the derivation path (upward) and allocation/ flow-down path
(downward) of requirements in the requirements hierarchy.
Requirements Traceability Matrix
A table that links requirements to their origin and traces them throughout the project life cycle. [ IEEE 1490 ]
Resource
Skilled human resources (specific disciplines either individually or in crews or teams), equipment, services, supplies, commodities, materiel, budgets, or funds. [ IEEE 1490 ]
Other Definitions
Resource [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15288 ]: Asset that is utilized or consumed during the execution of a process.
Resource [ ISO/IEC 15414 ]: A role (with respect to that action) in which the enterprise object fulfilling the role is essential to the action, requires allocation, or may become unavailable.
Resource [ ISO/IEC 15414 ]: An enterprise object which is essential to some behavior and which requires allocation or may become unavailable.
Example
Notes
Resource Utilisation
The capability of the software product to use appropriate amounts and types of resources when the software performs its function under stated conditions. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Notes
See also
Result
An output from performing project management processes and activities. Results include outcomes (e.g., integrated systems, revised process, restructured organization, tests, trained personnel, etc.) and documents (e.g., policies, plans, studies, procedures, specifications, reports, etc.). [ IEEE 1490 ]
Notes
Retirement
Withdrawal of active support by the operation and maintenance organization, partial or total replacement by a new system, or installation of an upgraded system. [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15288 ]
Other Definitions
Retirement [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Removal of support from an operational system or component.
Retirement [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Permanent removal of a system or component from its operational environment.
Reverse Engineering
Determining what existing software will do and how it is constructed (to make intelligent changes). [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Reverse Engineering [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Software engineering approach that derives a system’s design or requirements from its code.
Risk
An uncertain event or condition that, if it occurs, has a positive or negative effect on a project’s objectives. [ IEEE 1490 ]
Other Definitions
Risk [ IEEE 829 ]: The combination of the probability of an abnormal event or failure and the consequence(s) of that event or failure to a system’s components, operators, users, or environment.
Risk [ ISO/IEC 15026 ]: A function of the probability of occurrence of a given threat and the potential adverse consequences of that threat’s occurrence.
Risk [ IEEE 829 ]: The combination of the probability of occurrence and the consequences of a given future undesirable event.
Notes
Risk Acceptance
Acknowledgment of a risk factor’s existence along with a decision to accept the consequences if the corresponding problem occurs. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Risk Acceptance [ IEEE 1490 ]: A risk response planning technique that indicates that the project team has decided not to change the project management plan to deal with a risk, or is unable to identify any other suitable response strategy.
Notes
Risk Analysis
The process of examining identified risk factors for probability of occurrence, potential loss, and potential risk-handling strategies. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Robustness
The degree to which a system or component can function correctly in the presence of invalid inputs or stressful environmental conditions. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Routine
A subprogram that is called by other programs and subprograms. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Risk [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A function or procedure invocable for a single purpose.
Risk [ ISO/IEC 2382 ]: A program, or part of a program, that may have some general or frequent use.
Notes
Run
In software engineering, a single, usually continuous, execution of a computer program. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Safety
The capability of the software product to achieve acceptable levels of risk of harm to people, business, software, property or the environment in a specified context of use. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Other Definitions
Safety [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765, ISO/IEC 15026 ]: The expectation that a system does not, under defined conditions, lead to a state in which human life, health, property, or the environment is endangered.
Satisfaction
The capability of the software product to satisfy users in a specified context of use. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Notes
See also
Scale
Ordered set of values, continuous or discrete, or a set of categories to which the attribute is mapped. [ ISO/IEC 99, ISO/IEC 15939, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Other Definitions
Scale [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A set of values with defined properties.
Notes
-
The type of scale depends on the nature of the relationship between values on the scale. Four types of scales are commonly defined:
:; Nominal: The measurement values are categorical. For example, the classification of defects by their type does not imply order among the categories.
:; Ordinal: The measurement values are rankings. For example, the assignment of defects to a severity level is a ranking.
:; Interval: The measurement values have equal distances corresponding to equal quantities of the attribute. For example, cyclomatic complexity has the minimum value of one, but each increment represents an additional path. The value of zero is not possible.
:; Ratio: The measurement values have equal distances corresponding to equal quantities of the attribute where the value of zero corresponds to none of the attribute. For example, the size of a software component in terms of LOC is a ratio scale because the value of zero corresponds to no lines of code and each additional increments represents equal amounts of code.
: These are just examples of the types of scales. Roberts[9] defines more types of scales. [ ISO/IEC 15939 ]
Example
Security
The capability of the software product to protect information and data so that unauthorised persons or systems cannot read or modify them and authorised persons or systems are not denied access to them. [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Other Definitions
Security [ ISO/IEC 15026 ]: The protection of system items from accidental or malicious access, use, modification, destruction, or disclosure.
Security [ ISO/IEC 15288 ]: All aspects related to defining, achieving, and maintaining confidentiality, integrity, availability, non-repudiation, accountability, authenticity, and reliability of a system.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Service
Performance of activities, work, or duties associated with a product. [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15939 ]
Other Definitions
Software Service [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15939 ]: Performance of activities, work, or duties connected with a software product, such as its development, maintenance, and operation.
Service Level Agreement
Written agreement between a service provider and a customer that documents services and agreed service levels. [ ISO/IEC 20000 ]
Simplicity
The degree to which a system or component has a design and implementation that is straightforward and easy to understand. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Simplicity [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Software attributes that provide implementation of functions in the most understandable manner.
Software
All or part of the programs, procedures, rules, and associated documentation of an information processing system. [ ISO/IEC 2382, ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Other Definitions
Software [ IEEE 829 ]: Computer programs, procedures, and possibly associated documentation and data pertaining to the operation of a computer system.
Software [ ISO/IEC 26514 ]: Program or set of programs used to run a computer.
Example
Software Asset Management
Effective management, control and protection of software assets within an organization. [ ISO/IEC 19770 ]
Software Development Process
The process by which user needs are translated into a software product. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Software Engineering
The systematic application of scientific and technological knowledge, methods, and experience to the design, implementation, testing, and documentation of software. [ ISO/IEC 2382 ]
Other Definitions
Software Engineering [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: the application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of software; that is, the application of engineering to software.
Software Item
Identifiable part of a software product. [ ISO/IEC 90003 ]
Other Definitions
Software Item [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: An aggregation of software, such as a computer program or database, that satisfies an end use function and is designated for specification, qualification testing, interfacing, configuration management, or other purposes.
Software Item [ ISO/IEC 12207 ]: Source code, object code, control code, control data, or a collection of these items.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Software Life Cycle
The period of time that begins when a software product is conceived and ends when the software is no longer available for use. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Software Life Cycle [ IEEE 1074 ]: The project-specific sequence of activities that is created by mapping the activities of this standard onto a
selected software life cycle model (SLCM).
Software Life Cycle [ IEEE 1362 ]: The system or product cycle initiated by a user need or a perceived customer need and terminated by discontinued use of the product.
Software Product Evaluation
Technical operation that consists of producing an assessment of one or more characteristics of a software product according to a specified procedure. [ ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Notes
Software Quality
Capability of a software product to satisfy stated and implied needs when used under specified conditions. [ ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Software Quality Characteristic
Category of software quality attributes that bears on software quality. [ ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Notes
Software Quality Evaluation
Systematic examination of the extent to which a software product is capable of satisfying stated and implied needs. [ ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Software Quality Measure
Measure of internal software quality, external software quality or software quality in use. IEEE 1490 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Software Repository
A software library providing permanent, archival storage for software and related documentation. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Software Unit
Separately compilable piece of code. [ ISO/IEC 12207 ]
Other Definitions
Software Unit [ ISO/IEC 12207 ]: The lowest element in one or more software components.
Source Code
Computer instructions and data definitions expressed in a form suitable for input to an assembler, compiler, or other translator. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Specification
A document that specifies, in a complete, precise, verifiable manner, the requirements, design, behavior, or other characteristics of a system, component, product, result, or service and, often, the procedures for determining whether these provisions have been satisfied. [ IEEE 1490 ]
Other Definitions
Specification [ ISO/IEC 2382 ]: A detailed formulation, in document form, which provides a definitive description of a system for the purpose of developing or validating the system.
Specification [ IEEE 1220 ]: A document that fully describes a design element or its interfaces in terms of requirements (functional, performance, constraints, and design characteristics) and the qualification conditions and procedures for each requirement.
Stability
The capability of the software product to avoid unexpected effects from modifications of the software. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
See also
Stage
Period within the life cycle of an entity that relates to the state of its description or realization. [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15288 ]
Notes
-
Stages relate to major progress and achievement milestones of the system through its life cycle. Stages may
be overlapping. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Stakeholder
Individual or organisation that sponsors measurement, provides data, is a user of the measurement results or otherwise participates in the measurement process. [ ISO/IEC 15939 ]
Other Definitions
Stakeholder [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15288, ISO/IEC 15939 ]: Individual or organization having a right, share, claim, or interest in a system or in its possession of characteristics that meet their needs and expectations.
Stakeholder [ IEEE 1490 ]: Person or organization (e.g. customer, sponsor, performing organization, or the public) that is actively involved in the project, or whose
interests may be positively or negatively affected by execution or completion of the project. A stakeholder may also exert influence over the project and its deliverables.
Examples
Notes
Standard
Set of mandatory requirements established by consensus and maintained by a recognized body to prescribe a disciplined uniform approach or specify a product, that is, mandatory conventions and practices. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Standard [ IEEE 1490 ]: A document that provides, for common and repeated use, rules, guidelines or characteristics for activities or their results, aimed at the achievement of the optimum degree of order in a given context.
Standard Process
The set of definitions of the basic processes that guide all processes in an organization. [ ISO/IEC 15504 ]
Notes
Statement
In a programming language, a meaningful expression that defines data, specifies program actions, or directs the assembler or compiler. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Statement Testing
Testing designed to execute each statement of a computer program. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Statement of Work
Document used by the acquirer to describe and specify the tasks to be performed under the contract. [ ISO/IEC 12207 ]
Other Definitions
Statement of Work [ IEEE 1490 ]: A narrative description of products, services, or results to be supplied.
Static Analysis
The process of evaluating a system or component based on its form, structure, content, or documentation. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Statistical Process Control
Statistically based analysis of a process and measures of process performance, which identify common and special causes of variation in process performance and maintain process performance within limits. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Statistical Process Control is an effective method of monitoring a process through the use of control charts.
In general, if a process exceeds the limits, we assume that it’s out of control and the project team should search for special causes to deal with it.
There are many kinds of charts, such as the 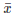 chart and r-chart, etc.
chart and r-chart, etc.
The c-chart
The c-chart plots the number of defects in a process.
If 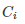 denotes the number of defects obtained in the ith observation, the c-chart plots the data points at the height
denotes the number of defects obtained in the ith observation, the c-chart plots the data points at the height 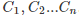 . The c-chart also has a center line (CL) at height
. The c-chart also has a center line (CL) at height 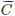 (the average of
(the average of 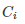 and the following 3σ lines:
and the following 3σ lines:
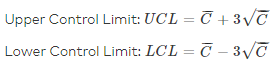
If LCL is negative, it is set to zero. The c-chart assumes the Poisson distribution of defects and is thus approximative.
Use of SPC in software engineering is still under debate. One major issue is that formal SPC requires data to be independent variables from homogeneous sources of variation. As exposed in Software Engineering Metrics: What Do They Measure And How Do We Know, software engineering data is often affected by many variations sources. Furthermore, software engineering is domain-specific (requirements may vary from one domain to another) and limits may vary.
See also
Glossary:
Papers:
Standards:
Step
One element (numbered list item) in a procedure that tells a user to perform an action (or actions). [ ISO/IEC 26514 ]
Other Definitions
Step [ ISO/IEC 15414 ]: An abstraction of an action, used in a process, that may leave unspecified objects that participate in that action.
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Stress Testing
Testing conducted to evaluate a system or component at or beyond the limits of its specified requirements. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Structural Testing
Testing that takes into account the internal mechanism of a system or component. Syn: glass-box testing, white-box testing. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Notes
Stub
A skeletal or special-purpose implementation of a software module, used to develop or test a module that calls or is otherwise dependent on it. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Stub [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A computer program statement substituting for the body of a software module that is or will be defined elsewhere.
Stub [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Scaffolding code written for the purpose of exercising higher-level code before the lower-level routines that will ultimately be used are available.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Suitability
The capability of the software product to provide an appropriate set of functions for specified tasks and user objectives. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Supplier
Organisation that enters into an agreement with the acquirer for the supply of a system, software product or software service under the terms of that agreement. [ ISO/IEC 9126, ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15939 ]
Support
The set of activities necessary to ensure that an operational system or component fulfills its original requirements and any subsequent modifications to those requirements. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Software Support [ ISO 9127 ]: The act of maintaining the software and its associated documentation in a functional state.
Examples
Notes
Support Manual
A document that provides the information necessary to service and maintain an operational system or component throughout its life cycle. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
System
Integrated composite that consists of one or more of the processes, hardware, software, facilities and people, that provides a capability to satisfy a stated need or objective. [ ISO/IEC 9126, ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15939 ]
Other Definitions
Software System [ IEEE 1362 ]: A software-intensive system for which software is the only component to be developed or modified.
System Testing
Task
The activities required to achieve a goal. [ ISO/IEC 9126 ]
Other Definitions
Task [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15288 ]: Required, recommended, or permissible action, intended to contribute to the achievement of one or more outcomes of a process.
Task [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: In software design, a [[Software Component|software component that can operate in parallel with other software components.
Task [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A concurrent object with its own thread of control.
Task [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A sequence of instructions treated as a basic unit of work by the supervisory program of an operating system.
Task [ IEEE 829 ]: Smallest unit of work subject to management accountability; a well-defined work assignment for one or more project members.
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Technical Requirement
Requirements relating to the technology and environment, for the development, maintenance, support and execution of the software. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Examples
Technique
Methods and skills required to carry out a specific activity. [ ISO/IEC 25001, ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15939 ]
Other Definitions
Technique [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Technical or managerial procedure that aids in the evaluation and improvement of the software development process.
Test
An activity in which a system or component is executed under specified conditions, the results are observed or recorded, and an evaluation is made of some aspect of the system or component. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Test [ IEEE 829 ]: A set of one or more test cases and procedures.
Test Case
A set of inputs, execution preconditions, and expected outcomes developed for a particular objective to exercise a particular program path or to verify compliance with a specific requirement. [ IEEE 1012, SIGIST ]
Other Definitions
Test Case [ IEEE 610.12 ]: A documented instruction for the tester that specifies how a function or a combination of functions shall or should be tested. A test case includes detailed information on the following issues:
-
the test objective;
-
the functions to be tested;
-
the testing environment and other conditions;
-
the test data;
-
the procedure;
-
the expected behaviour of the system.
Test Case Suite
A collection of one or more test cases for the software under test. [ SIGIST ]
See also
Test Coverage
Extent to which the test cases test the requirements for the system or software product. [ ISO/IEC 12207 ]
Other Definitions
Test Coverage [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The degree to which a given test or set of tests addresses all specified requirements for a given system or component.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Test Documentation
Collection of the documentation inherent to the testing activities. [ ISO/IEC 25051 ]
Other Definitions
Test Documentation [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Documentation describing plans for, or results of, the testing of a system or component.
Test Environment
Hardware and software configuration necessary to conduct the test case. [ ISO/IEC 25051 ]
Test Objective
Identified set of software features to be measured under specified conditions by comparing actual behavior with the required behavior. [ ISO/IEC 25051, ISO/IEC 25062 ]
Test Plan
A document describing the scope, approach, resources, and schedule of intended test activities. [ IEEE 1012, ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15939 ]
Other Definitions
Test Plan [ IEEE 1012 ]: A document that describes the technical and management approach to be followed for testing a system or component.
Test Plan [ ISO/IEC 2382 ]: A plan that establishes detailed requirements, criteria, general methodology, responsibilities, and general planning for test and evaluation of a system.
Notes
Test Procedure
Detailed instructions for the setup, execution, and evaluation of results for a given test case. [ IEEE 1012 ]
Other Definitions
Test Procedure [ IEEE 1012 ]: Documentation that specifies a sequence of actions for the execution of a test.
Testability
The capability of the software product to enable modified software to be validated. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Other Definitions
Testability [ ISO/IEC 12207 ]: Extent to which an objective and feasible test can be designed to determine whether a requirement is met.
Testability [ IEEE 1233 ]: The degree to which a requirement is stated in terms that permit establishment of test criteria and performance of tests to determine whether those criteria have been met.
Testability [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]:
-
The degree to which a system can be unit tested and system tested.
-
The effort required to test software.
-
The degree to which a system or component facilitates the establishment of test criteria and the performance of tests to determine whether those criteria have been met.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Testing
Activity in which a system or component is executed under specified conditions, the results are observed or recorded, and an evaluation is made of some aspect of the system or component. [ IEEE 829 ]
Other Definitions
Software Testing [ ISO/IEC 19759 ]: The dynamic verification of the behavior of a program on a finite set of test cases, suitably selected from the usually infinite executions domain, against the expected behavior.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Testing Description
Description of the test execution conditions (i.e. test procedure). [ ISO/IEC 25051, ISO/IEC 25062 ]
Time Behaviour
The capability of the software product to provide appropriate response and processing times and throughput rates when performing its function, under stated conditions. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
See also
Tool
A software product that provides support for software and system life cycle processes. [ ISO/IEC 15474 ]
Other Definitions
Tool [ IEEE 1490 ]: Something tangible, such as a template or software program, used in performing an activity to produce a product or result.
Notes
Total Quality Management
A holistic approach to quality improvement in all life-cycle phases. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Traceability
The degree to which a relationship can be established between two or more products of the development process, especially products having a predecessor-successor or master-subordinate relationship to one another. [ IEEE 1233 ]
Other Definitions
Traceability [ IEEE 1362 ]: The identification and documentation of derivation paths (upward) and allocation or flowdown paths (downward) of work products in the work product hierarchy.
Traceability [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The degree to which each element in a software development product establishes its reason for existing.
Traceability [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Discernible association among two or more logical entities, such as requirements, system elements, verifications, or tasks.
Traceable
Having components whose origin can be determined. [ ISO/IEC 12207 ]
Trunk
The software’s main line of development; the main starting point of most branches. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Understandability
The capability of the software product to enable the user to understand whether the software is suitable, and how it can be used for particular tasks and conditions of use. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Other Definitions
Understandability [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The ease with which a system can be comprehended at both the system-organizational and detailed-statement levels.
Unit Test
Testing of individual routines and modules by the developer or an independent tester. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
Unit Test [ ISO/IEC 2382 ]: A test of individual programs or modules in order to ensure that there are no analysis or programming errors.
Unit Test [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: A test of individual hardware or software units or groups of related units.
Unit of Measurement
Particular quantity, defined and adopted by convention, with which other quantities of the same kind are compared in order to express their magnitude relative to that quantity. [ ISO/IEC 99, ISO/IEC 15939, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Notes
Usability
The capability of the software product to be understood, learned, used and attractive to the user, when used under specified conditions. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
Other Definitions
Usability [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: The ease with which a user can learn to operate, prepare inputs for, and interpret outputs of a system or component.
Usability [ ISO/IEC 25062 ]: The extent to which a product can be used by specified users to achieve specified goals with effectiveness, efficiency and satisfaction in a specified context of use.
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Usability Compliance
The capability of the software product to adhere to standards, conventions, style guides or regulations relating to usability. [ ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]
See also
User
Individual or organisation that uses the system to perform a specific function. [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15939 ]
Other Definitions
User [ ISO/IEC 9126 ]: An individual that uses the software product to perform a specific function.
User [ ISO/IEC 26514 ]: Person who performs one or more tasks with software; a member of a specific audience.
User [ ISO/IEC 25062 ]: Person who interacts with the product.
User [ IEEE 1362 ]: Individual or organization who uses a software-intensive system in daily work activities or recreational pursuits.
User [ ISO/IEC 15288, ISO/IEC 15939 ]: Individual or group that benefits from a system during its utilization.
User [ ISO/IEC 14143, ISO/IEC 29881 ]: Any person or thing that communicates or interacts with the software at any time.
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
User Documentation
Documentation for users of a system, including a system description and procedures for using the system to obtain desired results. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
User Documentation [ ISO/IEC 26514 ]: Information to describe, explain, or instruct how to use software.
User Manual
A document that presents the information necessary to employ a system or component to obtain desired results. [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]
Other Definitions
User Manual [ ISO/IEC 2382 ]: A document that describes how to use a functional unit, and that may include description of the rights and responsibilities of the user, the owner, and the supplier of the unit.
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Validation
Determination of the correctness of the products of software development with respect to the user needs and requirements. [ SIGIST ]
Other Definitions
Validation [ ISO 8402, ISO/IEC 9126-1 ]: Confirmation by examination and provision of objective evidence that the particular requirements for a specific intended use are fulfilled.
Validation [ ISO/IEC 15288 ]: Confirmation, through the provision of objective evidence, that the requirements for a specific intended use or application have been fulfilled.
Validation [ IEEE 1012 ]: The process of providing evidence that the software and its associated products satisfy system requirements allocated to software at the end of each life cycle activity, solve the right problem, and satisfy intended use and user needs.
Validation [ ISO/IEC 12207 ]: In a life cycle context, the set of activities ensuring and gaining confidence that a system is able to accomplish its intended use, goals and objectives.
Validation [ IEEE 1233 ]: The process of evaluating a system or component during or at the end of the development process to determine whether a system or component satisfies specified requirements.
Validation [ IEEE 1490 ]: The assurance that a product, service, or system meets the needs of the customer and other identified stakeholders. It often involves acceptance and suitability with external customers.
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Value
Number or category assigned to an attribute of an entity by making a measurement. [ ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Other Definitions
Value [ ISO/IEC 15939 ]: Numerical or categorical result assigned to a base measure, derived measure, or indicator. [ ISO/IEC 15939 ]
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Verification
Confirmation, through the provision of objective evidence, that specified requirements have been fulfilled. [ ISO/IEC 12207, ISO/IEC 15288, ISO/IEC 25000 ]
Other Definitions
Verification [ IEEE 1012, SIGIST ]: The process of evaluating a system or component to determine whether the products of a given development phase satisfy the conditions imposed at the start of that phase.
Verification [ ISO 8402, ISO/IEC 9126 ]: Confirmation by examination and provision of objective evidence that specified requirements have been fulfilled.
Verification [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: Formal proof of program correctness.
Verification [ IEEE 1490 ]: The evaluation of whether or not a product, service, or system complies with a regulation, requirement, specification, or imposed condition. It is often an internal process.
Verification [ IEEE 829 ]: Process of providing objective evidence that the software and its associated products comply with requirements (e.g., for correctness, completeness, consistency, and accuracy) for all life cycle activities during each life cycle process (acquisition, supply, development, operation, and maintenance), satisfy standards, practices, and conventions during life cycle processes, and successfully complete each life cycle activity and satisfy all the criteria for initiating succeeding life cycle activities (e.g., building the software correctly).
Notes
See also
Glossary:
Standards:
Version
Identified instance of an item. [ ISO/IEC 12207 ]
Other Definitions
Version [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: An initial release or re- release of a computer software configuration item, associated with a complete compilation or recompilation of the computer software configuration item.
Version [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: An initial release or complete re- release of a document, as opposed to a revision resulting from issuing change pages to a previous release.
Version [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: An operational software product that differs from similar products in terms of capability, environmental requirements, and configuration.
Version [ ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765 ]: An identifiable instance of a specific file or release of a complete system.
Notes
Work Breakdown Structure
A deliverable-oriented hierarchical decomposition of the work to be executed by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables. It organizes and defines the total scope of the project. [ IEEE 1490 ]
Work Product
An artifact associated with the execution of a process. [ ISO/IEC 15504 ]
Other Definitions
Work Product [ IEEE 1058 ]: A tangible item produced during the process of developing or modifying software.
7. Standards
CMMi
CMMi stands for Capability Maturity Model Integration.
CMMi is a process developed by the Carnegie Mellon Software Engineering Institute.
Structure
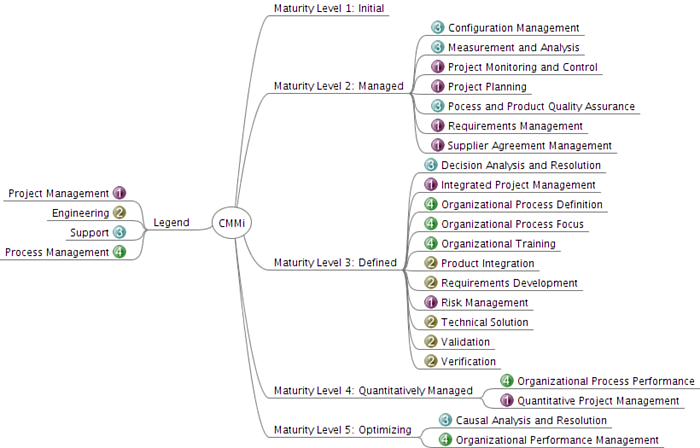
DOD-STD-2167A
Military Standard - Defense System Software Development
DOD-STD-2167A.
IEC 61508
International Standard IEC 61508
Functional safety of electrical / electronic / programmable electronic safety related systems
Year: 1998, 2000, 2002, 2010
Contents
Part 1: General requirements
Part 2: Requirements for electrical/electronic/programmable electronic safety-related systems
Part 4: Definitions and abbreviations
Part 5: Examples of methods for the determination of safety integrity levels
Part 6: Guidelines on the application of IEC 61508-2 and IEC 61508-3
See also
IEC 61508-3
International Standard IEC 61508-3
Functional safety of electrical / electronic / programmable electronic safety related systems
Part 3: Software requirements
Year: 1998
See also
IEC 61508-7
International Standard IEC 61508-7
Functional safety of electrical / electronic / programmable electronic safety related systems
Part 7: Overview on techniques and measures
Year: 2000
See also
IEEE 1012
International Standard IEEE 1012
IEEE Standard for Software Verification and Validation
Year: 1986
This standard has been superseded.
Access
Online IEEE Catalog: http://standards.ieee.org/findstds/standard/1012-1998.html
IEEE 1058
International Standard IEEE 1058
IEEE Standard for Software Project Management Plans
Year: 1998
Access
Online IEEE Catalog: http://standards.ieee.org/findstds/standard/1058-1998.html
IEEE 1061
International Standard IEEE 1061
Standard for a Software Quality Metrics Methodology
Year: 1998
Access
Online IEEE Catalog: http://standards.ieee.org/findstds/standard/1061-1998.html
IEEE 1074
International Standard IEEE 1074
IEEE Standard for Developing Software Life Cycle Processes
Year: 1997
This standard has been superseded.
Access
Online IEEE Catalog: http://standards.ieee.org/findstds/standard/1074-1997.html
IEEE 1220
International Standard IEEE 1220-2005
1220-2005 - IEEE Standard for Application and Management of the Systems Engineering Process
Year: 2005
Access
Online IEEE Catalog: http://standards.ieee.org/findstds/standard/1220-2005.html
IEEE 1233
International Standard IEEE 1233
IEEE Guide for Developing System Requirements Specifications
Year: 1996
Access
Online IEEE Catalog: http://standards.ieee.org/findstds/standard/1233-1996.html
IEEE 1320
International Standard IEEE 1320.2
IEEE Standard for Conceptual Modeling Language - Syntax and Semantics for IDEF1X97 (IDEFobject)
Years: 1998
IEEE 1362
International Standard IEEE 1362
IEEE Guide for Information Technology - System Definition - Concept of Operations (ConOps) Document
Year: 1998
Access
Online IEEE Catalog: http://standards.ieee.org/findstds/standard/1362-1998.html
IEEE 1490
International Standard IEEE 1490
IEEE Guide Adoption of PMI Standard - A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge
Year: 2003
This standard has been withdrawn.
Access
Online IEEE Catalog: http://standards.ieee.org/findstds/standard/1490-2003.html
IEEE 610.12
International Standard IEEE 610.12
Standard Glossary of Software Engineering Terminology
Year: 1990
Access
Online IEEE Catalog: http://standards.ieee.org/findstds/standard/610.12-1990.html
IEEE 829
International Standard IEEE 829
IEEE Standard for Software Test Documentation
Year: 1983.
This standard has been superseded.
IEEE 830
International Standard IEEE 830
IEEE Recommended Practice for Software Requirements Specifications
Year: 1998.
IEEE 982
International Standard IEEE 982
IEEE Standard Dictionary of Measures to Produce Reliable Software
Year: 1988.
ISO 5806
International Standard ISO 5806
Information processing — Specification of single-hit decision tables
Year: 1984
Access
ISO 9001
International Standard ISO 9001.
Quality systems - Model for quality assurance in design, development, production, installation and servicing
Year: 1994, 2000, 2008.
Access
ISO 9127
International Standard ISO 9127
Information processing systems — User documentation and cover information for consumer software packages
Year: 1988.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
ISO 9241
International Standard ISO 9241
Ergonomic requirements for office work with visual display terminals (VDTs)
Years: 1992-2011.
Contents / Access
The following parts link to the online ISO catalog:
-
Part 100: Introduction to standards related to software ergonomics
-
Part 300: Introduction to electronic visual display requirements
-
Part 304: User performance test methods for electronic visual displays
-
Part 305: Optical laboratory test methods for electronic visual displays
-
Part 306: Field assessment methods for electronic visual displays
-
Part 307: Analysis and compliance test methods for electronic visual displays
-
Part 308: Surface-conduction electron-emitter displays (SED)
-
Part 310: Visibility, aesthetics and ergonomics of pixel defects
-
Part 400: Principles and requirements for physical input devices
See also
ISO 9241-10
International Standard ISO 9241-10
Ergonomic requirements for office work with visual display terminals (VDTs)
Part 10: Dialogue principles
Year: 1996.
This standard is withdrawn, and revised by ISO 9241-110:2006
Access
See also
ISO 9241-11
International Standard ISO 9241-11
Ergonomic requirements for office work with visual display terminals (VDTs)
Part 11: Guidance on usability
Year: 1998.
Contents
Extract from www.ansi.org:
ISO 9241-11 defines usability and explains how to identify the information which is necessary to take into account when specifying or evaluating usability of a visual display terminal in terms of measures of user performance and satisfaction. Guidance is given on how to describe the context of use of the product (hardware, software or service) and the relevant measures of usability in an explicit way. The guidance is given in the form of general principles and techniques, rather than in the form of requirements to use specific methods.
The guidance in ISO 9241-11 can be used in procurement, design, development, evaluation, and communication of information about usability. ISO 9241-11 includes guidance on how the usability of a product can be specified and evaluated. It applies both to products intended for general application and products being acquired for or being developed within a specific organization.
ISO 9241-11 also explains how measures of user performance and satisfaction can be used to measure how any component of a work system affects the whole work system in use. The guidance includes procedures for measuring usability but does not detail all the activities to be undertaken. Specification of detailed user-based methods of measurement is beyond the scope of ISO 9241-11, but further information can be found in Annex B and the bibliography in Annex E.
ISO 9241-11 applies to office work with visual display terminals. It can also apply in other situations where a user is interacting with a product to achieve goals. ISO 9241 parts 12 to 17 provide conditional recommendations which are applicable in specific contexts of use. The guidance in this Part of ISO 9241 can be used in conjunction with ISO 9241 Parts 12 to 17 in order to help identify the applicability of individual recommendations.
ISO 9241-11 focuses on usability and does not provide comprehensive coverage of all objectives of ergonomic design referred to in ISO 6385. However, design for usability will contribute positively to ergonomic objectives, such as the reduction of possible adverse effects of use on human health, safety and performance.
ISO 9241-11 does not cover the processes of system development. Human-centred design processes for interactive systems are described in ISO 13407.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
See also
ISO/IEC 12119
Information technology - Software packages - Quality requirements and testing
Year: 1994
ISO/IEC 12207
International Standard ISO/IEC 12207
Information technology — Software lifecycle processes
Year: 1995, 2008.
Access
Online ISO/IEC Catalog: http://www.iso.org/iso/catalogue_detail.htm?csnumber=43447
ISO/IEC 14143
International Standard ISO/IEC 14143
Information technology — Software measurement — Functional size measurement
Contents
-
Part 1: Definition of concepts
-
Part 2: Conformity evaluation of software size measurement methods to ISO/IEC 14143-1:1998
-
-
Part 3: Verification of functional size measurement methods
-
Part 4: Reference model
-
Part 5: Determination of functional domains for use with functional size measurement
-
Part 6: Guide for use of ISO/IEC 14143 series and related International Standards
-
ISO/IEC 14143-1
International Standard ISO/IEC 14143-1
Information technology — Software measurement — Functional size measurement
Part 1: Definition of concepts
Years: 1998, 2007.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
ISO/IEC 14143-3
International Standard ISO/IEC 14143-1
Information technology — Software measurement — Functional size measurement
Part 3: Verification of functional size measurement methods
Year: 2003.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
ISO/IEC 14598
International Standard ISO/IEC 14598.
Information technology — Software product evaluation
Contents / Access
Online ISO/IEC catalog:
ISO/IEC 14598-1
International Standard ISO/IEC 14598-1
Information technology - Software product evaluation
Part 1: General overview
Year: 1999
This standard is revised by the ISO/IEC 25040:2011 standard.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
ISO/IEC 14598-2
International Standard ISO/IEC 14598-2
Information technology - Software product evaluation
Part 2: Planning and management
Year: 2000.
This standard is revised by the ISO/IEC 25001:2007 standard.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
ISO/IEC 14598-3
International Standard ISO/IEC 14598-3
Information technology - Software product evaluation
Part 3: Process for developers
Year: 2000.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
ISO/IEC 14598-4
International Standard ISO/IEC 14598-4
Information technology - Software product evaluation
Part 4: Process for acquirers
Year: 1999.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
ISO/IEC 14598-5
International Standard ISO/IEC 14598-5
Information technology - Software product evaluation
Part 5: Process for evaluators
Year: 1998
Access
Online ISO catalog:
ISO/IEC 14598-6
International Standard ISO/IEC 14598-6
Information technology - Software product evaluation
Part 6: Documentation of evaluation modules
Year: 2001.
This standard is revised by the ISO/IEC DIS 25041 standard.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
ISO/IEC 14756
International Standard ISO/IEC 14756
Information technology — Measurement and rating of performance of computer-based software systems
Year: 1999
Access
ISO/IEC 14764
International Standard ISO/IEC 14764
Software Engineering — Software Life Cycle Processes — Maintenance
Years: 1999, 2006.
Access
Online IEEE Catalog:
ISO/IEC 15026
International Standard ISO/IEC 15026
Information technology — System and software integrity levels
Year: 1998, 2010, 2011.
See also
ISO/IEC 15026-1
International Standard ISO/IEC 15026-1
Systems and software engineering — Systems and software assurance — Part 1: Concepts and vocabulary
Year: 2010.
See also
ISO/IEC 15026-2
International Standard ISO/IEC 15026-2
Systems and software engineering — Systems and software assurance — Part 2: Assurance case
Year: 2011.
See also
ISO/IEC 15288
International Standard ISO/IEC 15288.
Systems and software engineering — System life cycle processes
Years: 2002.
ISO/IEC 15289
International Standard ISO/IEC 15289.
Systems and software engineering — Content of systems and software life cycle process information products (Documentation)
Year: 2006.
This standard is revised by the ISO/IEC/IEEE 15289 standard.
ISO/IEC 15414
International Standard ISO/IEC 15414
Information technology — Open distributed processing — Reference model — Enterprise language
Years: 2002, 2006.
Access
ISO/IEC 15474
International Standard ISO/IEC 15474
Information technology — CDIF framework
See also
ISO/IEC 15474-1
International Standard 15474-1
Information technology — CDIF framework
Part 1: Overview
Year: 2002.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
ISO/IEC 15474-2
International Standard 15474-2
Information technology — CDIF framework
Part 2: Modelling and extensibility
Year: 2002.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
ISO/IEC 15504
International Standard ISO/IEC 15504.
Information technology - Software Process Assessment
Also known as SPICE — Software Process Improvement and Capability dEtermination.
Years: 1998, 2003, 2004, 2008.
Contents
See also
Standards:
External Links:
ISO/IEC 15504-1
International Standard ISO/IEC 15504.
Information technology - Software Process Assessment
Part 1: Concepts and vocabulary
Year: 1998, 2004.
This standard revises the ISO/IEC TR 15504-1:1998 and ISO/IEC TR 15504-9:1998 standards.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
See also
Standards:
ISO/IEC 15504-2
International Standard ISO/IEC 15504.
Information technology - Software Process Assessment
Part 2: Performing an assessment
Year: 1998, 2003.
This standard revises the ISO/IEC TR 15504-2:1998 and ISO/IEC TR 15504-3:1998 standards.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
See also
Standards:
ISO/IEC 15504-3
International Standard ISO/IEC 15504.
Information technology - Software Process Assessment
Part 3: Guidance on performing an assessment
Year: 1998, 2004.
This standard revises the ISO/IEC TR 15504-4:1998 and ISO/IEC TR 15504-6:1998 standards.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
See also
Standards:
ISO/IEC 15504-4
International Standard ISO/IEC 15504.
Information technology - Software Process Assessment
Part 4: Guidance on use for process improvement and process capability determination
Year: 1998, 2004.
This standard revises the ISO/IEC TR 15504-7:1998 and ISO/IEC TR 15504-8:1998 standards.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
See also
Standards:
ISO/IEC 15504-5
International Standard ISO/IEC 15504.
Information technology - Software Process Assessment
Part 5: An exemplar Process Assessment Model
Year: 1998, 2006.
This standard revises the ISO/IEC TR 15504-5:1998 standard.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
See also
Standards:
ISO/IEC 15504-6
International Standard ISO/IEC 15504.
Information technology - Software Process Assessment
Part 6: An exemplar system life cycle process assessment model
Year: 1998, 2008.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
See also
Standards:
ISO/IEC 15504-7
International Standard ISO/IEC 15504.
Information technology - Software Process Assessment
Part 7: Assessment of organizational maturity
Year: 1998, 2008.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
See also
Standards:
ISO/IEC 15846
International Standard ISO/IEC 15846
Information technology — Software life cycle processes — Configuration Management
Year: 1998.
This standard has been withdrawn.
Access
Online ISO Catalog:
ISO/IEC 15910
International Standard ISO/IEC 15910.
Information technology — Software user documentation process
Year:1999.
This standard is revised by the ISO/IEC 26512:2011 standard.
Notes
Extract from www.techstreet.com:
This International Standard specifies the minimum process for creating all forms of user documentation for software which has a user interface. Such forms of documentation include printed documentation (e.g. user manuals and quick-reference cards), on-line documentation, help text and on-line documentation systems.
This International Standard conforms with ISO/IEC 12207:1995, Information technology Software life cycle processes, as an implementation of the user documentation part of 6.1: Documentation.
If effectively applied, this International Standard will support the development of documentation which meets the needs of the users.
This International Standard is intended for use by anyone who produces or buys user documentation.
This International Standard is applicable to not only printed documentation, but also help screens, the help delivery system, and the on-line text and delivery system.
This International Standard is intended for use in a two-party situation and may be equally applied where the two parties are from the same organization. The situation may range from an informal agreement up to a legally binding contract. This International Standard may be used by a single party as self-imposed tasks.
ISO/IEC 15939
International Standard ISO/IEC 15939
Software engineering - Software measurement process
Year: 2002, 2007.
See also
ISO/IEC 19759
International Standard ISO/IEC 19759
Software Engineering — Guide to the Software Engineering Body of Knowledge (SWEBOK)
Year: 2005.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
ISO/IEC 19770
International Standard ISO/IEC 19770
Information technology — Software asset management
ISO/IEC 19770-1
International Standard ISO/IEC 19770-1
Information technology — Software asset management
Part 1: Processes
Year: 2006.
See also
ISO/IEC 19770-2
International Standard ISO/IEC 19770-2
Information technology — Software asset management
Part 2: Software identification tag
Year: 2009.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
See also
ISO/IEC 20000
International Standard ISO/IEC 20000
Information technology — Service management
Contents/Access
This list links to the online ISO catalog:
ISO/IEC 2382
International Standard ISO/IEC 2382
Information processing systems — Vocabulary
Contents
See also
ISO/IEC 2382-1
International Standard ISO/IEC 2382
Information technology - Vocabulary
Part 1: Fundamental terms
Year: 1993.
Access
ISO/IEC 25000
International Standard ISO/IEC 25000
Software Engineering — Software product Quality Requirements and Evaluation (SQuaRE) — Guide to SQuaRE.
year: 2005.
This series of standards revises the ISO/IEC 9126 and ISO/IEC 14598 series.
See also
ISO/IEC 25001
International Standard ISO/IEC 25001
Software engineering — Software product Quality Requirements and Evaluation (SQuaRE) — Planning and management
year: 2007.
This standard revises the ISO/IEC 14598-2.
ISO/IEC 25010
International Standard ISO/IEC 25010
Systems and software engineering — Systems and software Quality Requirements and Evaluation (SQuaRE) — System and software quality models
year: 2011.
See also
ISO/IEC 25012
International Standard ISO/IEC 25012
Software engineering — Software product Quality Requirements and Evaluation (SQuaRE) — Data quality model
year: 2008.
See also
ISO/IEC 25020
International Standard ISO/IEC 25020
Software engineering — Software product Quality Requirements and Evaluation (SQuaRE) — Measurement reference model and guide
Year: 2007.
ISO/IEC 25021
International Standard ISO/IEC 25021
Software engineering — Software product Quality Requirements and Evaluation (SQuaRE) — Quality measure elements
Year: 2007.
ISO/IEC 25030
International Standard ISO/IEC 25030
Software engineering — Software product Quality Requirements and Evaluation (SQuaRE) — Quality requirements
year: 2007.
See also
ISO/IEC 25040
International Standard ISO/IEC 25040
Systems and software engineering — Systems and software Quality Requirements and Evaluation (SQuaRE) — Evaluation process
year: 2011.
This standard revises the ISO/IEC 14598-1 standard.
See also
ISO/IEC 25045
International Standard ISO/IEC 25045
Systems and software engineering — Systems and software Quality Requirements and Evaluation (SQuaRE) — Evaluation module for recoverability
Year: 2010.
See also
ISO/IEC 25051
International Standard ISO/IEC 25000
Software engineering — Software product Quality Requirements and Evaluation (SQuaRE) — Requirements for quality of Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) software product and instructions for testing
year: 2006, 2007.
This standard revises the ISO/IEC 12119 standard.
ISO/IEC 25060
International Standard ISO/IEC 25060
Systems and software engineering — Systems and software product Quality Requirements and Evaluation (SQuaRE) — Common Industry Format (CIF) for usability: General framework for usability-related information
Year: 2010.
See also
ISO/IEC 25062
International Standard ISO/IEC 25062
Software engineering — Software product Quality Requirements and Evaluation (SQuaRE) — Common Industry Format (CIF) for usability test reports
Year: 2006.
See also
ISO/IEC 26514
International Standard ISO/IEC 26514
Systems and software engineering — Requirements for designers and developers of user documentation
Year: 2008
Access
Online IEEE Catalog: http://www.iso.org/iso/catalogue_detail?csnumber=43073
ISO/IEC 29881
International Standard ISO/IEC/IEEE 29881
Information Technology — Software and Systems Engineering
Year: 2008, 2010
Access
ISO/IEC 90003
International Standard ISO/IEC 90003
Software engineering — Guidelines for the application of ISO 9001:2000 to computer software
Year: 2004
Access
Online IEEE Catalog: http://www.iso.org/iso/catalogue_detail?csnumber=35867
ISO/IEC 9126
International Standard ISO/IEC 9126
Software engineering — Product quality
Years: 1991, 2001
This standard is revised by ISO/IEC 25010:2011.
Contents
Structure
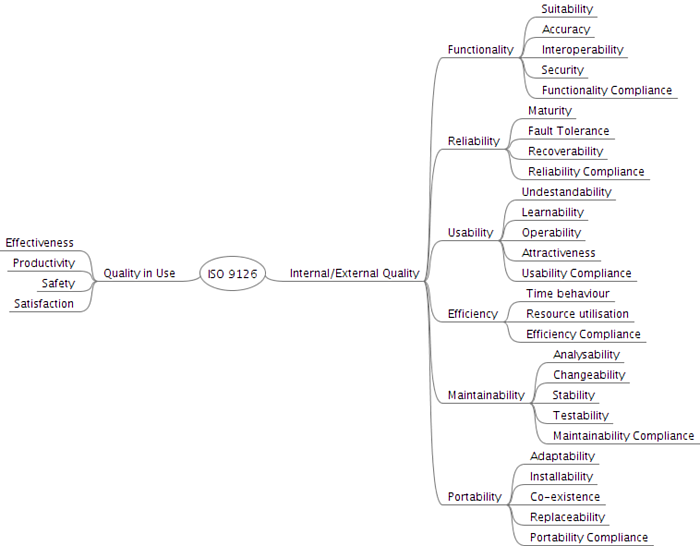
ISO/IEC 9126-1
International Standard ISO/IEC 9126-1
Software engineering — Product quality
Part 1: Quality Model
Years: 1991, 2001.
This standard is revised by ISO/IEC 25010:2011.
Access
Online ISO Catalog:
ISO/IEC 9126-2
International Standard ISO/IEC 9126-2
Software engineering — Product quality
Part 2: External metrics
Years: 1991, 2001.
This standard is revised by ISO/IEC 25010:2011.
Access
Online ISO Catalog:
ISO/IEC 9126-3
International Standard ISO/IEC 9126-3
Software engineering — Product quality
Part 3: Internal metrics
Years: 1991, 2001.
This standard is revised by ISO/IEC 25010:2011.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
ISO/IEC 9126-4
International Standard ISO/IEC 9126-4
Software engineering — Product quality
Part 4: Quality in use metrics
Years: 1991, 2001, 2004.
This standard is revised by ISO/IEC 25010:2011.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
ISO/IEC 9294
International Standard ISO/IEC 9294
Information technology — Guidelines for the management of software documentation
Years: 1990, 2005.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
ISO/IEC 99
International Standard ISO/IEC 99
International vocabulary of metrology — Basic and general concepts and associated terms
Years: 1993, 2007.
ISO/IEC SQuaRE
International Standard ISO/IEC SQuaRE
Systems and software Quality Requirements and Evaluation (SQuaRE)
SQuaRE is a series of International Standards (25000-25099) edited by the ISO/IEC organisation and related to Systems and Software Quality.
It is composed of the following ISO/IEC standards:
They are meant to replace older standards addressing the same topics, mainly (but not only) ISO/IEC 9126 and ISO/IEC 14598.
Structure
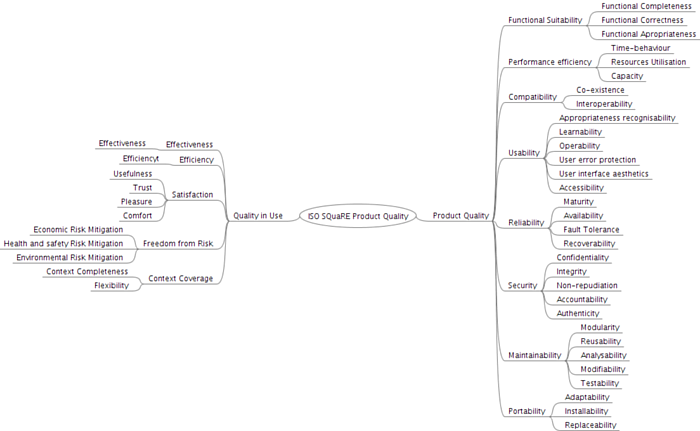
ISO/IEC/IEEE 15289
International Standard ISO/IEC/IEEE 15289.
Systems and software engineering — Content of life-cycle information products (documentation)
Years: 2006, 2011.
This standard revises the ISO/IEC 15289 standard.
Access
Online ISO catalog:
ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765
International Standard ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765
Systems and software engineering — Vocabulary
First edition: 2010-12-15
Access
Online IEEE Catalog: http://www.iso.org/iso/catalogue_detail.htm?csnumber=50518
RTCA/EUROCAE
Software Considerations in Airborne Systems and Equipments Certification
Requirements and Technical Concepts for Aviation - RTCA SC167/DO-178B
European Organization for Civil Aviation Electronics - EUROCAE ED-12B
SIGIST
Glossary of terms used in Software testing
British Computer Society - Specialist Interest Group In Software Testing
Team Software Process
Team Software Process is a process developed by the Carnegie-Mellon Software Engineering Institute.
The Team Software Process (TSP) helps engineering teams develop and deliver high-quality software-intensive systems within planned cost and schedule commitments. TSP integrates software engineering, estimating, planning and tracking, quality management, and self-directed teaming concepts into a defined process and measurement framework. TSP was designed to be easily integrated with an organization’s existing practices, and complements CMMI.
See also
Appendix A: Data Provider Frameworks
Current Frameworks
The following Data Provider frameworks support importing all kinds of data into Squore. Whether you choose one or the other depends on the ability of your script or executable to produce CSV or XML data. Note that these frameworks are recommended over the legacy frameworks described in Legacy Frameworks, which are deprecated as of Squore 18.0.
csv_import Reference
==============
= csv_import =
==============
The csv_import framework allows you to create Data Providers that produce CSV files that the framework will translate into XML files that can be imported in your analysts results. This framework is useful if writing XML files directly from your script is not practical.
Using csv_import, you can import metrics, findings (including relaxed findings), textual information, and links between artefacts (including to and from source code artefacts).
This framework replaces all the legacy frameworks that wrote CSV files in previous versions.
Note that this framework can be called by your Data Provider simply by creating an exec-tool phase that calls the part of the framework located in the configuration folder:
<exec-tool name="csv_import">
<param key="csv" value="${getOutputFile(output.csv)}" />
<param key="separator" value=";" />
<param key="delimiter" value=""" />
</exec-tool>
For a full description of all the parameters that can be used, consult the section called "CSV Import" in the "Data Providers" chapter of this manual.
============================================
= CSV format expected by the data provider =
============================================
- Line to define an artefact (like a parent artefact for instance):
Artefact
- Line to add n metrics to an artefact:
Artefact;(MetricId;Value)*
- Line to add n infos to an artefact:
Artefact;(InfoId;Value)*
- Line to add a key to an artefact:
Artefact;Value
- Line to add a finding to an artefact:
Artefact;RuleId;Message;Location
- Line to add a relaxed finding to an artefact:
Artefact;RuleId;Message;Location;RelaxStatus;RelaxMessage
- Line to add a link between artefacts:
Artefact;LinkId;Artefact
where:
- MetricId is the id of the metric as declared in the Analysis Model
- InfoId is the id of the information to import
- Value is the value of the metric or the information or the key to import (a key is a UUID used to reference an artefact)
- RuleId is the id of the rule violated as declared in the Analysis Model
- Message is the message of the finding, which is displayed after the rule description
- Location is the location of the finding (a line number for findings attached source code artefacts, a url for findings attached to any other kind of artefact)
- RelaxStatus is one of DEROGATION, FALSE_POSITIVE or LEGACY and defines the relaxation stat of the imported finding
- RelaxMessage is the justification message for the relaxation state of the finding
- LinkId is the id of the link to create between artefacts, as declared in the Analysis Model
==========================
= Manipulating Artefacts =
==========================
The following functions are available to locate and manipulate source code artefacts in the project:
- ${artefact(type,path)} ==> Identify an artefact by its type and full path
- ${artefact(type,path,uid)} ==> Identify an artefact by its type and full path and assign it the unique identifier uid
- ${uid(value)} ==> Identify an artefact by its unique identifier (value)
- ${file(path)} ==> Tries to find a source code file matching the "path" in the project
- ${function(fpath,line)} ==> Tries to find a source code function at line "line" in file matching the "fpath" in the project
- ${function(fpath,name)} ==> Tries to find a source code function whose name matches "name" in the file matching the "fpath" in the project
- ${class(fpath,line)} ==> Tries to find a source code class at line "line" in the file matching the "fpath" in the project
- ${class(fpath,name)} ==> Tries to find a source code class whose name matches "name" in the file matching the "fpath" in the project
Note: In the above definitions if "name" contains either '(' or ',' characters then the full name has to be between simple quote
e.g. ${function(main.c,'main(int argc, char* argv)')}
===============
= Input Files =
===============
The data provider accepts the following files:
Metrics file accepts:
Artefact definition line
Metrics line
Findings file accepts:
Artefact definition line
Findings line
Keys file accepts:
Artefact definition line
Keys line
Information file accepts:
Artefact definition line
Information line
Links file accepts:
Artefact definition line
Links line
It is also possible to mix every kind of line in a single csv file, as long as each line is prefixed with the kind of data it contains.
In this case, the first column must contain one of:
DEFINE (or D): when the line is used to define an artefact
METRIC (or M): to add a metric
INFO (or I): to add an information
KEY (or K): to add a key
FINDING (or F): to add a finding, relaxed or not
LINK (or L): to add link between artefacts
The following is an example of a csv file containing mixed lines:
D;${artefact(CR_FOLDER,/CRsCl)}
M;${artefact(CR,/CRsCl/cr2727,2727)};NB;2
M;${artefact(CR,/CRsCl/cr1010,1010)};NB;4
I;${uid(1010)};NBI;Bad weather
K;${artefact(CR,/CRsCl/cr2727,2727)};#CR2727
I;${artefact(CR,/CRsCl/cr2727,2727)};NBI;Nice Weather
F;${artefact(CR,/CRsCl/cr2727,2727)};BAD;Malformed
M;${uid(2727)};NB_EXT;3
I;${uid(2727)};NBI_EXT;Another Info
F;${uid(2727)};BAD_EXT;Badlyformed
F;${uid(2727)};BAD_EXT1;Badlyformed1;;FALSE_POSITIVE;Everything is in the title]]>
F;${function(machine.c,41)};R_GOTO;"No goto; neither togo;";41
F;${function(machine.c,42)};R_GOTO;No Goto;42;LEGACY;Was done a long time ago
F;${function(main.c,'main(int argc, char* argv)')};R_GOTO;No Goto;42
L;${uid(1010)};CR2CR;${uid(2727)}
L;${uid(2727)};CR2CR;${uid(1010)}xml Reference
=======
= xml =
=======
The xml framework is an implementation of a data provider that allows to import an xml file, potentially after an xsl transformation. The transformed XML file is expected to follow the syntax expected by other data providers (see input-data.xml specification).
This framework can be extended like the other frameworks, by creating a folder for your data provider in your configuration/tools folder and creating a form.xml. Following are three examples of the possible uses of this framework.
Example 1 - User enters an xml path and an xsl path, the xml is transformed using the xsl and then imported
=========
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<tags baseName="xml">
<tag type="text" key="xml" />
<tag type="text" key="xslt" />
<exec-phase id="add-data">
<exec name="java" failOnError="true" failOnStdErr="true">
<arg value="${javaClasspath(groovy,xml-resolver-1.2.jar)}"/>
<arg value="groovy.lang.GroovyShell" />
<arg value="xml.groovy" />
<arg value="${outputDirectory}" />
<arg tag="xml"/>
<arg tag="xsl" />
</exec>
</exec-phase>
</tags>
Example 2 - The user enter an xml path, the xsl file is predefined (input-data.xsl) and present in the same directory as form.xml
=========
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<tags baseName="xml">
<tag type="text" key="xml" />
<exec-phase id="add-data">
<exec name="java" failOnError="true" failOnStdErr="true">
<arg value="${javaClasspath(groovy,xml-resolver-1.2.jar)}"/>
<arg value="groovy.lang.GroovyShell" />
<arg value="xml.groovy" />
<arg value="${outputDirectory}" />
<arg tag="xml" />
<arg value="${getToolConfigDir(input-data.xsl)}" />
</exec>
</exec-phase>
</tags>
Example 3 - The user enter an xml path of a file already in the expected format
=========
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<tags baseName="xml">
<tag type="text" key="xml" />
<exec-phase id="add-data">
<exec name="java" failOnError="true" failOnStdErr="true">
<arg value="${javaClasspath(groovy,xml-resolver-1.2.jar)}"/>
<arg value="groovy.lang.GroovyShell" />
<arg value="xml.groovy" />
<arg value="${outputDirectory}" />
<arg tag="xml" />
</exec>
</exec-phase>
</tags>Legacy Frameworks
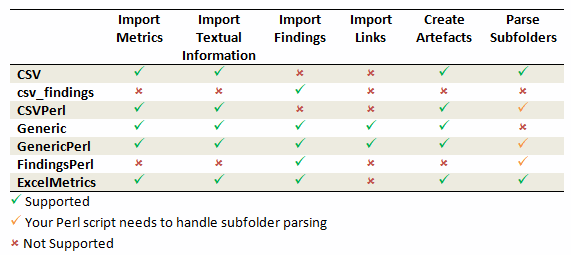
-
Csv
The Csv framework is used to import metrics or textual information and attach them to artefacts of type Application or File. While parsing one or more input CSV files, if it finds the same metric for the same artefact several times, it will only use the last occurrence of the metric and ignore the previous ones. Note that the type of artefacts you can attach metrics to is limited to Application and File artefacts. If you are working with File artefacts, you can let the Data Provider create the artefacts by itself if they do not exist already. Refer to the full Csv Reference for more information.
-
csv_findings
The csv_findings framework is used to import findings in a project and attach them to artefacts of type Application, File or Function. It takes a single CSV file as input and is the only framework that allows you to import relaxed findings directly. Refer to the full csv_findings Reference for more information.
-
CsvPerl
The CsvPerl framework offers the same functionality as Csv, but instead of dealing with the raw input files directly, it allows you to run a perl script to modify them and produce a CSV file with the expected input format for the Csv framework. Refer to the full CsvPerl Reference for more information.
-
FindingsPerl
The FindingsPerl framework is used to import findings and attach them to existing artefacts. Optionally, if an artefact cannot be found in your project, the finding can be attached to the root node of the project instead. When launching a Data Provider based on the FindingsPerl framework, a perl script is run first. This perl script is used to generate a CSV file with the expected format which will then be parsed by the framework. Refer to the full FindingsPerl Reference for more information.
-
Generic
The Generic framework is the most flexible Data Provider framework, since it allows attaching metrics, findings, textual information and links to artefacts. If the artefacts do not exist in your project, they will be created automatically. It takes one or more CSV files as input (one per type of information you want to import) and works with any type of artefact. Refer to the full Generic Reference for more information.
-
GenericPerl
The GenericPerl framework is an extension of the Generic framework that starts by running a perl script in order to generate the metrics, findings, information and links files. It is useful if you have an input file whose format needs to be converted to match the one expected by the Generic framework, or if you need to retrieve and modify information exported from a web service on your network. Refer to the full GenericPerl Reference for more information.
-
ExcelMetrics
The ExcelMetrics framework is used to extract information from one or more Microsoft Excel files (.xls or .xslx). A detailed configuration file allows defining how the Excel document should be read and what information should be extracted. This framework allows importing metrics, findings and textual information to existing artefacts or artefacts that will be created by the Data Provider. Refer to the full ExcelMetrics Reference for more information.
After you choose the framework to extend, you should follow these steps to make your custom Data Provider known to Squore:
-
Create a new configuration tools folder to save your work in your custom configuration folder: MyConfiguration/configuration/tools.
-
Create a new folder for your data provider inside the new tools folder: CustomDP. This folder needs to contain the following files:
-
form.xml defines the input parameters for the Data Provider, and the base framework to use, as described in Defining Data Provider Parameters
-
form_en.properties contains the strings displayed in the web interface for this Data Provider, as described in Localising your Data Provider
-
config.tcl contains the parameters for your custom Data Provider that are specific to the selected framework
-
CustomDP.pl is the perl script that is executed automatically if your custom Data Provider uses one of the *Perl frameworks.
-
-
Edit Squore Server’s configuration file to register your new configuration path, as described in the Installation and Administration Guide.
-
Log into the web interface as a Squore administrator and reload the configuration.
Your new Data Provider is now known to Squore and can be triggered in analyses. Note that you may have to modify your Squore configuration to make your wizard aware of the new Data Provider and your model aware of the new metrics it provides. Refer to the relevant sections of the Configuration Guide for more information.
Csv Reference
=======
= Csv =
=======
The Csv framework is used to import metrics or textual information and attach them to artefacts of type Application, File or Function. While parsing one or more input CSV files, if it finds the same metric for the same artefact several times, it will only use the last occurrence of the metric and ignore the previous ones. Note that the type of artefacts you can attach metrics to is limited to Application, File and Function artefacts. If you are working with File artefacts, you can let the Data Provider create the artefacts by itself if they do not exist already.
============
= form.xml =
============
You can customise form.xml to either:
- specify the path to a single CSV file to import
- specify a pattern to import all csv files matching this pattern in a directory
In order to import a single CSV file:
=====================================
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<tags baseName="Csv" needSources="true">
<tag type="text" key="csv" defaultValue="/path/to/mydata.csv" />
</tags>
Notes:
- The csv key is mandatory.
- Since Csv-based data providers commonly rely on artefacts created by Squan Sources, you can set the needSources attribute to force users to specify at least one repository connector when creating a project.
In order to import all files matching a pattern in a folder:
===========================================================
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<tags baseName="Csv" needSources="true">
<!-- Root directory containing Csv files to import-->
<tag type="text" key="dir" defaultValue="/path/to/mydata" />
<!-- Pattern that needs to be matched by a file name in order to import it-->
<tag type="text" key="ext" defaultValue="*.csv" />
<!-- search for files in sub-folders -->
<tag type="booleanChoice" defaultValue="true" key="sub" />
</tags>
Notes:
- The dir and ext keys are mandatory
- The sub key is optional (and its value set to false if not specified)
==============
= config.tcl =
==============
Sample config.tcl file:
=======================
# The separator used in the input CSV file
# Usually \t or ;
set Separator "\t"
# The delimiter used in the input CSV file
# This is normally left empty, except when you know that some of the values in the CSV file
# contain the separator itself, for example:
# "A text containing ; the separator";no problem;end
# In this case, you need to set the delimiter to \" in order for the data provider to find 3 values instead of 4.
# To include the delimiter itself in a value, you need to escape it by duplicating it, for example:
# "A text containing "" the delimiter";no problemo;end
# Default: none
set Delimiter \"
# ArtefactLevel is one of:
# Application: to import data at application level
# File: to import data at file level. In this case ArtefactKey has to be set
# to the value of the header (key) of the column containing the file path
# in the input CSV file.
# Function : to import data at function level, in this case:
# ArtefactKey has to be set to the value of the header (key) of the column containing the path of the file
# FunctionKey has to be set to the value of the header (key) of the column containing the name and signature of the function
# Note that the values are case-sensitive.
set ArtefactLevel File
set ArtefactKey File
# Should the File paths be case-insensitive?
# true or false (default)
# This is used when searching for a matching artefact in already-existing artefacts.
set PathsAreCaseInsensitive "false"
# Should file artefacts declared in the input CSV file be created automatically?
# true (default) or false
set CreateMissingFile "true"
# FileOrganisation defines the layout of the input CSV file and is one of:
# header::column: values are referenced from the column header
# header::line: NOT AVAILABLE
# alternate::line: lines are a sequence of {Key Value}
# alternate::column: columns are a sequence of {Key Value}
# There are more examples of possible CSV layouts later in this document
set FileOrganisation header::column
# Metric2Key contains a case-sensitive list of paired metric IDs:
# {MeasureID KeyName [Format]}
# where:
# - MeasureID is the id of the measure as defined in your analysis model
# - KeyName, depending on the FileOrganisation, is either the name of the column or the name
# in the cell preceding the value to import as found in the input CSV file
# - Format is the optional format of the data, the only accepted format
# is "text" to attach textual information to an artefact, for normal metrics omit this field
set Metric2Key {
{BRANCHES Branchs}
{VERSIONS Versions}
{CREATED Created}
{IDENTICAL Identical}
{ADDED Added}
{REMOV Removed}
{MODIF Modified}
{COMMENT Comment text}
}
==========================
= Sample CSV Input Files =
==========================
Example 1:
==========
FileOrganisation : header::column
ArtefactLevel : File
ArtefactKey : Path
Path Branchs Versions
./foo.c 15 105
./bar.c 12 58
Example 2:
==========
FileOrganisation : alternate::line
ArtefactLevel : File
ArtefactKey : Path
Path ./foo.c Branchs 15 Versions 105
Path ./bar.c Branchs 12 Versions 58
Example 3:
==========
FileOrganisation : header::column
ArtefactLevel : Application
ChangeRequest Corrected Open
27 15 11
Example 4:
==========
FileOrganisation : alternate::column
ArtefactLevel : Application
ChangeRequest 15
Corrected 11
Example 5:
==========
FileOrganisation : alternate::column
ArtefactLevel : File
ArtefactKey : Path
Path ./foo.c
Branchs 15
Versions 105
Path ./bar.c
Branchs 12
Versions 58
Example 6:
==========
FileOrganisation : header::column
ArtefactLevel : Function
ArtefactKey : Path
FunctionKey : Name
Path Name Decisions Tested
./foo.c end_game(int*,int*) 15 3
./bar.c bar(char) 12 6
Working With Paths:
===================
- Path seperators are unified: you do not need to worry about handling differences between Windows and Linux
- With the option PathsAreCaseInsensitive, case is ignored when searching for files in the Squore internal data
- Paths known by Squore are relative paths starting at the root of what was specified in the repository connector durign the analysis. This relative path is the one used to match with a path in a csv file.
Here is a valid example of file matching:
1. You provide C:\A\B\C\D as the root folder in a repository connector
2. C:\A\B\C\D contains E\e.c then Squore will know E/e.c as a file
3. You provide a csv file produced on linux and containing
/tmp/X/Y/E/e.c as path, then Squore will be able to match it with the known file.
Squore uses the longest possible match.
In case of conflict, no file is found and a message is sent to the log.csv_findings Reference
================
= csv_findings =
================
The csv_findings data provider is used to import findings (rule violations) and attach them to artefacts of type Application, File or Function.
The format of the csv file given as parameter has to be:
FILE;FUNCTION;RULE_ID;MESSAGE;LINE;COL;STATUS;STATUS_MESSAGE;TOOL
where:
=====
FILE : is the full path of the file where the finding is located
FUNCTION : is the name of the function where the finding is located
RULE_ID : is the Squore ID of the rule which is violated
MESSAGE : is the specific message of the violation
LINE: is the line number where the violation occurs
COL: (optional, leave empty if not provided) is the column number where the violation occurs
STATUS: (optional, leave empty if not provided) is the staus of the relaxation if the violation has to be relaxed (DEROGATION, FALSE_POSITIVE, LEGACY)
STATUS_MSG: (optional, leave empty if not provided) is the message for the relaxation when relaxed
TOOL: is the tool providing the violation
The header line is read and ignored (it has to be there)
The separator (semicolon by default) can be changed in the config.tcl file (see below)
The delimiter (no delimiter by default) can be changed in the config.tcl (see below)
==============
= config.tcl =
==============
Sample config.tcl file:
=======================
# The separator used in the input CSV file
# Usually ; or \t
set Separator \;
# The delimiter used in the CSV input file
# This is normally left empty, except when you know that some of the values in the CSV file
# contain the separator itself, for example:
# "A text containing ; the separator";no problem;end
# In this case, you need to set the delimiter to \" in order for the data provider to find 3 values instead of 4.
# To include the delimiter itself in a value, you need to escape it by duplicating it, for example:
# "A text containing "" the delimiter";no problemo;end
# Default: none
set Delimiter \"
# You can add some patterns to avoid new findings when some strings in the finding message changes
# i.e. Unreachable code Default switch clause is unreachable. switch-expression at line 608 (column 12).
# In this case we do not want the line number to be part of the signagture of the finding,
# to achieve this user will add a pattern as shown below (patterns are TCL regex patterns):
lappend InconstantFindingsPatterns {at line [0-9]+}CsvPerl Reference
===========
= CsvPerl =
===========
The CsvPerl framework offers the same functionality as Csv, but instead of dealing with the raw input files directly, it allows you to run a perl script to modify them and produce a CSV file with the expected input format for the Csv framework.
============
= form.xml =
============
In your form.xml, specify the input parameters you need for your Data Provider.
Our example will use two parameters: a path to a CSV file and another text parameter:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<tags baseName="CsvPerl" needSources="true">
<tag type="text" key="csv" defaultValue="/path/to/csv" />
<tag type="text" key="param" defaultValue="MyValue" />
</tags>
- Since Csv-based data providers commonly rely on artefacts created by Squan Sources, you can set the needSources attribute to force users to specify at least one repository connector when creating a project.
==============
= config.tcl =
==============
Refer to the description of config.tcl for the Csv framework.
For CsvPerl one more option is possible:
# The variable NeedSources is used to request the perl script to be executed once for each
# repository node of the project. In that case an additional parameter is sent to the
# perl script (see below for its position)
#set ::NeedSources 1
==========================
= Sample CSV Input Files =
==========================
Refer to the examples for the Csv framework.
===============
= Perl Script =
===============
The perl scipt will receive as arguments:
- all parameters defined in form.xml (as -${key} $value)
- the input directory to process (only if ::NeedSources is set to 1 in the config.tcl file)
- the location of the output directory where temporary files can be generated
- the full path of the csv file to be generated
For the form.xml we created earlier in this document, the command line will be:
perl <configuration_folder>/tools/CustomDP/CustomDP.pl -csv /path/to/csv -param MyValue <output_folder> <output_folder>/CustomDP.csv
Example of perl script:
======================
#!/usr/bin/perl
use strict;
use warnings;
$|=1 ;
($csvKey, $csvValue, $paramKey, $paramValue, $output_folder, $output_csv) = @ARGV;
# Parse input CSV file
# ...
# Write results to CSV
open(CSVFILE, ">" . ${output_csv}) || die "perl: can not write: $!\n";
binmode(CSVFILE, ":utf8");
print CSVFILE "ChangeRequest;15";
close CSVFILE;
exit 0;Generic Reference
===========
= Generic =
===========
The Generic framework is the most flexible Data Provider framework, since it allows attaching metrics, findings, textual information and links to artefacts. If the artefacts do not exist in your project, they will be created automatically. It takes one or more CSV files as input (one per type of information you want to import) and works with any type of artefact.
============
= form.xml =
============
In form.xml, allow users to specify the path to a CSV file for each type of data you want to import.
You can set needSources to true or false, depending on whether or not you want to require the use of a repository connector when your custom Data Provider is used.
Example of form.xml file:
=========================
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<tags baseName="Generic" needSources="false">
<!-- Path to CSV file containing Metrics data -->
<tag type="text" key="csv" defaultValue="mydata.csv" />
<!-- Path to CSV file containing Findings data: -->
<tag type="text" key="fdg" defaultValue="mydata_fdg.csv" />
<!-- Path to CSV file containing Information data: -->
<tag type="text" key="inf" defaultValue="mydata_inf.csv" />
<!-- Path to CSV file containing Links data: -->
<tag type="text" key="lnk" defaultValue="mydata_lnk.csv" />
</tags>
Note: All tags are optional. You only need to specify the tag element for the type of data you want to import with your custom Data Provider.
==============
= config.tcl =
==============
Sample config.tcl file:
=======================
# The separator used in the input csv files
# Usually \t or ; or ,
# In our example below, a space is used.
set Separator " "
# The delimiter used in the input CSV file
# This is normally left empty, except when you know that some of the values in the CSV file
# contain the separator itself, for example:
# "A text containing ; the separator";no problem;end
# In this case, you need to set the delimiter to \" in order for the data provider to find 3 values instead of 4.
# To include the delimiter itself in a value, you need to escape it by duplicating it, for example:
# "A text containing "" the delimiter";no problemo;end
# Default: none
set Delimiter \"
# The path separator in an artefact's path
# in the input CSV file.
# Note that artefact is spellt with an "i"
# and not an "e" in this option.
set ArtifactPathSeparator "/"
# If the data provider needs to specify a different toolName (optional)
set SpecifyToolName 1
# Metric2Key contains a case-sensitive list of paired metric IDs:
# {MeasureID KeyName [Format]}
# where:
# - MeasureID is the id of the measure as defined in your analysis model
# - KeyName is the name in the cell preceding the value to import as found in the input CSV file
# - Format is the optional format of the data, the only accepted format
# is "text" to attach textual information to an artefact. Note that the same result can also
# be achieved with Info2Key (see below). For normal metrics omit this field.
set Metric2Key {
{CHANGES Changed}
}
# Finding2Key contains a case-sensitive list of paired rule IDs:
# {FindingID KeyName}
# where:
# - FindingID is the id of the rule as defined in your analysis model
# - KeyName is the name in the finding name in the input CSV file
set Finding2Key {
{R_NOTLINKED NotLinked}
}
# Info2Key contains a case-sensitive list of paired info IDs:
# {InfoID KeyName}
# where:
# - InfoID is the id of the textual information as defiend in your analysis model
# - KeyName is the name of the information name in the input CSV file
set Info2Key
{SPECIAL_LABEL Label}
}
# Ignore findings for artefacts that are not part of the project (orphan findings)
# When set to 1, the findings are ignored
# When set to 0, the findings are imported and attached to the APPLICATION node
# (default: 1)
set IgnoreIfArtefactNotFound 1
# If data in csv concerns source code artefacts (File, Class or Function), the way to
# match file paths can be case-insensitive
# true or false (default)
# This is used when searching for a matching artefact in already-existing artefacts.
set PathsAreCaseInsensitive "false"
# For findings of a type that is not in your ruleset, set a default rule ID.
# The value for this parameter must be a valid rule ID from your analysys model.
# (default: empty)
set UnknownRuleId UNKNOWN_RULE
# Save the total count of orphan findings as a metric at application level
# Specify the ID of the metric to use in your analysys model
# to store the information
# (default: empty)
set OrphanArteCountId NB_ORPHANS
# Save the total count of unknown rules as a metric at application level
# Specify the ID of the metric to use in your analysys model
# to store the information
# (default: empty)
set OrphanRulesCountId NB_UNKNOWN_RULES
# Save the list of unknown rule IDs as textual information at application level
# Specify the ID of the metric to use in your analysys model
# to store the information
# (default: empty)
set OrphanRulesListId UNKNOWN_RULES_INFO
====================
= CSV File Format =
====================
All the examples listed below assume the use of the following config.tcl:
set Separator ","
set ArtifactPathSeparator "/"
set Metric2Key {
{CHANGES Changed}
}
set Finding2Key {
{R_NOTLINKED NotLinked}
}
set Info2Key
{SPECIAL_LABEL Label}
}
How to reference an artefact:
============================
==> artefact_type artefact_path
Example:
REQ_MODULES,Requirements
REQ_MODULE,Requirements/Module
REQUIREMENT,Requirements/Module/My_Req
References the following artefact
Application
Requirements (type: REQ_MODULES)
Module (type: REQ_MODULE)
My_Req (type: REQUIREMENT)
Note: For source code artefacts there are 3 special artefact kinds:
==> FILE file_path
==> CLASS file_path (Name|Line)
==> FUNCTION file_path (Name|Line)
Examples:
FUNCTION src/file.c 23
references the function which contains line 23 in the source file src/file.c, if no
function found the line whole line of the csv file is ignored.
FUNCTION src/file.c foo()
references a function named foo in source file src/file.c. If more than one function foo
is defined in this file, then the signature of the function (which is optional) is used
to find the best match.
Layout for Metrics File:
========================
==> artefact_type artefact_path (Key Value)*
When the parent artefact type is not given it defaults to <artefact_type>_FOLDER.
Example:
REQ_MODULE,Requirements/Module
REQUIREMENT,Requirements/Module/My_Req,Changed,1
will produce the following artefact tree:
Application
Requirements (type: REQ_MODULE_FOLDER)
Module (type: REQ_MODULE)
My_Req : (type: REQUIREMENT) with 1 metric CHANGES = 1
Note: the key "Changed" is mapped to the metric "CHANGES", as specified by the Metric2Key parameter, so that it matches what is expected by the model.
Layout for Findings File:
=========================
==> artefact_type artefact_path key message
When the parent artefact type is not given it defaults to <artefact_type>_FOLDER.
Example:
REQ_MODULE,Requirements/Module
REQUIREMENT,Requirements/Module/My_Req,NotLinked,A Requiremement should always been linked
will produce the following artefact tree:
Application
Requirements (type: REQ_MODULE_FOLDER)
Module (type: REQ_MODULE)
My_Req (type: REQUIREMENT) with 1 finding R_NOTLINKED whose description is "A Requiremement should always been linked"
Note: the key "NotLinked" is mapped to the finding "R_NOTLINKED", as specified by the Finding2Key parameter, so that it matches what is expected by the model.
Layout for Textual Information File:
====================================
==> artefact_type artefact_path label value
When the parent artefact type is not given it defaults to <artefact_type>_FOLDER.
Example:
REQ_MODULE,Requirements/Module
REQUIREMENT,Requirements/Module/My_Req,Label,This is the label of the req
will produce the following artefact tree:
Application
Requirements (type: REQ_MODULE_FOLDER)
Module (type: REQ_MODULE)
My_Req (type: REQUIREMENT) with 1 information of type SPECIAL_LABEL whose content is "This is the label of the req"
Note: the label "Label" is mapped to the finding "SPECIAL_LABEL", as specified by the Info2Key parameter, so that it matches what is expected by the model.
Layout for Links File:
======================
==> artefact_type artefact_path dest_artefact_type dest_artefact_path link_type
When the parent artefact type is not given it defaults to <artefact_type>_FOLDER
Example:
REQ_MODULE Requirements/Module
TEST_MODULE Tests/Module
REQUIREMENT Requirements/Module/My_Req TEST Tests/Module/My_test TESTED_BY
will produce the following artefact tree:
Application
Requirements (type: REQ_MODULE_FOLDER)
Module (type: REQ_MODULE)
My_Req (type: REQUIREMENT) ------>
Tests (type: TEST_MODULE_FOLDER) |
Module (type: TEST_MODULE) |
My_Test (type: TEST) <------------+ link (type: TESTED_BY)
The TESTED_BY relationship is created with My_Req as source of the link and My_test as the destination
CSV file organisation when SpecifyToolName is set to 1
======================================================
When the variable SpecifyToolName is set to 1 (or true) a column has to be added
at the beginning of each line in each csv file. This column can be empty or filled with a different toolName.
Example:
,REQ_MODULE,Requirements/Module
MyReqChecker,REQUIREMENT,Requirements/Module/My_Req Label,This is the label of the req
The finding of type Label will be set as reported by the tool "MyReqChecker".GenericPerl Reference
===============
= GenericPerl =
===============
The GenericPerl framework is an extension of the Generic framework that starts by running a perl script in order to generate the metrics, findings, information and links files. It is useful if you have an input file whose format needs to be converted to match the one expected by the Generic framework, or if you need to retrieve and modify information exported from a web service on your network.
============
= form.xml =
============
In your form.xml, specify the input parameters you need for your Data Provider.
Our example will use two parameters: a path to a CSV file and another text parameter:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<tags baseName="CsvPerl" needSources="false">
<tag type="text" key="csv" defaultValue="/path/to/csv" />
<tag type="text" key="param" defaultValue="MyValue" />
</tags>
==============
= config.tcl =
==============
Refer to the description of config.tcl for the Generic framework for the basic options.
Additionally, the following options are available for the GenericPerl framework, in order to know which type of information your custom Data Provider should try to import.
# If the data provider needs to specify a different toolName (optional)
#set SpecifyToolName 1
# Set to 1 to import metrics csv file, 0 otherwise
# ImportMetrics
# When set to 1, your custom Data Provider (CustomDP) will try to import
# metrics from a file called CustomDP.mtr.csv that your perl script
# should generate according to the expected format described in the
# documentation of the Generic framework.
set ImportMetrics 1
# ImportInfos
# When set to 1, your custom Data Provider (CustomDP) will try to import
# textual information from a file called CustomDP.inf.csv that your perl script
# should generate according to the expected format described in the
# documentation of the Generic framework.
set ImportInfos 0
# ImportFindings
# When set to 1, your custom Data Provider (CustomDP) will try to import
# findings from a file called CustomDP.fdg.csv that your perl script
# should generate according to the expected format described in the
# documentation of the Generic framework.
set ImportFindings 1
# ImportLinks
# When set to 1, your custom Data Provider (CustomDP) will try to import
# artefact links from a file called CustomDP.lnk.csv that your perl script
# should generate according to the expected format described in the
# documentation of the Generic framework.
set ImportLinks 0
# Ignore findings for artefacts that are not part of the project (orphan findings)
# When set to 1, the findings are ignored
# When set to 0, the findings are imported and attached to the APPLICATION node
# (default: 1)
set IgnoreIfArtefactNotFound 1
# For findings of a type that is not in your ruleset, set a default rule ID.
# The value for this parameter must be a valid rule ID from your analysys model.
# (default: empty)
set UnknownRuleId UNKNOWN_RULE
# Save the total count of orphan findings as a metric at application level
# Specify the ID of the metric to use in your analysys model
# to store the information
# (default: empty)
set OrphanArteCountId NB_ORPHANS
# Save the total count of unknown rules as a metric at application level
# Specify the ID of the metric to use in your analysys model
# to store the information
# (default: empty)
set OrphanRulesCountId NB_UNKNOWN_RULES
# Save the list of unknown rule IDs as textual information at application level
# Specify the ID of the metric to use in your analysys model
# to store the information
# (default: empty)
set OrphanRulesListId UNKNOWN_RULES_INFO
====================
= CSV File Format =
====================
Refer to the examples in the Generic framework.
===============
= Perl Script =
===============
The perl scipt will receive as arguments:
- all parameters defined in form.xml (as -${key} $value)
- the location of the output directory where temporary files can be generated
- the full path of the metric csv file to be generated (if ImportMetrics is set to 1 in config.tcl)
- the full path of the findings csv file to be generated (if ImportFindings is set to 1 in config.tcl)
- the full path of the textual information csv file to be generated (if ImportInfos is set to 1 in config.tcl)
- the full path of the links csv file to be generated (if ImportLinks is set to 1 in config.tcl)
- the full path to the output directory used by this data provider in the previous analysis
For the form.xml and config.tcl we created earlier in this document, the command line will be:
perl <configuration_folder>/tools/CustomDP/CustomDP.pl -csv /path/to/csv -param MyValue <output_folder> <output_folder>/CustomDP.mtr.csv <output_folder>/CustomDP.fdg.csv <previous_output_folder>
The following perl functions are made available in the perl environment so you can use them in your script:
- get_tag_value(key) (returns the value for $key parameter from your form.xml)
- get_output_metric()
- get_output_finding()
- get_output_info()
- get_output_link()
- get_output_dir()
- get_input_dir() (returns the folder containing sources if needSources is set to 1)
- get_previous_dir()
Example of perl script:
======================
#!/usr/bin/perl
use strict;
use warnings;
$|=1 ;
# Parse input CSV file
my $csvFile = get_tag_value("csv");
my $param = get_tag_value("param");
# ...
# Write metrics to CSV
open(METRICS_FILE, ">" . get_output_metric()) || die "perl: can not write: $!\n";
binmode(METRICS_FILE, ":utf8");
print METRICS_FILE "REQUIREMENTS;Requirements/All_Requirements;NB_REQ;15";
close METRICS_FILE;
# Write findings to CSV
open(FINDINGS_FILE, ">" . get_output_findings()) || die "perl: can not write: $!\n";
binmode(FINDINGS_FILE, ":utf8");
print FINDINGS_FILE "REQUIREMENTS;Requirements/All_Requirements;R_LOW_REQS;\"The minimum number of requirement should be at least 25.\"";
close FINDINGS_FILE;
exit 0;FindingsPerl Reference
================
= FindingsPerl =
================
The FindingsPerl framework is used to import findings and attach them to existing artefacts. Optionally, if an artefact cannot be found in your project, the finding can be attached to the root node of the project instead. When launching a Data Provider based on the FindingsPerl framework, a perl script is run first. This perl script is used to generate a CSV file with the expected format which will then be parsed by the framework.
============
= form.xml =
============
In your form.xml, specify the input parameters you need for your Data Provider.
Our example will use two parameters: a path to a CSV file and another text parameter:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<tags baseName="CsvPerl" needSources="true">
<tag type="text" key="csv" defaultValue="/path/to/csv" />
<tag type="text" key="param" defaultValue="MyValue" />
</tags>
- Since FindingsPerl-based data providers commonly rely on artefacts created by Squan Sources, you can set the needSources attribute to force users to specify at least one repository connector when creating a project.
==============
= config.tcl =
==============
Sample config.tcl file:
=======================
# The separator to be used in the generated CSV file
# Usually \t or ;
set Separator ";"
# The delimiter used in the input CSV file
# This is normally left empty, except when you know that some of the values in the CSV file
# contain the separator itself, for example:
# "A text containing ; the separator";no problem;end
# In this case, you need to set the delimiter to \" in order for the data provider to find 3 values instead of 4.
# To include the delimiter itself in a value, you need to escape it by duplicating it, for example:
# "A text containing "" the delimiter";no problemo;end
# Default: none
set Delimiter \"
# Should the perl script execcuted once for each repository node of the project ?
# 1 or 0 (default)
# If true an additional parameter is sent to the
# perl script (see below for its position)
set ::NeedSources 0
# Should the violated rules definitions be generated?
# true or false (default)
# This creates a ruleset file with rules that are not already
# part of your analysis model so you can review it and add
# the rules manually if needed.
set generateRulesDefinitions false
# Should the File paths be case-insensitive?
# true or false (default)
# This is used when searching for a matching artefact in already-existing artefacts.
set PathsAreCaseInsensitive false
# Should file artefacts declared in the input CSV file be created automatically?
# true (default) or false
set CreateMissingFile true
# Ignore findings for artefacts that are not part of the project (orphan findings)
# When set to 0, the findings are imported and attached to the APPLICATION node instead of the real artefact
# When set to 1, the findings are not imported at all
# (default: 0)
set IgnoreIfArtefactNotFound 0
# For findings of a type that is not in your ruleset, set a default rule ID.
# The value for this parameter must be a valid rule ID from your analysis model.
# (default: empty)
set UnknownRuleId UNKNOWN_RULE
# Save the total count of orphan findings as a metric at application level
# Specify the ID of the metric to use in your analysys model
# to store the information
# (default: empty)
set OrphanArteCountId NB_ORPHANS
# Save the total count of unknown rules as a metric at application level
# Specify the ID of the metric to use in your analysys model
# to store the information
# (default: empty)
set OrphanRulesCountId NB_UNKNOWN_RULES
# Save the list of unknown rule IDs as textual information at application level
# Specify the ID of the metric to use in your analysys model
# to store the information
# (default: empty)
set OrphanRulesListId UNKNOWN_RULES_INFO
# The tool version to specify in the generated rules definitions
# The default value is ""
# Note that the toolName is the name of the folder you created
# for your custom Data Provider
set ToolVersion ""
# FileOrganisation defines the layout of the CSV file that is produced by your perl script:
# header::column: values are referenced from the column header
# header::line: NOT AVAILABLE
# alternate::line: NOT AVAILABLE
# alternate::column: NOT AVAILABLE
set FileOrganisation header::column
# In order to attach a finding to an artefact of type FILE:
# - Tool (optional) if present it overrides the name of the tool providing the finding
# - Path has to be the path of the file
# - Type has to be set to FILE
# - Line can be either empty or the line in the file where the finding is located
# Rule is the rule identifier, can be used as is or translated using Rule2Key
# Descr is the description message, which can be empty
#
# In order to attach a finding to an artefact of type FUNCTION:
# - Tool (optional) if present it overrides the name of the tool providing the finding
# - Path has to be the path of the file containing the function
# - Type has to be FUNCTION
# - If line is an integer, the system will try to find an artefact function
# at the given line of the file
# - If no Line or Line is not an integer, Name is used to find an artefact in
# the given file having name and signature as found in this column.
# (Line and Name are optional columns)
# Rule2Key contains a case-sensitive list of paired rule IDs:
# {RuleID KeyName}
# where:
# - RuleID is the id of the rule as defined in your analysis model
# - KeyName is the rule ID as written by your perl script in the produced CSV file
# Note: Rules that are not mapped keep their original name. The list of unmapped rules is in the log file generated by your Data Provider.
set Rule2Key {
{ ExtractedRuleID_1 MappedRuleId_1 }
{ ExtractedRuleID_2 MappedRuleId_2 }
}
====================
= CSV File Format =
====================
According to the options defined earlier in config.tcl, a valid csv file would be:
Path;Type;Line;Name;Rule;Descr
/src/project/module1/f1.c;FILE;12;;R1;Rule R1 is violated because variable v1
/src/project/module1/f1.c;FUNCTION;202;;R4;Rule R4 is violated because function f1
/src/project/module2/f2.c;FUNCTION;42;;R1;Rule R1 is violated because variable v2
/src/project/module2/f2.c;FUNCTION;;skip_line(int);R1;Rule R1 is violated because variable v2
Working With Paths:
===================
- Path seperators are unified: you do not need to worry about handling differences between Windows and Linux
- With the option PathsAreCaseInsensitive, case is ignored when searching for files in the Squore internal data
- Paths known by Squore are relative paths starting at the root of what was specified in the repository connector durign the analysis. This relative path is the one used to match with a path in a csv file.
Here is a valid example of file matching:
1. You provide C:\A\B\C\D as the root folder in a repository connector
2. C:\A\B\C\D contains E\e.c then Squore will know E/e.c as a file
3. You provide a csv file produced on linux and containing
/tmp/X/Y/E/e.c as path, then Squore will be able to match it with the known file.
Squore uses the longest possible match.
In case of conflict, no file is found and a message is sent to the log.
===============
= Perl Script =
===============
The perl scipt will receive as arguments:
- all parameters defined in form.xml (as -${key} $value)
- the input directory to process (only if ::NeedSources is set to 1)
- the location of the output directory where temporary files can be generated
- the full path of the findings csv file to be generated
For the form.xml and config.tcl we created earlier in this document, the command line will be:
perl <configuration_folder>/tools/CustomDP/CustomDP.pl -csv /path/to/csv -param MyValue <output_folder> <output_folder>/CustomDP.fdg.csv <output_folder>/CustomDP.fdg.csv
Example of perl script:
======================
#!/usr/bin/perl
use strict;
use warnings;
$|=1 ;
($csvKey, $csvValue, $paramKey, $paramValue, $output_folder, $output_csv) = @ARGV;
# Parse input CSV file
# ...
# Write results to CSV
open(CSVFILE, ">" . ${output_csv}) || die "perl: can not write: $!\n";
binmode(CSVFILE, ":utf8");
print CSVFILE "Path;Type;Line;Name;Rule;Descr";
print CSVFILE "/src/project/module1/f1.c;FILE;12;;R1;Rule R1 is violated because variable v1";
close CSVFILE;
exit 0;ExcelMetrics Reference
================
= ExcelMetrics =
================
The ExcelMetrics framework is used to extract information from one or more Microsoft Excel files (.xls or .xslx). A detailed configuration file allows defining how the Excel document should be read and what information should be extracted. This framework allows importing metrics, findings and textual information to existing artefacts or artefacts that will be created by the Data Provider.
============
= form.xml =
============
You can customise form.xml to either:
- specify the path to a single Excel file to import
- specify a pattern to import all Excel files matching this pattern in a directory
In order to import a single Excel file:
=====================================
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<tags baseName="ExcelMetrics" needSources="false">
<tag type="text" key="excel" defaultValue="/path/to/mydata.xslx" />
</tags>
Notes:
- The excel key is mandatory.
In order to import all files matching a patter in a folder:
===========================================================
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<tags baseName="ExcelMetrics" needSources="false">
<!-- Root directory containing Excel files to import-->
<tag type="text" key="dir" defaultValue="/path/to/mydata" />
<!-- Pattern that needs to be matched by a file name in order to import it-->
<tag type="text" key="ext" defaultValue="*.xlsx" />
<!-- search for files in sub-folders -->
<tag type="booleanChoice" defaultValue="true" key="sub" />
</tags>
Notes:
- The dir and ext keys are mandatory
- The sub key is optional (and its value set to false if not specified)
==============
= config.tcl =
==============
Sample config.tcl file:
=======================
# The separator to be used in the generated csv file
# Usually \t or ; or ,
set Separator ";"
# The delimiter used in the input CSV file
# This is normally left empty, except when you know that some of the values in the CSV file
# contain the separator itself, for example:
# "A text containing ; the separator";no problem;end
# In this case, you need to set the delimiter to \" in order for the data provider to find 3 values instead of 4.
# To include the delimiter itself in a value, you need to escape it by duplicating it, for example:
# "A text containing "" the delimiter";no problemo;end
# Default: none
set Delimiter \"
# The path separator in an artefact's path
# in the generated CSV file.
set ArtefactPathSeparator "/"
# Ignore findings for artefacts that are not part of the project (orphan findings)
# When set to 1, the findings are ignored
# When set to 0, the findings are imported and attached to the APPLICATION node
# (default: 1)
set IgnoreIfArtefactNotFound 1
# For findings of a type that is not in your ruleset, set a default rule ID.
# The value for this parameter must be a valid rule ID from your analysys model.
# (default: empty)
set UnknownRuleId UNKNOWN_RULE
# Save the total count of orphan findings as a metric at application level
# Specify the ID of the metric to use in your analysys model
# to store the information
# (default: empty)
set OrphanArteCountId NB_ORPHANS
# Save the total count of unknown rules as a metric at application level
# Specify the ID of the metric to use in your analysys model
# to store the information
# (default: empty)
set OrphanRulesCountId NB_UNKNOWN_RULES
# Save the list of unknown rule IDs as textual information at application level
# Specify the ID of the metric to use in your analysys model
# to store the information
# (default: empty)
set OrphanRulesListId UNKNOWN_RULES_INFO
# The list of the Excel sheets to read, each sheet has the number of the first line to read
# A Perl regexp pattern can be used instead of the name of the sheet (the first sheet matching
# the pattern will be considered)
set Sheets {{Baselines 5} {ChangeNotes 5}}
# ######################
# # COMMON DEFINITIONS #
# ######################
#
# - <value> is a list of column specifications whose values will be concatened. When no column name is present, the
# text is taken as it appears. Optional sheet name can be added (with ! char to separate from the column name)
# Examples:
# - {C:} the value will be the value in column C on the current row
# - {C: B:} the value will be the concatenation of values found in column C and B of the current row
# - {Deliveries} the value will be Deliveries
# - {BJ: " - " BL:} the value will be the concatenation of value found in column BJ,
# string " - " and the value found in column BL fo the current row
# - {OtherSheet!C:} the value will be the value in column C from the sheet OtherSheet on the current row
#
# - <condition> is a list of conditions. An empty condition is always true. A condition is a column name followed by colon,
# optionally followed by a perl regexp. Optional sheet name can be added (with ! char to separate from the column name)
# Examples:
# - {B:} the value in column B must be empty on the current row
# - {B:.+} the value in column B can not be empty on the current row
# - {B:R_.+} the value in column B is a word starting by R_ on the current row
# - {A: B:.+ C:R_.+} the value in column A must be empty and the value in column B must contain something and
# the column C contains a word starting with R_ on the current row
# - {OtherSheet!B:.+} the value in column B from sheet OtherSheet on the current row can not be empty.
# #############
# # ARTEFACTS #
# #############
# The variable is a list of artefact hierarchy specification:
# {ArtefactHierarchySpec1 ArtefactHierarchySpec2 ... ArtefactHierarchySpecN}
# where each ArtefactHierarchySpecx is a list of ArtefactSpec
#
# An ArtefactSpec is a list of items, each item being:
# {<(sheetName!)?artefactType> <conditions> <name> <parentType>? <parentName>?}
# where:
# - <(sheetName!)?artefactType>: allows specifying the type. Optional sheetName can be added (with ! char to separate from the type) to limit
# the artefact search in one specific sheet. When Sheets are given with regexp, the same regexp has to be used
# for the sheetName.
# If the type is followed by a question mark (?), this level of artefact is optional.
# If the type is followed by a plus char (+), this level is repeatable on the next row
# - <condition>: see COMMON DEFINITIONS
# - <value>: the name of the artefact to build, see COMMON DEFINITIONS
#
# - <parentType>: This element is optional. When present, it means that the current element will be attached to a parent having this type
# - <parentValue>: This is a list like <value> to build the name of the artefact of type <parentType>. If such artefact is not found,
# the current artefact does not match
#
# Note: to add metrics at application level, specify an APPLICATION artefact which will match only one line:
# e.g. {APPLICATION {A:.+} {}} will recognize as application the line having column A not empty.
set ArtefactsSpecs {
{
{DELIVERY {} {Deliveries}}
{RELEASE {E:.+} {E:}}
{SPRINT {O:SW_Software} {Q:}}
}
{
{DELIVERY {} {Deliveries}}
{RELEASE {O:SY_System} {Q:}}
}
{
{WP {BL:.+ AF:.+} {BJ: " - " BL:} SPRINT {AF:}}
{ChangeNotes!TASK {D:(added|changed|unchanged) T:imes} {W: AD:}}
}
{
{WP {} {{Unplanned imes}} SPRINT {AF:}}
{TASK {BL: D:(added|changed|unchanged) T:imes W:.+} {W: AD:}}
}
}
# ###########
# # METRICS #
# ###########
# Specification of metrics to be retreived
# This is a list where each element is:
# {<artefactTypeList> <metricId> <condition> <value> <format>}
# Where:
# - <artefactTypeList>: the list of artefact types for which the metric has to be used
# each element of the list is (sheetName!)?artefactType where sheetName is used
# to restrict search to only one sheet. sheetName is optional.
# - <metricId>: the name of the MeasureId to be injected into Squore, as defined in your analysis model
# - <confition>: see COMMON DEFINITIONS above. This is the condition for the metric to be generated.
# - <value> : see COMMON DEFINITIONS above. This is the value for the metric (can be built from multi column)
# - <format> : optional, defaults to NUMBER
# Possible format are:
# * DATE_FR, DATE_EN for date stored as string
# * DATE for cell formatted as date
# * NUMBER_FR, NUMBER_EN for number stored as string
# * NUMBER for cell formatted as number
# * LINES for counting the number of text lines in a cell
# - <formatPattern> : optional
# Only used by the LINES format.
# This is a pattern (can contain perl regexp) used to filter lines to count
set MetricsSpecs {
{{RELEASE SPRINT} TIMESTAMP {} {A:} DATE_EN}
{{RELEASE SPRINT} DATE_ACTUAL_RELEASE {} {S:} DATE_EN}
{{RELEASE SPRINT} DATE_FINISH {} {T:} DATE_EN}
{{RELEASE SPRINT} DELIVERY_STATUS {} {U:}}
{{WP} WP_STATUS {} {BO:}}
{{ChangeNotes!TASK} IS_UNPLAN {} {BL:}}
{{TASK WP} DATE_LABEL {} {BP:} DATE_EN}
{{TASK WP} DATE_INTEG_PLAN {} {BD:} DATE_EN}
{{TASK} TASK_STATUS {} {AE:}}
{{TASK} TASK_TYPE {} {AB:}}
}
# ############
# # FINDINGS #
# ############
# This is a list where each element is:
# {<artefactTypeList> <findingId> <condition> <value> <localisation>}
# Where:
# - <artefactTypeList>: the list of artefact type for which the metric has to be used
# each element of the list is (sheetName!)?artefactType where sheetName is used
# to restrict search to only one sheet. sheetName is optional.
# - <findingId>: the name of the FindingId to be injected into Squore, as defined in your analysis model
# - <confition>: see COMMON DEFINITIONS above. This is the condition for the finding to be triggered.
# - <value>: see COMMON DEFINITIONS above. This is the value for the message of the finding (can be built from multi column)
# - <localisation>: this a <value> representing the localisation of the finding (free text)
set FindingsSpecs {
{{WP} {BAD_WP} {BL:.+ AF:.+} {{This WP is not in a correct state } AF:.+} {A:}}
}
# #######################
# # TEXTUAL INFORMATION #
# #######################
# This is a list where each element is:
# {<artefactTypeList> <infoId> <condition> <value>}
# Where:
# - <artefactTypeList> the list of artefact types for which the info has to be used
# each element of the list is (sheetName!)?artefactType where sheetName is used
# to restrict search to only one sheet. sheetName is optional.
# - <infoId> : is the name of the Information to be attached to the artefact, as defined in your analysis model
# - <confition> : see COMMON DEFINITIONS above. This is the condition for the info to be generated.
# - <value> : see COMMON DEFINITIONS above. This is the value for the info (can be built from multi column)
set InfosSpecs {
{{TASK} ASSIGN_TO {} {XB:}}
}
# ########################
# # LABEL TRANSFORMATION #
# ########################
# This is a list value specification for MeasureId or InfoId:
# <MeasureId|InfoId> { {<LABEL1> <value1>} ... {<LABELn> <valuen>}}
# Where:
# - <MeasureId|InfoId> : is either a MeasureId, an InfoId, or * if it is available for every measureid/infoid
# - <LABELx> : is the label to macth (can contain perl regexp)
# - <valuex> : is the value to replace the label by, it has to match the correct format for the metrics (no format for infoid)
#
# Note: only metrics which are labels in the excel file or information which need to be rewriten, need to be described here.
set Label2ValueSpec {
{
STATUS {
{OPENED 0}
{ANALYZED 1}
{CLOSED 2}
{.* -1}
}
}
{
* {
{FATAL 0}
{ERROR 1}
{WARNING 2}
{{LEVEL:\s*0} 1}
{{LEVEL:\s*1} 2}
{{LEVEL:\s*[2-9]+} 3}
}
}
}
Note that a sample Excel file with its associated config.tcl is available in $SQUORE_HOME/addons/tools/ExcelMetrics in order to further explain available configuration options.Appendix B: Squore XML Schemas
input-data-2.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified">
<xs:simpleType name="id">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value="[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="relax-status">
<xs:restriction base="id">
<xs:enumeration value="RELAXED_DEROGATION"/>
<xs:enumeration value="RELAXED_LEGACY"/>
<xs:enumeration value="RELAXED_FALSE_POSITIVE"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:element name="bundle">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:choice maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="artifact"/>
<xs:element ref="finding"/>
<xs:element ref="info"/>
<xs:element ref="link"/>
<xs:element ref="metric"/>
</xs:choice>
<xs:attribute name="version" use="required" type="xs:integer" fixed="2"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="artifact">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="artifact"/>
<xs:element ref="finding"/>
<xs:element ref="metric"/>
<xs:element ref="key"/>
<xs:element ref="info"/>
<xs:element ref="link"/>
<xs:element ref="milestone"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="alias"/>
<xs:attribute name="art-location"/>
<xs:attribute name="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="local-art-location"/>
<xs:attribute name="local-key"/>
<xs:attribute name="local-parent"/>
<xs:attribute name="location"/>
<xs:attribute name="name"/>
<xs:attribute name="parent"/>
<xs:attribute name="path"/>
<xs:attribute name="type" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="view-path"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="info">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="local-ref"/>
<xs:attribute name="name" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="ref"/>
<xs:attribute name="tool"/>
<xs:attribute name="value" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="key">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="value" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="metric">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="local-ref"/>
<xs:attribute name="name" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="ref"/>
<xs:attribute name="tool"/>
<xs:attribute name="value" type="xs:decimal" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="link">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="dst"/>
<xs:attribute name="local-dst" type="xs:integer"/>
<xs:attribute name="local-src" type="xs:integer"/>
<xs:attribute name="name" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="src"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="finding">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="location"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1" ref="relax"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="descr"/>
<xs:attribute name="local-ref"/>
<xs:attribute name="location" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="name" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="p0"/>
<xs:attribute name="p1"/>
<xs:attribute name="p2"/>
<xs:attribute name="p3"/>
<xs:attribute name="p4"/>
<xs:attribute name="p5"/>
<xs:attribute name="p6"/>
<xs:attribute name="p7"/>
<xs:attribute name="p8"/>
<xs:attribute name="p9"/>
<xs:attribute name="q0"/>
<xs:attribute name="q1"/>
<xs:attribute name="q2"/>
<xs:attribute name="q3"/>
<xs:attribute name="q4"/>
<xs:attribute name="q5"/>
<xs:attribute name="q6"/>
<xs:attribute name="q7"/>
<xs:attribute name="q8"/>
<xs:attribute name="q9"/>
<xs:attribute name="ref"/>
<xs:attribute name="tool"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="location">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="local-ref"/>
<xs:attribute name="location" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="ref"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="relax">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:simpleContent>
<xs:extension base="xs:string">
<xs:attribute name="status" type="relax-status"/>
</xs:extension>
</xs:simpleContent>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="milestone">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="goal"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="date" use="required" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:attribute name="name" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="displayName" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="goal">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="name" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="value" use="required" type="xs:decimal"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>form.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified">
<xs:simpleType name="id">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value='[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+' />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="project-status">
<xs:restriction base="id">
<xs:enumeration value="IGNORE"/>
<xs:enumeration value="WARNING"/>
<xs:enumeration value="ERROR"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:element name="tags">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element maxOccurs="0" ref="tag"/>
<xs:element maxOccurs="0" ref="exec-phase"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="baseName"/>
<xs:attribute name="deleteTmpSrc" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="image"/>
<xs:attribute name="needSources" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="projectStatusOnFailure" type="project-status"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="tag">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="values"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="value"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="displayIf"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="changeable" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="credentialType"/>
<xs:attribute name="defaultValue"/>
<xs:attribute name="displayType"/>
<xs:attribute name="key" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="optionTitle"/>
<xs:attribute name="required" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="style"/>
<xs:attribute name="type" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="multi" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="hide" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="converter"/>
<xs:attribute name="image"/>
<xs:attribute name="inverted" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="acceptedTypes"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="value">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="key" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="name"/>
<xs:attribute name="option"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="values">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="type" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="displayIf">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="and"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="or"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="notEmpty"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="equals"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="and">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="and"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="or"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="notEmpty"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="equals"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="or">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="and"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="or"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="notEmpty"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="equals"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="notEmpty">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="key" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="equals">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="key" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="value"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="exec-phase">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" ref="exec"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" ref="exec-tool"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="id" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="exec">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element maxOccurs="0" ref="arg"/>
<xs:element maxOccurs="0" ref="env"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="name" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="arg">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="tag"/>
<xs:attribute name="value"/>
<xs:attribute name="defaultValue"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="env">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="key" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="value"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="exec-tool">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element maxOccurs="0" ref="param"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="name" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="param">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="key" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="tag"/>
<xs:attribute name="value"/>
<xs:attribute name="defaultValue"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>properties-1.2.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" version="1.0">
<xs:element name="Bundle" type="bundleType"/>
<xs:complexType name="bundleType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element name="help" type="helpType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
<xs:element name="hideObsoleteModels" type="obsoleteType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="hideModel" type="hiddenType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
<xs:element name="explorerTabs" type="tabsType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="explorerTrees" type="treesType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xs:element name="option" type="optionType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="version" use="required" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="helpType">
<xs:attribute name="label" use="required" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:attribute name="url" use="required" type="xs:anyURI"/>
<xs:attribute name="profiles" use="optional" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="optionType">
<xs:attribute name="name" use="required" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:attribute name="value" use="required" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="obsoleteType">
<xs:attribute name="value" use="optional" default="false" type="xs:boolean"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="hiddenType">
<xs:attribute name="name" use="required" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="tabsType">
<xs:sequence maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element name="tab" type="tabType" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="hideSettings" use="optional" default="false" type="xs:boolean"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="tabType">
<xs:attribute name="name" use="required" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:attribute name="default" use="optional" default="false" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="mandatory" use="optional" default="false" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="rendered" use="optional" default="true" type="xs:boolean"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="treesType">
<xs:sequence maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element name="tree" type="treeType" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="treeType">
<xs:attribute name="name" use="required" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:attribute name="rendered" use="optional" default="true" type="xs:boolean"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>config-1.3.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" version="1.0">
<xs:element name="squore" type="squoreType"/>
<xs:complexType name="squoreType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="paths" type="pathsType"/>
<xs:element name="database" type="databaseType" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="phantomjs" type="phantomjsType" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="configuration" type="directoriesType"/>
<xs:element name="addons" type="directoriesType"/>
<xs:element name="client" type="dataDirectoriesType" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="tmp" type="directoryType" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="projects" type="projectType" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="sources" type="directoryType" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="workspace" type="directoryType" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="type" use="required" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:attribute name="version" use="required" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="pathsType">
<xs:sequence maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element name="path" type="pathType"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="pathType">
<xs:attribute name="name" use="required" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:attribute name="path" use="required" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="directoriesType">
<xs:sequence maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element name="path" type="directoryType"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="directoryType">
<xs:attribute name="directory" use="required" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="databaseType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="postgresql" type="directoryType" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="cluster" type="directoryType" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="backup" type="directoryType"/>
<xs:element name="security" type="securityType" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="phantomjsType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="socket-binding" type="socketBindingType" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="socketBindingType">
<xs:attribute name="address" type="xs:string" default="127.0.0.1"/>
<xs:attribute name="port" type="xs:short" default="3003"/>
<xs:attribute name="squore-url" type="xs:string" default=""/>
<xs:attribute name="distant-url" type="xs:string" default=""/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="securityType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="user-name" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="dataDirectoriesType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="tmp" type="directoryType" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="projects" type="projectType" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="sources" type="directoryType" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="projectType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="data-providers" type="dpType" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="directory" use="required" type="xs:string"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="dpType">
<xs:attribute name="keep-data-files" use="required" type="xs:boolean"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>analysis.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified">
<xs:simpleType name="id">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value='[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+' />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="list-id">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value='[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+(;[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+)*' />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="families">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value='[A-Z0-9_]+(;[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+)*' />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="categories">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value='[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+\.[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+(;[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+\.[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+)*' />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="measure-type">
<xs:restriction base="id">
<xs:enumeration value="METRIC"/>
<xs:enumeration value="RULE"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="format">
<xs:restriction base="id">
<xs:enumeration value="NUMBER"/>
<xs:enumeration value="PERCENT"/>
<xs:enumeration value="INTEGER"/>
<xs:enumeration value="DATE"/>
<xs:enumeration value="DATETIME"/>
<xs:enumeration value="TIME"/>
<xs:enumeration value="DAYS"/>
<xs:enumeration value="HOURS"/>
<xs:enumeration value="MINUTES"/>
<xs:enumeration value="SECONDS"/>
<xs:enumeration value="MILLISECONDS"/>
<xs:enumeration value="MAN_DAYS"/>
<xs:enumeration value="MAN_HOURS"/>
<xs:enumeration value="MAN_MINUTES"/>
<xs:enumeration value="MAN_SECONDS"/>
<xs:enumeration value="MAN_MILLISECONDS"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="datetime-style">
<xs:restriction base="id">
<xs:enumeration value="DEFAULT"/>
<xs:enumeration value="SHORT"/>
<xs:enumeration value="MEDIUM"/>
<xs:enumeration value="LONG"/>
<xs:enumeration value="FULL"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="rounding-mode">
<xs:restriction base="id">
<xs:enumeration value="UP"/>
<xs:enumeration value="DOWN"/>
<xs:enumeration value="CEILING"/>
<xs:enumeration value="FLOOR"/>
<xs:enumeration value="HALF_UP"/>
<xs:enumeration value="HALF_DOWN"/>
<xs:enumeration value="HALF_EVEN"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="bounds-type">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value='[\[\]]((-)*[0-9](\.[0-9]+)?)*;((-)*[0-9](.[0-9]+)?)*[\[\]]' />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="path-scope">
<xs:restriction base="id">
<xs:enumeration value="CHILDREN"/>
<xs:enumeration value="DESCENDANTS"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:complexType name="elements">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="ArtefactType"/>
<xs:element ref="Indicator"/>
<xs:element ref="Measure"/>
<xs:element ref="Package"/>
<xs:element ref="package"/>
<xs:element ref="Scale"/>
<xs:element ref="ScaleMacro"/>
<xs:element ref="Constant"/>
<xs:element ref="RootIndicator"/>
<xs:element ref="UpdateRules"/>
<xs:element ref="UpdateRule"/>
<xs:element ref="Link"/>
<xs:element ref="ComputedLink"/>
<xs:element ref="FindingStatus"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="providedBy"/>
<xs:attribute name="name"/>
<xs:attribute name="storedOnlyIfDisplayed" type="xs:boolean"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:element name="Bundle" type="elements" />
<xs:element name="Package" type="elements"/>
<xs:element name="package" type="elements"/>
<xs:element name="Constant">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="id" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="value" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="RootIndicator">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="artefactTypes" use="required" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="indicatorId" use="required" type="id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="UpdateRules">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="UpdateRule"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="UpdateRule">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="categories" type="categories"/>
<xs:attribute name="disabled" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="measureId" use="required" type="id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Measure">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="Computation"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="acceptMissingValue" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="categories" type="categories"/>
<xs:attribute name="dataBounds" type="bounds-type"/>
<xs:attribute name="dateStyle" type="datetime-style"/>
<xs:attribute name="decimals" type="xs:integer"/>
<xs:attribute name="defaultValue" type="xs:decimal"/>
<xs:attribute name="excludingTypes" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="invalidValue"/>
<xs:attribute name="families" type="families"/>
<xs:attribute name="format" type="format"/>
<xs:attribute name="manual" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="measureId" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="noValue"/>
<xs:attribute name="pattern"/>
<xs:attribute name="roundingMode" type="rounding-mode"/>
<xs:attribute name="suffix"/>
<xs:attribute name="targetArtefactTypes"/>
<xs:attribute name="timeStyle" type="datetime-style"/>
<xs:attribute name="toolName"/>
<xs:attribute name="toolVersion"/>
<xs:attribute name="type" type="measure-type"/>
<xs:attribute name="usedForRelaxation" type="xs:boolean"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Computation">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="continueOnRelaxed" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="excludingTypes" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="result" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="stored" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="targetArtefactTypes" use="required" type="list-id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Indicator">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="displayedScale" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="displayedValue" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="displayTypes" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="excludingTypes" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="families" type="families"/>
<xs:attribute name="indicatorId" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="measureId" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="scaleId" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="targetArtefactTypes" type="list-id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Scale">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="ScaleLevel"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="isDynamic" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="macro" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="scaleId" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="targetArtefactTypes" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="excludingTypes" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="vars"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="ScaleMacro">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="ScaleLevel"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="id" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="isDynamic" type="xs:boolean"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="ArtefactType">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="heirs" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="id" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="manual" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="parents" type="list-id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="ScaleLevel">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="bounds" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="levelId" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="rank" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Link">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="id" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="inArtefactTypes" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="outArtefactTypes" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="srcArtefactTypes" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="dstArtefactTypes" type="list-id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="ComputedLink">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="1" ref="StartPath"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="NextPath"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="id" use="required" type="id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="StartPath">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="link" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="scope" type="path-scope"/>
<xs:attribute name="srcArtefactTypes" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="dstArtefactTypes" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="srcCondition"/>
<xs:attribute name="dstCondition"/>
<xs:attribute name="recurse" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="keepIntermediateLinks" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="dstToSrc" type="xs:boolean"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="NextPath">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="link" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="scope" type="path-scope"/>
<xs:attribute name="dstArtefactTypes" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="dstCondition"/>
<xs:attribute name="recurse" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="keepIntermediateLinks" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="dstToSrc" type="xs:boolean"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="FindingStatus">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="id" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="type" use="required" type="id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>decision.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified">
<xs:simpleType name="id">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value='[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+' />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="list-id">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value='[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+(;[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+)*' />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="categories">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value='[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+\.[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+(;[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+\.[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+)*' />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="criterion-type">
<xs:restriction base="id">
<xs:enumeration value="BENEFIT"/>
<xs:enumeration value="COST"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="preference-level">
<xs:restriction base="id">
<xs:enumeration value="VERY_LOW"/>
<xs:enumeration value="LOW"/>
<xs:enumeration value="MEDIUM"/>
<xs:enumeration value="HIGH"/>
<xs:enumeration value="VERY_HIGH"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:complexType name="elements">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="Package"/>
<xs:element ref="package"/>
<xs:element ref="DecisionCriteria"/>
<xs:element ref="DecisionCriterion"/>
<xs:element ref="FindingsActionPlan"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:element name="Bundle" type="elements"/>
<xs:element name="Package" type="elements"/>
<xs:element name="package" type="elements"/>
<xs:element name="DecisionCriteria" type="elements"/>
<xs:element name="DecisionCriterion">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element ref="Triggers"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="categories" type="categories"/>
<xs:attribute name="dcId" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="excludingTypes" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="families" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="roles" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="targetArtefactTypes" use="required" type="list-id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Triggers">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="Trigger"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Trigger">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="Test"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Test">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="bounds"/>
<xs:attribute name="descrId" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="expr" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="p0"/>
<xs:attribute name="p1"/>
<xs:attribute name="p2"/>
<xs:attribute name="p3"/>
<xs:attribute name="p4"/>
<xs:attribute name="p5"/>
<xs:attribute name="p6"/>
<xs:attribute name="p7"/>
<xs:attribute name="p8"/>
<xs:attribute name="p9"/>
<xs:attribute name="suspect"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="FindingsActionPlan">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="CategoryCriterion"/>
<xs:element ref="OccurrencesCriterion"/>
<xs:element ref="VariableCriterion"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="limit" type="xs:integer"/>
<xs:attribute name="priorityScaleId" type="id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="CategoryCriterion">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="type" type="criterion-type"/>
<xs:attribute name="preferenceLevel" type="preference-level"/>
<xs:attribute name="scaleId" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="excludeLevels" type="list-id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="OccurrencesCriterion">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="type" type="criterion-type"/>
<xs:attribute name="preferenceLevel" type="preference-level"/>
<xs:attribute name="scaleId" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="excludeLevels" type="list-id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="VariableCriterion">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="type" type="criterion-type"/>
<xs:attribute name="preferenceLevel" type="preference-level"/>
<xs:attribute name="indicatorId" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="excludeLevels" type="list-id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>description.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified">
<xs:complexType name="elements">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="Package"/>
<xs:element ref="package"/>
<xs:element ref="Properties"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:element name="Bundle">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="Package"/>
<xs:element ref="package"/>
<xs:element ref="Properties"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="available"/>
<xs:attribute name="default"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Package" type="elements"/>
<xs:element name="package" type="elements"/>
<xs:element name="Properties">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="src" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>exports.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified">
<xs:simpleType name="type-id">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value='[A-Z0-9_]*' />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:element name="Package">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="Package" />
<xs:element ref="Role" />
<xs:element ref="ExportScript" />
<xs:element ref="ExportDef" />
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Bundle">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="Package" />
<xs:element ref="Role" />
<xs:element ref="ExportScript" />
<xs:element ref="ExportDef" />
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Role">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="Export" />
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="name" use="required" type="xs:string" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Export">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="ExportScript" />
<xs:element ref="ExportDef" />
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="type" use="required" type="type-id" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="ExportScript">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="arg" />
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="name" use="required" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="script" use="required" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="onArtefactTypes" />
<xs:attribute name="onExcludingTypes" />
<xs:attribute name="roles" />
<xs:attribute name="groups" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="arg">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="value" use="required" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="optional" use="optional" type="xs:boolean" default="false" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="ExportDef">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="name" use="required" />
<xs:attribute name="onArtefactTypes" />
<xs:attribute name="onExcludingTypes" />
<xs:attribute name="roles" />
<xs:attribute name="groups" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>highlights.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<xs:simpleType name="id">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value='[A-Z0-9_]*' />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="measure-id">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value='([BD].)?[A-Z0-9_]*' />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="info-id">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value='[A-Z0-9_]*' />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="indicator-id">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value='([I].)?[A-Z0-9_]*' />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="bounds-type">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value='[\[\]]((-)*[0-9](\.[0-9]+)?)*;((-)*[0-9](.[0-9]+)?)*[\[\]]' />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="top-order">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="ASC" />
<xs:enumeration value="DESC" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="link-direction">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="IN" />
<xs:enumeration value="OUT" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="result-size">
<xs:union>
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:positiveInteger" />
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="*" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:union>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="header-display-type">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="MNEMONIC" />
<xs:enumeration value="NAME" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="display-type">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="VALUE" />
<xs:enumeration value="RANK" />
<xs:enumeration value="ICON" />
<xs:enumeration value="DATE" />
<xs:enumeration value="DATETIME" />
<xs:enumeration value="TIME" />
<xs:enumeration value="NAME" />
<xs:enumeration value="MNEMONIC" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="date-style">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="SHORT" />
<xs:enumeration value="MEDIUM" />
<xs:enumeration value="DEFAULT" />
<xs:enumeration value="LONG" />
<xs:enumeration value="FULL" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:complexType name="elements">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="Package" />
<xs:element ref="Role" />
<xs:element ref="Filters" />
<xs:element ref="TopArtefacts" />
<xs:element ref="TopDeltaArtefacts" />
<xs:element ref="TopNewArtefacts" />
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:element name="Bundle" type="elements" />
<xs:element name="Package" type="elements"/>
<xs:element name="TopDeltaArtefacts" type="top-artefacts" />
<xs:element name="TopNewArtefacts" type="top-artefacts" />
<xs:element name="TopArtefacts">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:choice>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="Column" />
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="Where" />
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1" ref="where" />
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="OrderBy" />
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="id" use="required" type="id" />
<xs:attribute name="hideRating" use="optional" type="xs:boolean" />
<xs:attribute name="hidePath" use="optional" type="xs:boolean" />
<xs:attribute name="name" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="onArtefactTypes" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="roles" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="groups" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="artefactTypes" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="excludingTypes" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="measureId" use="optional" default="LEVEL" type="measure-id" />
<xs:attribute name="order" use="optional" default="ASC" type="top-order" />
<xs:attribute name="altMeasureId" use="optional" type="measure-id" />
<xs:attribute name="altOrder" use="optional" type="top-order" />
<xs:attribute name="resultSize" use="required" type="result-size" />
<xs:attribute name="linkType" use="optional" type="id" />
<xs:attribute name="linkDirection" use="optional" type="link-direction" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:complexType name="top-artefacts">
<xs:sequence maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:choice>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="Column" />
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="Where" />
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1" ref="where" />
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="OrderBy" />
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="id" use="required" type="id" />
<xs:attribute name="hideRating" use="optional" type="xs:boolean" />
<xs:attribute name="hidePath" use="optional" type="xs:boolean" />
<xs:attribute name="name" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="onArtefactTypes" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="roles" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="groups" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="artefactTypes" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="excludingTypes" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="measureId" use="optional" default="LEVEL" type="measure-id" />
<xs:attribute name="order" use="optional" default="ASC" type="top-order" />
<xs:attribute name="resultSize" use="required" type="result-size" />
<xs:attribute name="linkType" use="optional" type="id" />
<xs:attribute name="linkDirection" use="optional" type="link-direction" />
</xs:complexType>
<xs:element name="Role">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="Filters" />
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="name" use="required" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="preSelectedType" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Filters">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:choice>
<xs:element ref="TopArtefacts" />
<xs:element ref="TopDeltaArtefacts" />
<xs:element ref="TopNewArtefacts" />
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="type" use="required" type="xs:string" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Column">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="measureId" use="optional" type="measure-id" />
<xs:attribute name="infoId" use="optional" type="info-id" />
<xs:attribute name="indicatorId" use="optional" type="indicator-id" />
<xs:attribute name="artefactTypes" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="excludingTypes" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="headerDisplayType" use="optional" default="NAME" type="header-display-type" />
<xs:attribute name="displayType" use="optional" default="VALUE" type="display-type" />
<xs:attribute name="decimals" use="optional" default="2" type="xs:integer" />
<xs:attribute name="dateStyle" use="optional" default="DEFAULT" type="date-style" />
<xs:attribute name="timeStyle" use="optional" default="DEFAULT" type="date-style" />
<xs:attribute name="datePattern" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="suffix" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="useBackgroundColor" use="optional" type="xs:boolean" />
<xs:attribute name="showTrend" use="optional" type="xs:boolean" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="Where">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="measureId" use="optional" type="measure-id" />
<xs:attribute name="infoId" use="optional" type="info-id" />
<xs:attribute name="value" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="bounds" use="optional" type="bounds-type" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="where">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:choice>
<xs:element ref="measure" />
<xs:element ref="indicator" />
<xs:element ref="info" />
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="measure">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="measure-id" />
<xs:attribute name="values" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="bounds" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="invert" use="optional" type="xs:boolean" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="indicator">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="indicator-id" />
<xs:attribute name="levels" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="invert" use="optional" type="xs:boolean" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="info">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="id" type="info-id" />
<xs:attribute name="values" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="patterns" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="invert" use="optional" type="xs:boolean" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="OrderBy">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="measureId" use="required" type="measure-id" />
<xs:attribute name="order" use="optional" default="ASC" type="top-order" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>properties.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified">
<xs:simpleType name="id">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value='[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+' />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="list-id">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value='[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+(;[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+)*' />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="aggregation-type">
<xs:restriction base="id">
<xs:enumeration value="MIN"/>
<xs:enumeration value="MAX"/>
<xs:enumeration value="OCC"/>
<xs:enumeration value="AVG"/>
<xs:enumeration value="DEV"/>
<xs:enumeration value="SUM"/>
<xs:enumeration value="MED"/>
<xs:enumeration value="MOD"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:complexType name="elements">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="package"/>
<xs:element ref="hideMeasure"/>
<xs:element ref="findingsTab"/>
<xs:element ref="actionItemsTab"/>
<xs:element ref="rulesEdition"/>
<xs:element ref="scoreGroups"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:element name="bundle" type="elements"/>
<xs:element name="package" type="elements"/>
<xs:element name="hideMeasure">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="path" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="targetArtefactTypes" type="list-id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="findingsTab">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="orderBy" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="hideColumns" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="hideCharacteristicsFilter" type="xs:boolean"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="actionItemsTab">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="orderBy" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="hideColumns" type="list-id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="rulesEdition">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="scales" use="required" type="list-id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="scoreGroups">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="indicatorId" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="aggregationType" type="aggregation-type"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>tutorials.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<xs:simpleType name="external-id">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value="[A-Z]{1}[A-Z0-9_]*" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="positive-integer">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value="[0-9]+" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="opacity">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value='(0|1){1}\.?[0-9]\{0,2}' />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="actions">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="EXPAND_PORTFOLIO_TREE" />
<xs:enumeration value="EXPAND_ARTEFACT_TREE" />
<xs:enumeration value="EXPAND_MEASURE_TREE" />
<xs:enumeration value="COLLAPSE_PORTFOLIO_TREE" />
<xs:enumeration value="COLLAPSE_ARTEFACT_TREE" />
<xs:enumeration value="COLLAPSE_MEASURE_TREE" />
<xs:enumeration value="SELECT_MODEL" />
<xs:enumeration value="SELECT_PROJECT" />
<xs:enumeration value="SELECT_ARTEFACT" />
<xs:enumeration value="SELECT_ARTEFACT_LEAF" />
<xs:enumeration value="CLOSE_MEASURE_POPUP" />
<xs:enumeration value="SELECT_MEASURE" />
<xs:enumeration value="SHOW_REVIEW_SET" />
<xs:enumeration value="SHOW_PORTFOLIO_TREE" />
<xs:enumeration value="SHOW_DASHBOARD_TAB" />
<xs:enumeration value="SHOW_ACTION_ITEMS_TAB" />
<xs:enumeration value="SHOW_HIGHLIGHTS_TAB" />
<xs:enumeration value="SHOW_FINDINGS_TAB" />
<xs:enumeration value="SHOW_REPORTS_TAB" />
<xs:enumeration value="SHOW_FORMS_TAB" />
<xs:enumeration value="SHOW_INDICATORS_TAB" />
<xs:enumeration value="SHOW_MEASURES_TAB" />
<xs:enumeration value="SHOW_COMMENTS_TAB" />
<xs:enumeration value="SHOW_ACTION_ITEMS_ADVANCED_SEARCH" />
<xs:enumeration value="EXPAND_ACTION_ITEM" />
<xs:enumeration value="SHOW_FINDINGS_ADVANCED_SEARCH" />
<xs:enumeration value="SELECT_FINDING" />
<xs:enumeration value="SELECT_FINDING_ARTEFACT" />
<xs:enumeration value="EXPAND_FINDING" />
<xs:enumeration value="EXPAND_ATTRIBUTE" />
<xs:enumeration value="SWITCH_INDICATORS_PAGE" />
<xs:enumeration value="SWITCH_MEASURES_PAGE" />
<xs:enumeration value="SWITCH_COMMENTS_PAGE" />
<xs:enumeration value="CLOSE_CHART_POPUP" />
<xs:enumeration value="OPEN_CHART_POPUP" />
<xs:enumeration value="OPEN_MODEL_CHART_POPUP" />
<xs:enumeration value="SELECT_DESCR_TAB" />
<xs:enumeration value="SELECT_COMMENTS_TAB" />
<xs:enumeration value="SELECT_FAVORITES_TAB" />
<xs:enumeration value="COMPARE_CHART" />
<xs:enumeration value="QUIT_COMPARATIVE_MODE" />
<xs:enumeration value="QUIT_FULLDISPLAY_MODE" />
<xs:enumeration value="CLOSE_ARTEFACT_TREE_FILTER" />
<xs:enumeration value="SHOW_ARTEFACT_TREE_FILTER" />
<xs:enumeration value="OPEN_TABLE" />
<xs:enumeration value="CHANGE_PAGE" />
<xs:enumeration value="CREATE_NEW_PROJECT" />
<xs:enumeration value="SELECT_WIZARD" />
<xs:enumeration value="VALIDATE_WIZARD" />
<xs:enumeration value="VALIDATE_INFORMATION" />
<xs:enumeration value="VALIDATE_DP_OPTIONS" />
<xs:enumeration value="RUN_PROJECT_CREATION" />
<xs:enumeration value="OPEN_SUB_MENU_HELP" />
<xs:enumeration value="CLOSE_TUTORIAL_POPUP" />
<xs:enumeration value="OPEN_TUTORIAL_POPUP" />
<xs:enumeration value="NONE" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="alias">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="CUSTOM" />
<xs:enumeration value="BODY" />
<xs:enumeration value="BREADCRUMBS" />
<xs:enumeration value="MENU_HELP" />
<xs:enumeration value="SUB_MENU_HELP" />
<xs:enumeration value="SUB_MENU_HELP_ROW" />
<xs:enumeration value="SUB_MENU_HELP_ROW_FIRST" />
<xs:enumeration value="TUTORIAL_POPUP" />
<xs:enumeration value="TUTORIAL_POPUP_MODEL" />
<xs:enumeration value="TUTORIAL_POPUP_MODEL_FIRST" />
<xs:enumeration value="TUTORIAL_POPUP_TUTORIAL_NAME" />
<xs:enumeration value="TUTORIAL_POPUP_TUTORIAL_NAME_FIRST" />
<xs:enumeration value="TUTORIAL_POPUP_TUTORIAL_DESCR" />
<xs:enumeration value="TUTORIAL_POPUP_TUTORIAL_DESCR_FIRST" />
<xs:enumeration value="EXPLORER" />
<xs:enumeration value="DRILLDOWN" />
<xs:enumeration value="EXPLORER_TAB" />
<xs:enumeration value="ARTEFACT_TREE" />
<xs:enumeration value="MEASURE_TREE" />
<xs:enumeration value="EXPLORER_HEADER" />
<xs:enumeration value="PORTFOLIO_HEADER" />
<xs:enumeration value="ARTEFACT_TREE_SEARCH" />
<xs:enumeration value="ARTEFACT_TREE_FILTER" />
<xs:enumeration value="REVIEW_SET" />
<xs:enumeration value="PORTFOLIO_TREE" />
<xs:enumeration value="PORTFOLIO_TREE_PROJECT" />
<xs:enumeration value="PORTFOLIO_TREE_PROJECT_FIRST" />
<xs:enumeration value="MODEL_DASHBOARD" />
<xs:enumeration value="MODEL_CHARTS" />
<xs:enumeration value="MODEL_CHART_FIRST" />
<xs:enumeration value="MODEL_TABLE" />
<xs:enumeration value="MODEL_TABLE_ROW_FIRST" />
<xs:enumeration value="MODEL_CHART" />
<xs:enumeration value="MODEL_TABLE_ROW" />
<xs:enumeration value="MODEL_CHART_POPUP" />
<xs:enumeration value="MODEL_CHART_POPUP_GRAPH" />
<xs:enumeration value="MODEL_CHART_POPUP_PREVIOUS_ARROW" />
<xs:enumeration value="MODEL_CHART_POPUP_NEXT_ARROW" />
<xs:enumeration value="MODEL_CHART_POPUP_NAV_BAR" />
<xs:enumeration value="MODEL_CHART_POPUP_ASIDE" />
<xs:enumeration value="MODEL_CHART_POPUP_ASIDE_HEAD" />
<xs:enumeration value="MODEL_CHART_POPUP_DESCR" />
<xs:enumeration value="FILTER_POPUP" />
<xs:enumeration value="FILTER_LEVEL" />
<xs:enumeration value="FILTER_TYPE" />
<xs:enumeration value="FILTER_EVOLUTION" />
<xs:enumeration value="FILTER_STATUS" />
<xs:enumeration value="ARTEFACT_TREE_LEAF" />
<xs:enumeration value="MEASURE_TREE_LEAF" />
<xs:enumeration value="MENU_INDICATOR_ARTEFACT" />
<xs:enumeration value="DASHBOARD " />
<xs:enumeration value="SCORECARD" />
<xs:enumeration value="KPI" />
<xs:enumeration value="CHARTS" />
<xs:enumeration value="TABLES" />
<xs:enumeration value="CHART_FIRST" />
<xs:enumeration value="LINE" />
<xs:enumeration value="CHART" />
<xs:enumeration value="CHART_FIRST" />
<xs:enumeration value="TABLE" />
<xs:enumeration value="TABLE_FIRST" />
<xs:enumeration value="MEASURE_POPUP" />
<xs:enumeration value="MEASURE_POPUP_CONTENT" />
<xs:enumeration value="MEASURE_POPUP_LEVELS" />
<xs:enumeration value="MEASURE_POPUP_ROW_FIRST" />
<xs:enumeration value="MEASURE_POPUP_ROW" />
<xs:enumeration value="CHART_POPUP" />
<xs:enumeration value="CHART_POPUP_GRAPH" />
<xs:enumeration value="CHART_POPUP_COMPARE_OPTION" />
<xs:enumeration value="CHART_POPUP_PREVIOUS_ARROW" />
<xs:enumeration value="CHART_POPUP_NEXT_ARROW" />
<xs:enumeration value="CHART_POPUP_NAV_BAR" />
<xs:enumeration value="CHART_POPUP_ASIDE" />
<xs:enumeration value="CHART_POPUP_ASIDE_HEAD" />
<xs:enumeration value="CHART_POPUP_DESCR" />
<xs:enumeration value="CHART_POPUP_COMMENTS" />
<xs:enumeration value="CHART_POPUP_FAVORITES" />
<xs:enumeration value="CHART_POPUP_COMPARATIVE_CHART" />
<xs:enumeration value="ACTION_ITEMS" />
<xs:enumeration value="ACTION_ITEMS_TABLE" />
<xs:enumeration value="ACTION_ITEMS_TABLE_HEAD" />
<xs:enumeration value="ACTION_ITEMS_TABLE_HEAD_CHECK" />
<xs:enumeration value="ACTION_ITEMS_ADD_REVIEW_SET" />
<xs:enumeration value="ACTION_ITEMS_EXPORT_LIST" />
<xs:enumeration value="ACTION_ITEMS_EXPORT_BUTTON" />
<xs:enumeration value="ACTION_ITEMS_SEARCH" />
<xs:enumeration value="ACTION_ITEMS_ROW" />
<xs:enumeration value="ACTION_ITEMS_REASON" />
<xs:enumeration value="ACTION_ITEMS_ADVANCED_SEARCH" />
<xs:enumeration value="ACTION_ITEMS_ADVANCED_SEARCH_SELECT_FIRST" />
<xs:enumeration value="ACTION_ITEMS_ADVANCED_SEARCH_SELECT" />
<xs:enumeration value="HIGHLIGHTS" />
<xs:enumeration value="HIGHLIGHTS_TABLE" />
<xs:enumeration value="HIGHLIGHTS_TABLE_HEAD" />
<xs:enumeration value="HIGHLIGHTS_TABLE_HEAD_CHECK" />
<xs:enumeration value="HIGHLIGHTS_SEARCH" />
<xs:enumeration value="HIGHLIGHTS_SEARCH_FILTER" />
<xs:enumeration value="HIGHLIGHTS_SEARCH_TYPE" />
<xs:enumeration value="HIGHLIGHTS_EXPORT_BUTTON" />
<xs:enumeration value="HIGHLIGHTS_ADD_REVIEW_SET" />
<xs:enumeration value="HIGHLIGHTS_ROW_FIRST" />
<xs:enumeration value="FINDINGS" />
<xs:enumeration value="FINDINGS_TABLE" />
<xs:enumeration value="FINDINGS_TABLE_HEAD" />
<xs:enumeration value="FINDINGS_SEARCH" />
<xs:enumeration value="FINDINGS_INFO" />
<xs:enumeration value="FINDINGS_RULE" />
<xs:enumeration value="FINDINGS_ARTEFACT" />
<xs:enumeration value="FINDINGS_ROW_FIRST" />
<xs:enumeration value="FINDINGS_ADVANCED_SEARCH" />
<xs:enumeration value="FINDINGS_ADVANCED_SEARCH_SELECT_FIRST" />
<xs:enumeration value="FINDINGS_ADVANCED_SEARCH_SELECT" />
<xs:enumeration value="REPORTS" />
<xs:enumeration value="REPORTS_REGION" />
<xs:enumeration value="REPORTS_OPTIONS" />
<xs:enumeration value="REPORTS_OPTION_TEMPLATE" />
<xs:enumeration value="REPORTS_OPTION_FORMAT" />
<xs:enumeration value="REPORTS_OPTION_SYNTHETIC_VIEW" />
<xs:enumeration value="REPORTS_CREATE" />
<xs:enumeration value="EXPORT_REGION" />
<xs:enumeration value="EXPORT_OPTIONS" />
<xs:enumeration value="EXPORT_CREATE" />
<xs:enumeration value="FORMS" />
<xs:enumeration value="FORMS_ATTRIBUTE" />
<xs:enumeration value="FORMS_ATTRIBUTE_FIELD" />
<xs:enumeration value="FORMS_ATTRIBUTE_COMMENT" />
<xs:enumeration value="FORMS_HISTORY" />
<xs:enumeration value="FORMS_BLOCK" />
<xs:enumeration value="INDICATORS" />
<xs:enumeration value="INDICATORS_TABLE" />
<xs:enumeration value="INDICATORS_TABLE_HEAD" />
<xs:enumeration value="INDICATORS_ROW" />
<xs:enumeration value="MEASURES" />
<xs:enumeration value="MEASURES_TABLE" />
<xs:enumeration value="MEASURES_TABLE_HEAD" />
<xs:enumeration value="MEASURES_ROW" />
<xs:enumeration value="COMMENTS" />
<xs:enumeration value="COMMENTS_TABLE" />
<xs:enumeration value="COMMENTS_TABLE_HEAD" />
<xs:enumeration value="COMMENTS_ROW" />
<xs:enumeration value="CREATE_PROJECT_BUTTON" />
<xs:enumeration value="WIZARD_PANEL" />
<xs:enumeration value="WIZARD_ROW" />
<xs:enumeration value="WIZARD_ROW_FIRST" />
<xs:enumeration value="WIZARD_NEXT_BUTTON" />
<xs:enumeration value="GENERAL_INFORMATION" />
<xs:enumeration value="PROJECT_IDENTIFICATION_BLOCK " />
<xs:enumeration value="GENERAL_INFO_BLOCK" />
<xs:enumeration value="GENERAL_INFO_ROW" />
<xs:enumeration value="PROJECT_NEXT_BUTTON" />
<xs:enumeration value="DP_PANEL" />
<xs:enumeration value="DP_PANEL_BLOCK" />
<xs:enumeration value="DP_PANEL_ROW" />
<xs:enumeration value="DP_PANEL_NEXT_BUTTON" />
<xs:enumeration value="CONFIRMATION_PANEL" />
<xs:enumeration value="SUMMARY" />
<xs:enumeration value="CONFIRMATION_PANEL_PARAMETERS" />
<xs:enumeration value="RUN_NEW_PROJECT_BUTTON" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="colors">
<xs:union>
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value="#[A-Fa-f0-9]{6}" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value="(rgb|RGB)\([0-9]{3},[0-9]{3},[0-9]{3}\)" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="aqua" />
<xs:enumeration value="black" />
<xs:enumeration value="blue" />
<xs:enumeration value="gray" />
<xs:enumeration value="lime" />
<xs:enumeration value="green" />
<xs:enumeration value="maroon" />
<xs:enumeration value="navy" />
<xs:enumeration value="olive" />
<xs:enumeration value="orange" />
<xs:enumeration value="purple" />
<xs:enumeration value="red" />
<xs:enumeration value="silver" />
<xs:enumeration value="teal" />
<xs:enumeration value="white" />
<xs:enumeration value="yellow" />
<xs:enumeration value="transparent" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:union>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="text-positions">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="INTERNAL" />
<xs:enumeration value="EXTERNAL" />
<xs:enumeration value="LEFT" />
<xs:enumeration value="RIGHT" />
<xs:enumeration value="TOP" />
<xs:enumeration value="BOTTOM" />
<xs:enumeration value="CENTER" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="phase-type">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="PARALLEL" />
<xs:enumeration value="PROGRESSIVE" />
<xs:enumeration value="SEQUENTIAL" />
<xs:enumeration value="FREE" />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:complexType name="elements">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="help"/>
<xs:element ref="Package"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:element name="Bundle" type="elements" />
<xs:element name="Package" type="elements"/>
<xs:element name="item">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="element" use="required" type="external-id" />
<xs:attribute name="param" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="descrId" use="required" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="textPosition" use="optional" default="EXTERNAL" type="text-positions" />
<xs:attribute name="maskColor" use="optional" default="#2aa0d5" type="colors" />
<xs:attribute name="maskOpacity" use="optional" default="0.8" type="opacity" />
<xs:attribute name="textSize" use="optional" default="25" type="positive-integer" />
<xs:attribute name="textColor" use="optional" default="white" type="colors" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="preAction">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="action" use="required" type="actions" />
<xs:attribute name="param" use="optional" default="" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="clickIndicator" use="optional" default="false" type="xs:boolean" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="phase">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:choice>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="item" />
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="preAction" />
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="element" use="optional" type="external-id" />
<xs:attribute name="param" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="type" use="optional" default="PARALLEL" type="phase-type" />
<xs:attribute name="textPosition" use="optional" default="EXTERNAL" type="text-positions" />
<xs:attribute name="textSize" use="optional" default="25" type="positive-integer" />
<xs:attribute name="textColor" use="optional" default="white" type="colors" />
<xs:attribute name="maskColor" use="optional" default="#2aa0d5" type="colors" />
<xs:attribute name="maskOpacity" use="optional" default="0.6" type="opacity" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="help">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:choice>
<xs:element ref="phase" />
<xs:element ref="item" />
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="id" use="required" type="external-id" />
<xs:attribute name="opacity" use="optional" default="0.4" type="opacity" />
<xs:attribute name="textPosition" use="optional" default="EXTERNAL" type="text-positions" />
<xs:attribute name="textSize" use="optional" default="25" type="positive-integer" />
<xs:attribute name="textColor" use="optional" default="white" type="colors" />
<xs:attribute name="maskColor" use="optional" default="#2aa0d5" type="colors" />
<xs:attribute name="maskOpacity" use="optional" default="0.6" type="opacity" />
<xs:attribute name="firstConnectionGroup" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="users" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="groups" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="roles" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
<xs:attribute name="icon" use="optional" type="xs:string" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>wizards.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified">
<xs:simpleType name="id">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value='[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+' />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="list-id">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value='[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+(;[A-Z_][A-Z0-9_]+)*' />
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="alignment">
<xs:restriction base="id">
<xs:enumeration value="LEFT"/>
<xs:enumeration value="RIGHT"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="project-status">
<xs:restriction base="id">
<xs:enumeration value="IGNORE"/>
<xs:enumeration value="WARNING"/>
<xs:enumeration value="ERROR"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:element name="Bundle">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="tags"/>
<xs:element ref="wizard"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="tags">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="tag"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="textAlign" type="alignment"/>
<xs:attribute name="valueAlign" type="alignment"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="tag">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="value"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="defaultValue"/>
<xs:attribute name="displayType"/> <!-- Not display-type because it is case insensitive -->
<xs:attribute name="group"/>
<xs:attribute name="groupId" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="measureId" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="name"/>
<xs:attribute name="placeholder"/>
<xs:attribute name="required" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="review" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="suffix"/>
<xs:attribute name="targetArtefactTypes" type="list-id"/>
<xs:attribute name="textAlign" type="alignment"/>
<xs:attribute name="type" use="required"/> <!-- Not tag-type because it is case insensitive -->
<xs:attribute name="valueAlign" type="alignment"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="value">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="key" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="value" use="required" type="xs:decimal"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="wizard">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xs:element ref="tags"/>
<xs:element ref="milestones"/>
<xs:element ref="repositories"/>
<xs:element ref="tools"/>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="autoBaseline" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="group"/>
<xs:attribute name="groups"/>
<xs:attribute name="hideRulesEdition" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="img"/>
<xs:attribute name="users"/>
<xs:attribute name="versionPattern"/>
<xs:attribute name="wizardId" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="projectsSelection" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="name"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="milestones">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence minOccurs="0">
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="goals"/>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="milestone"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="canCreateMilestone" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="canCreateGoal" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="hide" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="skipUiValues" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="changeableMode" type="xs:boolean"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="goals">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence minOccurs="0">
<xs:element ref="goal"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="displayableFamilies" use="required" type="list-id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="goal">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="mandatory" use="required" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="measureId" use="required" type="id"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="milestone">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element ref="defaultGoal"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="id" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="mandatory" type="xs:boolean"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="defaultGoal">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="measureId" use="required" type="id"/>
<xs:attribute name="value" use="required" type="xs:integer"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="repositories">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="repository"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="all" use="required" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="hide" use="required" type="xs:boolean"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="repository">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" ref="param"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="checkedInUI" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="name" use="required"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="tools">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="tool"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="all" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="expandedInUI" type="xs:boolean"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="tool">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded" ref="param"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="checkedInUI" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="expandedInUI" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="name" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="optional" type="xs:boolean"/>
<xs:attribute name="projectStatusOnFailure" type="project-status"/>
<xs:attribute name="projectStatusOnWarning" type="project-status"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="param">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="availableChoices"/>
<xs:attribute name="name" use="required"/>
<xs:attribute name="value"/>
<xs:attribute name="hide" type="xs:boolean"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>Appendix C: Licences
Software Licence Agreement
Squore Software
End-User License and Support Agreement
Please read this document carefully. This is a legal agreement by which Vector Informatik GmbH ("Vector") permits use of its Software products ("Squore Software"). The user ("Customer") accepts the terms of this Agreement by taking any or all of the following actions: (a) by signing an order form or purchase order referencing either this Agreement or a Technical and Financial proposal issued by Vector (an "Order Form"), (b) by opening the package containing the Software, and/or (c) by installing the Software on a computer ("Target Hardware").
CUSTOMER CONSENTS TO BE LEGALLY BOUND BY THESE TERMS. IF CUSTOMER DOES NOT AGREE TO ALL OF THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT, CUSTOMER MUST NOT USE THE SOFTWARE AND MUST RETURN IT, INCLUDING ANY PRINTED ASSOCIATED DOCUMENTATION, TO VECTOR WITHIN FOURTEEN (14) DAYS TO RECEIVE A FULL REFUND OF THE PURCHASE PRICE.
1) DEFINITION
(a) "Squore Software" includes (i) the Software identified in an Order Form or delivered with this Agreement; (ii) any authorized copies thereof; (iii) all related documentation ("Documentation") delivered with or included in that software; and (iv) any update to that software that Customer may receive from Vector.
(b) Squore Software is based on a traditional 3-tier architecture consisting of:
. a database and a data folder for storing project and user management data
. an application server running the "Squore Server Software" and the "License Server Software"
. a client front-end accessible through a Web Browser and a Command Line Interface to interact with the application server from a client machine
(c) Target hardware ("Target Hardware") is uniquely identified by the hardware specification and the operating system running on it.
2) LICENSE
Vector grants to Customer, and Customer accepts from Vector, a non-exclusive and non-transferable right and license to use the Squore Software that is specified in the Order Form and/or that accompanies this Agreement, but only (i) in accordance with the related Documentation, (ii) subject to Customer's payment of applicable license fees and (iii) subject to the terms and conditions specified below.
Customer agrees that Customer does not have, and does not hereby acquire, any title or rights of ownership in any Squore Software or, except for the license rights hereby granted, any right to use, copy, transfer or disclose all or any portion of any Squore Software. The Squore Software is protected by copyright laws and international treaties.
3) FEES
The fees for the license under this Agreement are set forth in the applicable Order Form or, if no Order Form exists, in the applicable Technical and Financial proposal issued by Vector, or, if no proposal exists, then in accordance with Vector current list prices.
4) USE
(a) Unless otherwise stated in a special agreement, all dissemination or commercial exploitation of Squore Software results is strictly forbidden.
(b) The license granted by this Agreement is a license under which a maximum number of active users and projects specified in the Order Form may use the Squore Software. An "Active User" is a physical user registered in the Squore Software database. Active Users are not shared among several Squore software databases. A user is active if any activity has been recorded by the Squore Server Software in the past 6 months. Activities include remote project creation, viewing of analysis results, and e-mail notification.
(c) The management and regulation of Active Users is managed by the License Server Software hosted on the Target hardware designated by the Customer.
(d) Except for continuous integration purpose, it is strictly forbidden to share the same Squore Software login between different physical users.
(e) Customer will ensure that at least one of its employees has completed the two days on-site training course "Administrating Squore software" given by a Squore Software certified trainer, and that such trained employee(s) are the people within Customer's organization who are responsible for interactions with Squore on maintenance and support matters.
(f) Customer may make a reasonable number of back-up or archival copies of the Software. Customer will reproduce all confidentiality and proprietary notices on each of these copies and maintain an accurate record of the location of each of these copies.
(g) Customer will not:
. Reverse compile, disassemble, or otherwise reverse engineer any Squore Software, or allow anyone else to do so (except only to the extent such prohibition is contrary to applicable law).
. Remove or destroy any proprietary markings or legends or any encrypted license keys or similar security devices placed upon or contained in any Squore Software.
. Modify or adapt the Squore Software or create a derivative work based on or incorporate the Squore Software into or with other software.
. Unless otherwise stated in a special agreement, distribute, sublicense, share, display, or in any manner make the Squore Software available to any third party, with or without compensation.
. Use all or any part of the Squore Software to create other software a principal purpose of which is to perform the same or similar functions as, or to replace any component of, the Squore Software.
5. MAINTENANCE AND SUPPORT
(a) Depending on the type of licenses bought by the Customer, Vector will provide support and maintenance services according to the following schedule:
i. In case of perpetual licenses bought by Customer
. Maintenance fees will be charged in addition to the price of the purchase of the Squore Software licenses. The annual initial amount of maintenance fees will be calculated on the basis of a 20% percentage of the net list price of the software licenses purchased by the Customer.
. After one year, Maintenance and Support services will be renewed by tacit agreement of the parties, for annual periods. Before the anniversary date of each license for which Support Services are in effect, Vector shall advise the Customer of the applicable Maintenance and Support Service fees for the coming year.
. The termination of maintenance contract will be effective only by sending a registered letter with acknowledgement of receipt denouncing the contract at least 60 days before the end of the period of validity.
ii. In case of software licenses subscription
If the license to use the software is subject to a periodic subscription, the maintenance cost for these licenses is included in the subscription price. The maintenance is so provided during all the duration of the subscription, and stops automatically at the end of the subscription validity.
(b) Conditions. Maintenance and support services as defined hereafter in paragraph 5-(c) are applicable subject to the following conditions:
. Squore Software is covered by a valid maintenance contract for all acquired Squore software licenses.
. Squore Software was not modified by the Customer.
. The version of the installed Squore Software corresponds to one of the two latest annual major updates distributed by Vector.
. Customer engages to comply with the normal use of the software, strictly comply with the instructions given by Vector and to respect all provisions in the present agreement.
. Customer shall nominate from among its staff a technical coordinator and an alternate coordinator at the Customer Site(s), with up to date knowledge of Squore licensed products usage and sufficient technical knowledge to interact with Vector support staff. In case of change of the coordinators, the Customer will provide written notification to Vector.
(c) Maintenance and support services include:
. Assistance from support: the online support (hot line) is available during Vector normal business hours from 9 am to 6 pm (Central European Time) to answer the questions of the technical coordinator when technical facts encountered in the use of the Squore Software. Support will help to identify problems and provide, where appropriate, temporary fixing patches. Contact information for support is:
- support site: https://portal.vector.com
- email: support@vector.com
. Corrective maintenance: the corrective maintenance includes the development, to the extent commercially reasonable, of workarounds or program fixes for malfunctions submitted by Customer. Are considered as malfunctions recognized or reproducible defects resulting in distorted results compared to those defined in the software Manual and not coming from non-observance of the instructions of the said Manual.
. Updates: updates include the delivery of successive versions of the software, being either due to bug fixes or to enhancements of performances or features (this delivery does not necessarily provide new additional features). Customer will destroy any prior version before installing a new update.
. Rehost: any change of "Target hardware" implies a change of license keys and shall be subject to the prior written authorization of Vector and to the signature by the Customer of a letter of destruction of all the license files already installed.
d) Maintenance and support services do not include:
. Time spent, after request of the Customer by Vector staff not directly attributable to maintenance services: search for non-reproducible anomalies, malfunction due to non-compliance with the Manual without the Software itself being an issue, unavailability of the system, operating activities prior to the intervention (such as preliminary backup ...).
. Installation of the Software by Vector.
. Additional services which do not fall within the scope of maintenance services as defined above in paragraph 5-(c).
. On-site support: Vector may offer on-site support to Customer at additional charges
e) Procedure for the submission of requests:
. To be taken into account, Customer requests shall be sent using the support site at https://portal.vector.com or by email at support@vector.com
. Customer agrees to give, in support of a request for correction due to an anomaly, any information likely to facilitate the search for the causes of this anomaly, and to give for free to Vector an open access to its premises and development stations in the day and hours necessary to perform the contract, and to ensure the conservation, under the conditions of appropriate security and condition of the latest version, of the sources of programs in case of this is necessary to enable Vector to perform its maintenance services.
. Regarding correction of anomalies, Vector is committed to act as soon as possible to correct the anomalies detected. Vector will transfer to the Customer either a technique to bypass the anomaly or a patch of necessary corrections or a new version of the software.
. Any issues not resolved with the initial response will be investigated using the data provided. Below are the targeted response times for continued investigations.
- Blocker: 1 day, daily update. A request is "blocking" when the incident has a significative impact with a risk of operating loss or when datas are corrupted. The significative impact is appreciated by Vector.
- Serious: 2 days, weekly update
- Major: 3 days, monthly update
- Minor: 1 week, monthly update
(f) Limitations
. Vector is expressly subject to an obligation of means.
. Vector is not required to (i) develop and release any, or any particular type of enhancements or (ii) customize the enhancements to satisfy Customer's particular requirements.
. The Updates will not include any upgrade or new version of the Products that Vector decides, in its sole discretion, to make generally available as a separately priced item.
. Vector will be released from any responsibility in case of breach by the Customer of any provision of this maintenance terms and conditions.
6. WARRANTIES AND REMEDIES
(a) Limited Warranty. Vector warrants that it has the right to (i) enter into this Agreement and (ii) grant the licenses hereunder. Vector also warrants that the Squore Software will perform substantially as described in the Documentation during a 90 days Warranty Period. Customer acknowledges that (i) the Products may not satisfy all of Customer's requirements and (ii) the use of the Products may not be uninterrupted or error-free.
(b) Remedies. Vector or its representative will correct or replace any defective Software. Customer acknowledges that this paragraph sets forth Customer's exclusive remedy, and Vector exclusive liability, for any breach of warranty or other duty related to the quality of the Products.
(c) Disclaimer. EXCEPT AS EXPRESSLY PROVIDED IN THIS AGREEMENT OR REQUIRED BY APPLICABLE LAW, ALL WARRANTIES, CONDITIONS, REPRESENTATIONS, INDEMNITIES AND GUARANTEES WITH RESPECT TO THE PRODUCTS, WHETHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, ARISING BY LAW, CUSTOM, PRIOR ORAL OR WRITTEN STATEMENTS BY VECTOR, ITS REPRESENTATIVES OR OTHERWISE (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, SATISFACTION AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE) ARE HEREBY OVERRIDDEN, EXCLUDED AND DISCLAIMED.
IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AGGREGATE LIABILITY OF VECTOR TO CUSTOMER ON ACCOUNT OF ANY MATTER ARISING WITH RESPECT TO THE SQUORE SOFTWARE EXCEED THE LICENSE FEES PAID BY CUSTOMER UNDER THIS AGREEMENT.
(d) Infringement Indemnity. If an action is brought against Customer claiming that the Product infringes a patent, trade secret or copyright, Vector will defend Customer at Vector expense and, subject to this Section, pay the damages and costs finally awarded against Customer in the infringement action, but only if (i) Customer notifies Vector promptly upon learning that the claim might be asserted, (ii) Vector has sole control over the defense of the claim and any negotiation for its settlement or compromise, and (iii) Customer takes no action that is contrary to Vector interest. If a claim described above may be or has been asserted, Customer will permit Vector, at Vector option and expense, to (A) procure the right to continue using the Product, (B) replace or modify the Product to eliminate the infringement while providing functionally equivalent performance, or (C) accept the return of the Product and refund to Customer the License Fee actually paid to Vector for such Product, less depreciation based on a 5-year straight-line-depreciation schedule.
Vector shall have no indemnity obligation to Customer under this Section if the patent or copyright infringement claim results from (i) a correction or modification of the Product not provided by Vector, (ii) the failure to promptly install an Update or Enhancement at Vector direction with knowledge that installation thereof would have avoided the infringement or (iii) the combination of the Product with other non-Vector software or (iv) any unauthorized use of the Squore Software, or (v) any version of the Software other than the latest update offered by Vector to Customer at no additional charge.
7. LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCES WILL VECTOR OR ITS REPRESENTATIVES BE LIABLE FOR ANY CONSEQUENTIAL, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, PUNITIVE OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES OR LOST PROFITS, WHETHER FORESEEABLE OR UNFORSEEABLE, BASED ON CUSTOMER'S CLAIMS OR THOSE OF ITS CUSTOMERS (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, CLAIMS FOR LOSS OF DATA, GOODWILL, USE OF MONEY OR USE OF THE PRODUCTS, INTERRUPTION IN USE OR AVAILABILITY OF DATA, STOPPAGE OF OTHER WORK OR IMPAIRMENT OF OTHER ASSETS), ARISING OUT OF BREACH OR FAILURE OF EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, BREACH OF CONTRACT, MISREPRESENTATION, NEGLIGENCE, STRICT LIABILITY IN TORT OR OTHERWISE. IN NO EVENT WILL THE AGGREGATE LIABILITY WHICH VECTOR OR ITS REPRESENTATIVES MAY INCUR IN ANY ACTION OR PROCEEDING EXCEED THE LICENSE FEES ACTUALLY PAID BY CUSTOMER FOR THE SPECIFIC PRODUCT THAT DIRECTLY CAUSED THE DAMAGE. THIS SECTION WILL NOT APPLY ONLY WHEN AND TO THE EXTENT THAT APPLICABLE LAW SPECIFICALLY REQUIRES LIABILITY, DESPITE THE FOREGOING EXCLUSION AND LIMITATION.
8. OWNERSHIP
All trademarks, service marks, patents, copyrights, trade secrets and other proprietary rights in or related to the Products are and will remain the exclusive property of Vector, whether or not specifically recognized or perfected under local applicable law. Customer will not take any action that jeopardizes Vector proprietary rights or acquire any right in the Products, except the limited use rights specified in Section 4. Vector will own all rights in any copy, translation, modification, adaptation or derivation of the Products, including any improvement or development thereof.
9. CONFIDENTIALITY
(a) Confidentiality. Customer acknowledges that the Products constitute and incorporate confidential and proprietary information developed or acquired by or licensed to Vector. Customer will take all reasonable precautions necessary to safeguard the confidentiality of the Products, including at a minimum those taken by Customer to protect Customer's own confidential information. Customer will not allow the removal or defacement of any confidentiality or proprietary notice placed on the Products. The placement of copyright notices on these items will not constitute publication or otherwise impair their confidential nature.
(b) Disclosure. Customer will not disclose, in whole or in part, the Products or any portion thereof or other information that has been designated as confidential to any individual, entity or other person, except to those of Customer's employees or consultants who require access for Customer's authorized use of the Products, provided such consultants agree in writing to comply with the use and non-disclosure restrictions applicable to the Products under this Agreement. Customer acknowledges that any unauthorized use or disclosure of the Products may cause irreparable damage to Vector. If an unauthorized use or disclosure occurs, Customer will immediately notify Vector and take, at Customer's expense, all steps which may be available to recover the Products and to prevent their subsequent unauthorized use or dissemination. Vector agrees to take the same action regarding any information designated in writing as proprietary which it receives from Customer ("Customer Information").
(c) Limitation. Neither Vector nor Customer will have any confidentiality obligation with respect to any portion of the Products or Customer Information that (i) the receiving party knew or independently developed before receiving such Products or Customer Information under this Agreement, (ii) the receiving party lawfully obtained from a third party under no confidentiality obligation, or (iii) became available to the public other than as a result of any act or omission by the receiving party or any of receiving party's employees or consultants.
10. TERMINATION
Customer may terminate this Agreement or any Order Form, without right to refund, by notifying Vector of such termination and returning the Product and copies thereof to Vector. Vector may terminate this Agreement, upon reasonable notice and without judicial or administrative resolution, if Customer or any of Customer's employees or consultants breach any material term or condition hereof. This Agreement will terminate automatically if Customer becomes insolvent or enters into bankruptcy, suspension of payments, moratorium, or any other proceeding that relates to insolvency or protection or creditors' rights.
Upon the termination of this Agreement for any reason, all rights granted to Customer hereunder will cease, and Customer will stop using Squore Software, return or destroy all copies and so certify to Vector in writing. The provisions of Sections 6-8 will survive the termination of this Agreement.
11. INSPECTION
During the term of this Agreement, Vector or its representative, if in receipt of credible evidence of non-compliance, may, upon prior notice to Customer, inspect the files, computer processors, equipment and facilities of Customer during normal working hours to verify Customer's compliance with this Agreement. While conducting such inspection, Vector or its representative will be entitled to copy any item that Customer may possess in violation of this Agreement, without disruption of Vector business and violation of Laws and Regulations.
12. ASSIGNMENT
Customer shall not assign, delegate or otherwise transfer this Agreement or any of its rights or obligations hereunder without Vector prior approval which shall not he unreasonably withheld.
13. MISCELLANEOUS
. Any terms and conditions of any unilateral letter, memorandum, purchase order or other writing issued by Customer shall not be binding on Vector. Any waiver or modification of this Agreement will not be effective unless executed in writing and signed by an authorized representative of Vector and Customer. This Agreement will bind Customer's successors-in-interest.
. This Agreement will be governed by and interpreted in accordance with the laws of Germany. If any provision of this Agreement is held to be unenforceable, in whole or in part, such holding will not affect the validity of the other provisions of this Agreement, unless the Parties in good faith deem the unenforceable provision to be essential, in which case either Party may terminate this Agreement effective immediately upon notice to the other Party. This Agreement constitutes the complete and entire statement of all conditions and representations of the agreement between Vector and Customer with respect to its subject matter and supersedes all prior writings or understandings.Redistributed Software
Redistributed Software Version License File ---------------------- Wildfly 10.1.0.Final lgpl-2.1 PostgreSQL 8.4 postgresql-bsd Perl 5.12.3 al TCL 8.5 tcltkl,tcllib PhantomJS 2.1.1 bsd3 Components Sub component Version License File ---------- Richfaces 4.5.17 lgpl-2.1 PostgreSQL JDBC Driver 42.0.0 bsd2 Oracle JDBC driver 12.1.02 otn Omnifaces 2.6 apache-2.0 ANTLR 3.1 antlr3 JasperReports Library 4.8 lgpl-2.1 Checkstyle 5.6 lgpl-2.1 JTcl 2.8 jtcl, amd, itcl, janino, tcllib, tcltk, ucb log4j 1.2.17 apache-2.0 Apache Commons commons-lang3 3.1 apache-2.0 Apache HttpComponents httpclient 4.1.2 apache-2.0 Apache HttpComponents httpmime 4.1.2 apache-2.0 Apache XML Graphics batik-transcoder 1.7 apache-2.0 Bouncy Castle bcmail-jdk16 1.46 bouncy-castle com.beust jcommander 1.48 apache-2.0 com.google.collections google-collections 1.0 apache-2.0 com.googlecode.juniversalchardet juniversalchardet 1.0.3 mpl1.1 com.sun.mail javax.mail 1.5.3 gf commons-cli commons-cli 1.2 apache-2.0 commons-collections commons-collections 3.2.2 apache-2.0 javax.enterprise cdi-api 1.2 apache-2.0 javax.validation validation-api 1.1.0.Final apache-2.0 net.java.dev.jna jna 4.1.0 lgpl-2.1 net.sf.jsci jsci 1.2 lgpl-2.1 net.sf.saxon saxon-xom 8.7 mpl1.0 nux nux 1.6 nux org.glassfish javax.json 1.0.4 gf org.jdom jdom2 2.0.5 jdom Resources Version License File --------- CodeMirror 4.4.0 mit font-awesome 4.7.0 mit, ofl-1.1 JavaScript InfoVis Toolkit 2.0.1 mit jquery 1.12.3 jquery jquery-mobile 1.4.2 jquery-mobile jquery-ui-resizable 1.11.4 mit, jquery lodash.js 4.17.11 mit notify.js 0.4.2 mit gridstack.js 1.0.0 mit spectrum.js 1.8.0 mit
Index
@
A
- ABAP
- ADA
- Acceptance Testing
- Accessibility
- Accuracy
- Accuracy of Measurement
- Acquirer
- Action
- Activity
- Actor
- Adaptability
- Agreement
- Analysability
- Analysis Model
- Architecture
- Attractiveness
- Attribute
- Availability
B
- Base Measure
- Baseline
- Branch
- Branch Coverage
- Branch Testing
- Budget
- Build
C
- CMMi
- COBOL
- CPP
- CSHARP
- Call Graph
- Capability Maturity Model
- Certification
- Certification Criteria
- Change Control Board
- Change Control System
- Change Management
- Changeability
- Co-existence
- Code
- Code Coverage
- Code Freeze
- Code Review
- Code Verification
- Coding
- Cohesion
- Commercial-Off-The-Shelf (COTS)
- Commit
- Commitment
- Compatibility
- Complexity
- Component
- Conciseness
- Condition
- Configuration
- Configuration Control
- Configuration Item
- Configuration Management
- Configuration Management System
- Conflict
- Conformance
- Connectivity
- Consistency
- Constraint
- Content Coupling
- Context of Use
- Contract
- Control Coupling
- Control Flow
- Control Flow Diagram
- Convention
- Correctability
- Correctness
- Coupling
- Coverage
- Criteria
- Criticality
- Custom Software
- Customer
D
- DOD-STD-2167A
- Data
- Data Coupling
- Data Flow
- Data Flow Diagram
- Data Management
- Data Model
- Data Processing
- Data Provider
- Data Providers
-
- AntiC
- Automotive Coverage Import
- Automotive Tag Import
- Axivion
- BullseyeCoverage Code Coverage Analyzer
- CANoe
- CPD
- CPPTest
- CPU Data Import
- CSV Coverage Import
- CSV Findings
- CSV Import
- CSV Tag Import
- Cantata
- CheckStyle
- CheckStyle (plugin)
- CheckStyle for SQALE (plugin)
- Cobertura format
- CodeSniffer
- CodeSonar
- Compiler
- Configuration Checker
- Coverity
- Cppcheck
- Cppcheck (plugin)
- Csv
- CsvPerl
- ESLint
- Excel Import
- ExcelMetrics
- FindBugs-SpotBugs
- FindBugs-SpotBugs (plugin)
- FindingsPerl
- Frameworks
- Function Relaxer
- FxCop
- GCov
- GNATCompiler
- GNATcheck
- GNAThub
- Generic
- Generic Findings XML Import
- GenericPerl
- JSHint
- JUnit Format
- JaCoCo
- Jira
- Klocwork
- Klocwork MISRA
- MISRA Rule Checking using PC-lint
- MISRA Rule Checking with QAC
- MSTest
- MSTest Code Coverage
- Mantis
- MemUsage
- Memory Data Import
- NCover
- OSLC
- Oracle PLSQL compiler Warning checker
- PC Lint MISRA 2012
- PHP Code Coverage
- PMD
- PMD (plugin)
- Polyspace
- QAC 8.2
- QAC 8.2 CERT Import
- Rational Logiscope
- Rational Test RealTime
- ReqIF
- Requirement ASIL via Excel Import
- Requirement Data Import
- SQL Code Guard
- SonarQube
- Squan Sources
- Squore Import
- Squore Virtual Project
- Stack Data Import
- StyleCop
- StyleCop (plugin)
- Tessy
- Test Data Import
- Test Excel Import
- Testwell CTC++
- Ticket Data Import
- Vector Trace Items
- VectorCAST
- VectorCAST API
- csv_findings
- csv_import
- pep8
- pycodestyle / pep8 (plugin)
- pylint
- pylint (plugin)
- vTESTstudio Traceability
- Data Store
- Data Type
- Database
- Decision Criteria
- Decoupling
- Defect
- Degree of Confidence
- Deliverable
- Delivery
- Dependability
- Deployment
- Derived Measure
- Design
- Design Pattern
- Developer
- Development
- Development Testing
- Direct Measure
- Direct Metric
- Document
- Documentation
- Dynamic Analysis
E
- Earned Value
- Effectiveness
- Efficiency
- Efficiency Compliance
- Effort
- Encapsulation
- End User
- Entity
- Entry Point
- Environment
- Error
- Error Tolerance
- Evaluation
- Evaluation Activity
- Evaluation Group
- Evaluation Method
- Evaluation Module
- Evaluation Technology
- Evaluation Tool
- Execute
- Execution Efficiency
- Execution Time
- Exit
- Expandability
- Export Definitions
- Extendability
- External Attribute
- External Measure
- External Quality
- External Software Quality
F
- FORTRAN
- Facility
- Failure
- Failure Rate
- Fault
- Fault Tolerance
- Feasibility
- Feature
- Feature Freeze
- Finite State Machine
- Flexibility
- Frozen Branch
- Function
- Functional Analysis
- Functional Requirement
- Functional Size
- Functional Testing
- Functional Unit
- Functionality
- Functionality Compliance
G
- Generality
- Generic Practice
- Glossary
- Goal
- Granularity
H
- Historical Information
- Hybrid Coupling
I
- IEC 61508
- IEC 61508-3
- IEC 61508-7
- IEEE 1012
- IEEE 1058
- IEEE 1061
- IEEE 1074
- IEEE 1220
- IEEE 1233
- IEEE 1320
- IEEE 1362
- IEEE 1490
- IEEE 610.12
- IEEE 829
- IEEE 830
- IEEE 982
- ISO 5806
- ISO 8402
- ISO 9001
- ISO 9127
- ISO 9241
- ISO 9241-10
- ISO 9241-11
- ISO/IEC 12119
- ISO/IEC 12207
- ISO/IEC 14143
- ISO/IEC 14143-1
- ISO/IEC 14143-3
- ISO/IEC 14598
- ISO/IEC 14598-1
- ISO/IEC 14598-2
- ISO/IEC 14598-3
- ISO/IEC 14598-4
- ISO/IEC 14598-5
- ISO/IEC 14598-6
- ISO/IEC 14756
- ISO/IEC 14764
- ISO/IEC 15026
- ISO/IEC 15026-1
- ISO/IEC 15026-2
- ISO/IEC 15288
- ISO/IEC 15289
- ISO/IEC 15414
- ISO/IEC 15474
- ISO/IEC 15474-1
- ISO/IEC 15474-2
- ISO/IEC 15504
- ISO/IEC 15504-1
- ISO/IEC 15504-2
- ISO/IEC 15504-3
- ISO/IEC 15504-4
- ISO/IEC 15504-5
- ISO/IEC 15504-6
- ISO/IEC 15504-7
- ISO/IEC 15846
- ISO/IEC 15910
- ISO/IEC 15939
- ISO/IEC 19759
- ISO/IEC 19770
- ISO/IEC 19770-1
- ISO/IEC 19770-2
- ISO/IEC 20000
- ISO/IEC 2382
- ISO/IEC 2382-1
- ISO/IEC 25000
- ISO/IEC 25001
- ISO/IEC 25010
- ISO/IEC 25012
- ISO/IEC 25020
- ISO/IEC 25021
- ISO/IEC 25030
- ISO/IEC 25040
- ISO/IEC 25045
- ISO/IEC 25051
- ISO/IEC 25060
- ISO/IEC 25062
- ISO/IEC 26514
- ISO/IEC 29881
- ISO/IEC 90003
- ISO/IEC 9126
- ISO/IEC 9126-1
- ISO/IEC 9126-2
- ISO/IEC 9126-3
- ISO/IEC 9126-4
- ISO/IEC 9294
- ISO/IEC 99
- ISO/IEC SQuaRE
- ISO/IEC/IEEE 15289
- ISO/IEC/IEEE 24765
- Impact Analysis
- Implementation
- Implied Needs
- Incremental Development
- Indicator
- Indicator Value
- Indirect Measure
- Indirect Metric
- Information
- Information Analysis
- Information Management
- Information Need
- Information Product
- Inspection
- Installability
- Installation Manual
- Integration
- Integration Test
- Integrity
- Interface Testing
- Intermediate Software Product
- Internal Attribute
- Internal Measure
- Internal Quality
- Internal Software Quality
- Interoperability
- Interoperability Testing
- Interval Scale
- Item
- Iteration
J
- JAVA
- JAVASCRIPT
K
- Key Practices
- Key Process Area
- Knowledge Base
L
- Languages
-
- ABAP
- ADA
- COBOL
- CPP
- CSHARP
- FORTRAN
- JAVA
- JAVASCRIPT
- MINDC
- OBJECTIVEC
- PYTHON
- SQL
- SWIFT
- TSQL
- TYPESCRIPT
- VBNET
- XAML
- Learnability
- Lessons Learned
- Level of Performance
- Licences
- Life Cycle
- Life Cycle Model
M
- MINDC
- Maintainability
- Maintainability Compliance
- Maintainer
- Maintenance
- Maintenance Manual
- Maturity
- Measurable Concept
- Measurand
- Measure
- Measurement
- Measurement Analyst
- Measurement Experience Base
- Measurement Function
- Measurement Method
- Measurement Procedure
- Measurement Process
- Measurement Process Owner
- Measurement Sponsor
- Measurement User
- Metric
- Metrics
-
- % of parsed tokens
- AND operators
- Andthen Operators
- Arithmetic Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Blank Lines
- Brace Lines
- Break in Loop
- Break in Switch
- CALL Statements
- Call Graph Depth
- Call to exit
- Called Depth
- Called External Functions
- Called Functions
- Calling Depth
- Calling Functions
- Calls From
- Calls To
- Case Blocks
- Case Labels
- Catch Statements
- Cloned Code
- Cloned Control Flow Tokens
- Clones Number
- Code Cloning Line Counting
- Comment Lines
- Comment lines with code
- Comment lines without alphabetic characters
- Commented Statements
- Comments containing FIXME
- Comments containing TODO
- Comparison Operators
- Compiler FLAG Nested Level
- Conditions
- Constant Methods
- Constant Properties
- Constants
- Continue Statements
- Control Flow Token
- Cyclomatic Complexity
- DISPLAY statements
- Data Declarations
- Data Used
- Debug lines
- Declare Members
- Declare operators
- Declared functions
- Default Statement
- Delegate Members
- Delete Statements
- Depth of Descendant Tree
- Depth of Inheritance Tree
- Derived types
- Distinct Operands
- Distinct Operands in Data Div.
- Distinct Operands in Procedure Div.
- Distinct Operators
- Distinct Operators in Data Div.
- Distinct Operators in Procedure Div.
- Do While Statements
- EVALUATE Statements
- Else Statements
- End Statements
- Entry Statements
- Events
- Exception When blocks
- Exception handlers
- Exceptions
- Executable Statements
- Fiend Attributes
- File Declarations
- File Type Count
- Files Used
- For Statements
- Foreach Statements
- Friend Events
- Friend Members
- Friend Properties
- Generic object
- Goto Statements
- HTML Lines of Code
- Header Blocks Of Comment
- Header Lines Of Code
- Header Lines Of Comment
- IDMS calls for modification
- IDMS calls for reading/searching
- IDMS instructions called
- IDMS records called
- IDMS subschema definition
- IO Functions
- If Statements
- Insert Statements
- Internal Data
- Internal Methods
- Internal Properties
- Is IDMS active
- Label Statements
- Line Count
- Lines Added
- Lines Modified
- Lines Removed
- Loop Statements
- Max Nested Functions
- Maximum Nested Structures
- Memory Allocation
- Memory Freeing
- Methods without Accessibility
- Minimum Number of Cycles
- Minimum Number of Indirect Cycles
- Mixed Lines
- Multiple Inheritance Indicator
- Must Members
- Must Properties
- Non-Cyclic Paths
- Number Of Children
- Number of #DEFINE
- Number of #ELIF
- Number of #ELSE
- Number of #ENDIF
- Number of #ENDREGION
- Number of #ERROR
- Number of #IF
- Number of #IFDEF
- Number of #IFNDEF
- Number of #PRAGMA
- Number of #REGION
- Number of #UNDEF
- Number of #WARNING
- Number of Ancestors
- Number of Attributes
- Number of Check instruction
- Number of Descendants
- Number of DocString lines
- Number of Include
- Number of Methods
- Number of Parameters
- Number of Sections
- Number of XML elements
- Number of arithmetic if
- Number of attributes
- Number of comment blocks
- Number of data without accessibility
- Number of declarative statements
- Number of paragraphs
- Number of text blocks
- OR operators
- Operand Occurrences
- Operand Occurrences in Data Div.
- Operand Occurrences in Procedure Div.
- Operator Occurrences
- Operator Occurrences in Data Div.
- Operator Occurrences in Procedure Div.
- Orelse operators
- PERFORM Statements
- PHP Lines of Code
- PHP/HTML Mixed Lines
- Partial Members
- Partially parsed files
- Private Constant
- Private Data
- Private Events
- Private Methods
- Private Properties
- Private constant
- Private exceptions
- Private functions/Procedures
- Private types
- Private variables
- Properties
- Properties with Get
- Properties with Set
- Properties without Accessibility
- Protected Constant
- Protected Data
- Protected Events
- Protected Internal Data
- Protected Internal Methods
- Protected Internal Properties
- Protected Methods
- Protected Properties
- Protected objects
- Public Constant
- Public Data
- Public Events
- Public Methods
- Public Properties
- Public constants
- Public exceptions
- Public functions
- Public types
- Public variables
- Raise statements
- Real comment lines with alphabetic characters
- Recursive Calls
- Renamed objects
- Repeated Code Blocks
- Return Statements
- STOP Statements
- Select Statements
- Separate functions/procedures
- Separate packages
- Separate tasks
- Shadowed Attributes
- Shadowed Events
- Shadowed Members
- Shadowed Properties
- Shared Attributes
- Shared Events
- Shared Members
- Shared Properties
- Signal Functions
- Skipped Lines of Comment code
- Source Lines Of Code
- Special Operators
- Static Data
- Static Methods
- Static Properties
- Stop Statements
- String Conversions
- Structures Added
- Structures Modified
- Structures Removed
- Subtypes
- Switch Statements
- System Functions
- TIMES Clauses
- Ternary operators
- Throw Statements
- Time Handling
- Try Statements
- Types
- UNTIL Clauses
- Update Statements
- Use of longjump
- Use of offsetof
- Use of setjump
- VARYING Clauses
- Variables
- WHEN Clauses
- Weighted Method per Class
- While Statements
- With statements
- Milestone
- Mock Object
- Model
- Modifiability
- Modifiable
- Modularity
- Module
- Moke Object
- Multidimensional Analysis
N
- Network
- Nonfunctional Requirement
- Nontechnical Requirement
O
- OBJECTIVEC
- Object
- Object Model
- Object Oriented Design
- Observation
- Observation Period
- Operability
- Operand
- Operational Testing
- Operator
- Operator Manual
- Optional Attribute
- Optional Requirement
- Organisational Unit
P
- PYTHON
- Path
- Path Analysis
- Path Testing
- Pathological Coupling
- Peer Review
- Performance
- Performance Indicator
- Performance Testing
- Pilot Project
- Portability
- Portability Compliance
- Practice
- Precision
- Predictive Metric
- Procedure
- Process
- Process Assessment
- Process Assessment Model
- Process Capability
- Process Capability Determination
- Process Capability Level
- Process Context
- Process Improvement
- Process Improvement Objective
- Process Improvement Program
- Process Improvement Project
- Process Metric
- Process Outcome
- Process Performance
- Process Purpose
- Product
- Product Line
- Product Metric
- Productivity
- Programmer Manual
- Project
- Project Management
- Project Phase
- Prototype
Q
- Qualification
- Qualification Testing
- Quality
- Quality Assurance
- Quality Control
- Quality Evaluation
- Quality Factor
- Quality Management
- Quality Measure Element
- Quality Metric
- Quality Model
- Quality in Use
R
- RTCA/EUROCAE
- Rating
- Rating Level
- Readability
- Recoverability
- Recovery
- Redistributed Software
- Reengineering
- Regression Testing
- Release
- Reliability
- Reliability Compliance
- Repeatability of Results of Measurements
- Replaceability
- Repository Connectors
-
- CVS
- ClearCase
- Folder (use GNATHub)
- Folder Path
- Git
- Multiple Source Nodes
- PTC Integrity
- Perforce
- SVN
- Synergy
- TFS
- Zip Upload
- Reproducibility of Results of Measurements
- Request For Change
- Request For Information
- Request For Proposal
- Requirement
- Requirements Analysis
- Requirements Derivation
- Requirements Document
- Requirements Engineering
- Requirements Partitioning
- Requirements Review
- Requirements Specification
- Requirements Traceability
- Requirements Traceability Matrix
- Resource
- Resource Utilisation
- Result
- Retirement
- Reverse Engineering
- Risk
- Risk Acceptance
- Risk Analysis
- Robustness
- Role
- Routine
- Ruleset
-
- 'cycle' shall not be used
- 'star' parameter shall not be used.
- 'stop' shall not be used
- ALTER shall not be used
- Abort shall not be used
- Assignment in Boolean
- Assignment without Comparison
- Avoid Duplicated Blocks in Function
- Avoid GOTO jumps out of PERFORM range
- Avoid OPEN/CLOSE inside loops
- Avoid SELECT SQL statement with a WHERE clause containing the NOT EQUAL operator
- Avoid SELECT SQL statement without a WHERE clause
- Avoid UPDATE or DELETE SQL Statement without a WHERE clause
- Avoid accessing data by using the position and length
- Avoid calling a function module without handling exceptions
- Avoid mixing paragraphs and sections
- Avoid obsolete DATA BEGIN OF OCCURS statement
- Avoid using APPEND in SQL SELECT statements
- Avoid using APPEND statements in loops
- Avoid using BREAK-POINT
- Avoid using CHECK in SQL SELECT statements
- Avoid using COMMIT WORK statements in loops
- Avoid using GROUP BY in queries
- Avoid using INSERT in SQL SELECT statements
- Avoid using INSERT statements in loops
- Avoid using LIKE in SQL queries
- Avoid using READ statement without AT END clause
- Avoid using SELECT *
- Avoid using SELECT DISTINCT Statement
- Avoid using SQL Aggregate Functions
- Avoid using SQL INTO statements in loops
- Avoid using SUBMIT statements in loops
- Avoid using UPDATE
- Avoid using inline PERFORM with too many lines of code
- Avoid using the JOIN SQL clause
- Avoid using the SQL BYPASSING BUFFER clause
- Avoid using the WAIT statement
- BLOCK Clause
- Backward Goto shall not be used
- Bad indentation of scope terminator
- Bad paragraph position used in PERFORM
- Bad statement indentation
- COMPUTE instead of ADD
- COMPUTE instead of DIVIDE
- COMPUTE instead of MULTIPLY
- COMPUTE instead of SUBTRACT
- Cloned Algorithmic
- Cloned Classes
- Cloned Files
- Cloned Functions
- Close file once
- Close open file
- Column 7 for * and D Only
- Comment Before Paragraph
- Comment Division
- Comment FD
- Comment First Level
- Comment Variable 01 and 77
- Commented-out Source Code is not allowed
- Commit Used
- Continue shall not be used
- Delay shall not be used
- Do not use Native SQL instructions
- Dynamic Memory Allocation shall not be used
- Each loop shall be named
- Empty line after EXIT
- Empty line after SECTION
- Empty lines around DIVISION
- Exec shall not be used.
- Exit Label shall be named
- FIXME shall not be commited in sources code
- Factorizable Classes
- Factorizable Files
- Factorizable Functions
- Factorizable Packages
- Fallthrough shall be avoided
- Forbid call to a system function
- Forbid calls to GET RUN TIME.
- Forbid calls to dialog transactions
- Forbid use of GENERATE REPORT / SUBROUTINE POOL / DYNPRO
- Forbid use of INSERT/DELETE REPORT/TEXTPOOL
- Forbid use of SYSTEM-CALL
- Forbid uses of OFFSET in ASSIGN
- Function size
- Goto shall not be used
- Homonymous variable shall not be used
- IDMS FIND CURRENT
- IDMS One modify by PERFORM
- IDMS One same call
- IDMS Ready Protected Update
- IDMS Return Code
- IO Functions shall not be used
- Incorrect Function Name
- Incorrect Module Name
- Incorrect Program Name
- Incorrect Subroutine Name
- Label out a switch
- Macro longjmp or setjmp shall not be used
- Macro offsetof shall not be used
- Method should have self as first argument
- Method without parameter
- Missing Break
- Missing Case Else clause
- Missing Default
- Missing END-ADD
- Missing END-CALL
- Missing END-COMPUTE
- Missing END-DELETE
- Missing END-DIVIDE
- Missing END-EVALUATE
- Missing END-IF
- Missing END-MULTIPLY
- Missing END-READ
- Missing END-RETURN
- Missing END-REWRITE
- Missing END-SEARCH
- Missing END-START
- Missing END-STRING
- Missing END-SUBTRACT
- Missing END-UNSTRING
- Missing END-WRITE
- Missing FILLER
- Missing case in switch
- Missing compound if
- Missing compound statement
- Missing final else
- Multiple Exit (Function
- Multiple Exit Do statement
- Multiple Exit For statement
- Multiple Exit While statement
- Multiple Exit in loop
- Multiple break in loop are not allowed
- Multiple exit
- Multiple exits are not allowed
- Nested Program
- Nesting Level of Preprocessing directives is too high
- No Conditional GOTO
- No DEBUG MODE
- No INITIALIZE
- No MOVE CORRESPONDING
- No RENAMES
- No Resources
- No Variables S9(9)
- No case in Select
- No more than 3 nested IF
- No procedural COPY
- Number of parameters
- Open file once
- Paragraphs having exact same name
- Parameter name
- Parameters shall be ordered: 'IN'
- Perform with no THRU
- Prevent use of EDITOR-CALLS
- Print shall not be used.
- READ-WRITE Instruction
- Recursion are not allowed
- Relaxed violation
- Resources Filename
- Resources Folder
- Risky Empty Statement
- Rollback Used
- Signal or Raise shall not be used
- Single GOBACK
- Standard Label
- Statement shall be in uppercase
- TODO shall not be commited in sources code
- The class name should conform to the defined standard
- The form name should conform to the defined standard
- The function name should conform to the defined standard
- The macro name should conform to the defined standard
- The method name should conform to the defined standard
- The program or report name should conform to the defined standard
- There shall be a init method in the class.
- There shall be a no code before first case
- There shall be no 'when others' in exception handler
- There shall be only one Statement per line
- Time Handling Functions shall not be used
- Use 'exit when' instead of if… exit syntax
- Use COMP for OCCURS
- Use FILE STATUS
- Use SYNCHRONIZED
- Use WHEN OTHER
- Use of Exit Do statement
- Use of Exit For statement
- Use of Exit Function statement
- Use of Exit Property statement
- Use of Exit Select statement
- Use of Exit Sub statement
- Use of Exit Try statement
- Use of Exit While statement
- Use of Fortran 77
- Use of SAVE and DATA
- Use of allocate/deallocate
- Use of contains
- Use of continue is deprecated (Fortran)
- Use of exit is not recommended
- Use of module
- Variable declaration format
- Run
S
- SIGIST
- SQL
- SWIFT
- Safety
- Satisfaction
- Scale
- Security
- Service
- Service Level Agreement
- Simplicity
- Software
- Software Asset Management
- Software Development Process
- Software Engineering
- Software Item
- Software Licence Agreement
- Software Life Cycle
- Software Product Evaluation
- Software Quality
- Software Quality Characteristic
- Software Quality Evaluation
- Software Quality Measure
- Software Repository
- Software Unit
- Source Code
- Specification
- Stability
- Stage
- Stakeholder
- Standard
- Standard Process
- Statement
- Statement Testing
- Statement of Work
- Static Analysis
- Statistical Process Control
- Step
- Stress Testing
- Structural Testing
- Stub
- Suitability
- Supplier
- Support
- Support Manual
- System
- System Testing
T
- TSQL
- TYPESCRIPT
- Task
- Team Software Process
- Technical Requirement
- Technique
- Test
- Test Case
- Test Case Suite
- Test Coverage
- Test Documentation
- Test Environment
- Test Objective
- Test Plan
- Test Procedure
- Testability
- Testing
- Testing Description
- Time Behaviour
- Tool
- Total Quality Management
- Traceability
- Traceable
- Trunk
U
- Understandability
- Unit Test
- Unit of Measurement
- Usability
- Usability Compliance
- User
- User Documentation
- User Manual
V
- VBNET
- Validation
- Value
- Verification
- Version
W
- Work Breakdown Structure
- Work Product
X
- XAML
- XML Format Reference
- XML Schema
-
- analysis.xsd
- config-1.3.xsd
- decision.xsd
- description.xsd
- exports.xsd
- form.xsd
- highlights.xsd
- input-data-2.xsd
- properties-1.2.xsd
- properties.xsd
- tutorials.xsd
- wizards.xsd



